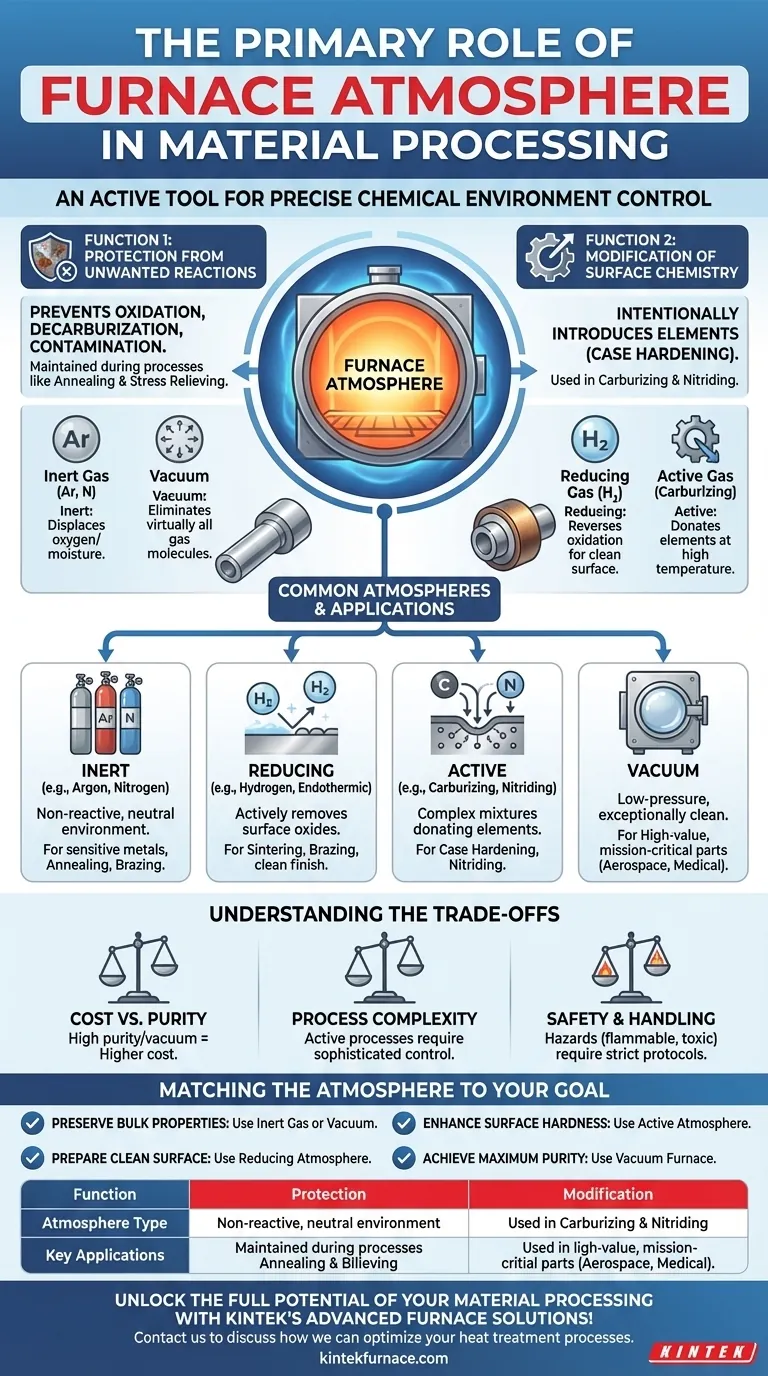
At its core, the primary role of a furnace atmosphere is to act as an active tool that precisely controls the chemical environment surrounding a material during heat treatment. This control serves one of two fundamental purposes: to protect the material from undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation, or to intentionally induce specific, beneficial reactions that modify the material's surface properties.
The furnace atmosphere should not be viewed as a passive background condition, but as a critical, controllable ingredient in the process. The choice of atmosphere—whether it's an inert gas, a reactive mixture, or a vacuum—directly determines the final chemical and physical properties of the component.
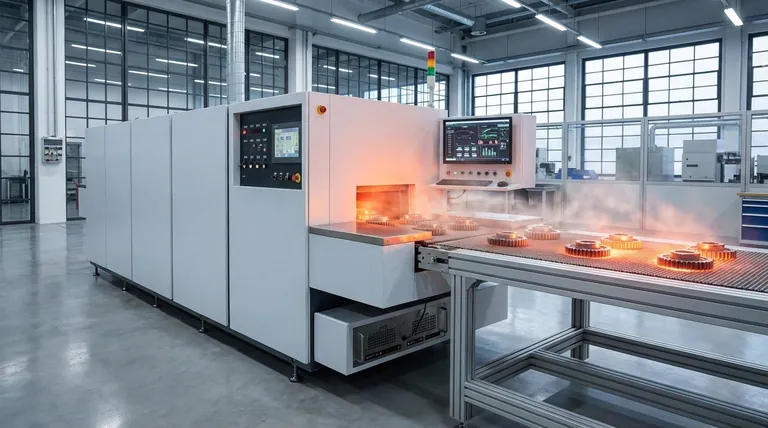

The Two Fundamental Functions of a Furnace Atmosphere
Every controlled atmosphere process can be categorized by its primary intent: to protect the material's existing state or to actively change it.
