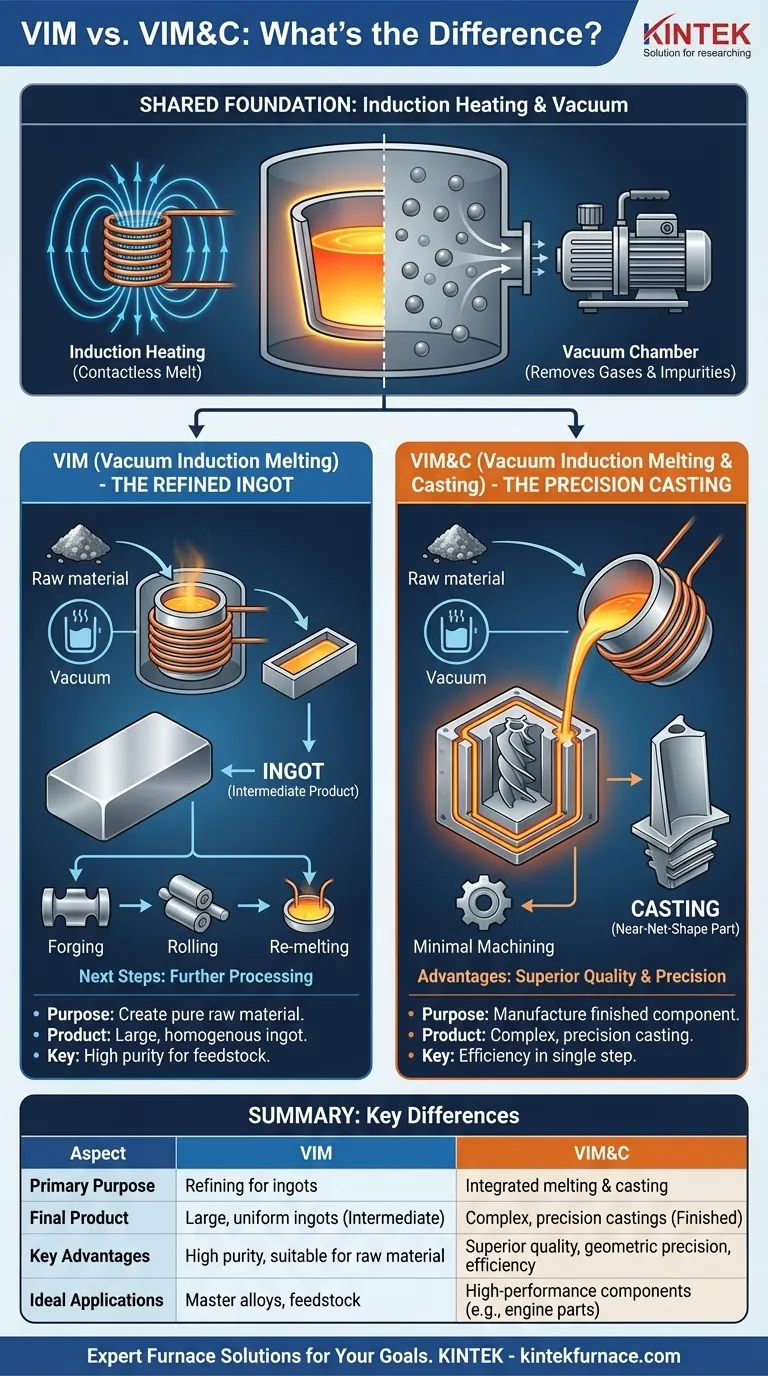
In short, the primary difference between Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) and Vacuum Induction Melting & Casting (VIM&C) lies in their final product and purpose. VIM is a refining process that produces large, uniform blocks of metal called ingots, which are intended for further processing. In contrast, VIM&C is an integrated process that both melts the metal and immediately casts it into a mold to create a complex, near-net-shape part, combining two critical manufacturing steps into one.
Choosing between these processes is a strategic decision based on your manufacturing goal. VIM is fundamentally about creating a highly pure, homogenous raw material (an ingot). VIM&C leverages that same purity to create a complex, finished component in a single, highly efficient operation.

The Foundation: How Vacuum Induction Works
To understand the difference in process, we must first recognize their shared technological core. Both VIM and VIM&C rely on the same two fundamental principles to achieve superior metal quality.
The Role of Induction Heating
Induction uses a powerful, alternating electromagnetic field generated by a copper coil to heat the conductive metal. Because the magnetic field passes through non-conductive materials, the melting can occur without any physical contact between the heat source and the metal.
This contactless heating is critical for maintaining purity, as it prevents contamination that can occur with traditional arc or flame-based melting.
The Importance of the Vacuum