Function 1: Protection from Unwanted Reactions
Many heat treatment processes, such as annealing or stress relieving, are intended to change a material's physical properties without altering its surface chemistry. In these cases, the atmosphere is purely protective.
The most common unwanted reaction is oxidation, which occurs when heated metals react with oxygen in the air. This forms a layer of scale that can degrade surface finish and component integrity.
A protective atmosphere displaces the ambient air, preventing this and other reactions like decarburization (the loss of carbon from steel's surface) or general contamination.
Function 2: Modification of Surface Chemistry
Conversely, many processes use the atmosphere to intentionally introduce elements into the material's surface, a technique often called case hardening.
A prime example is carburizing, where carbon-rich gases are used to diffuse carbon into the surface of a low-carbon steel part. This creates a hard, wear-resistant outer "case" while leaving the inner "core" tough and ductile.
This principle also extends to material synthesis, such as using a reducing atmosphere to create graphene from carbon-rich precursors or an inert atmosphere to synthesize metal nanoparticles.
Common Atmospheres and Their Applications
The specific goal of the process dictates the type of atmosphere required.
Inert Atmospheres (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen)
These gases are chemically non-reactive. Their sole purpose is to displace oxygen and moisture, creating a neutral environment. They are ideal for annealing and brazing sensitive metals where no surface reaction of any kind is desired.
Reducing Atmospheres (e.g., Hydrogen, Endothermic Gas)
Reducing atmospheres do more than just protect; they actively reverse oxidation. A common component, hydrogen, reacts with and removes surface oxides, resulting in a clean, bright finish.
This makes them essential for processes like brazing, where clean surfaces are critical for the filler metal to wet and flow, and sintering of powder metals.
Active Atmospheres (e.g., Carburizing, Nitriding)
These are complex gas mixtures precisely engineered to donate a specific element to the material's surface at high temperatures. Besides carburizing, nitriding uses ammonia-based atmospheres to diffuse nitrogen into steel for exceptional hardness and fatigue resistance.
Vacuum: The Ultimate Protective Environment
A vacuum is not the absence of an atmosphere, but rather a specific type of controlled, low-pressure atmosphere. By removing virtually all gas molecules, a vacuum furnace creates an exceptionally clean environment.
This eliminates any possibility of oxidation or contamination, making it the preferred method for processing high-value, mission-critical components for industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an atmosphere involves balancing performance requirements with practical constraints.
Cost vs. Purity
High-purity gases like argon and the equipment needed for a deep vacuum are significantly more expensive than generating simpler atmospheres like endothermic gas. The choice depends on whether the application truly demands the highest level of protection.
Process Complexity
Active processes like carburizing require sophisticated controls for gas composition, temperature, and time to achieve a specific case depth and hardness. A simple protective atmosphere for annealing is far less complex to manage.
Safety and Handling
Many atmospheric gases present safety hazards. Hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive, while the byproduct of some common atmospheres (like endothermic gas) is toxic carbon monoxide. Proper safety engineering and handling protocols are non-negotiable.
Matching the Atmosphere to Your Goal
The correct choice is always dictated by the desired end-state of the material.
- If your primary focus is preserving bulk properties without surface change (e.g., annealing): Use a protective inert gas (Nitrogen, Argon) or a vacuum.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface hardness and wear resistance (e.g., case hardening): Use a reactive atmosphere like one designed for carburizing or nitriding.
- If your primary focus is preparing a clean surface for joining or consolidation (e.g., brazing, sintering): Use a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen or carbon monoxide.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum cleanliness and purity for critical components: Use a vacuum furnace to eliminate any potential for gas-metal reactions.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is mastering the control of the furnace atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Function | Atmosphere Type | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Protection from unwanted reactions | Inert (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen), Vacuum | Annealing, stress relieving, brazing |
| Modification of surface chemistry | Reducing (e.g., Hydrogen), Active (e.g., Carburizing, Nitriding) | Case hardening, sintering, material synthesis |
Unlock the full potential of your material processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for protection, surface modification, or purity. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















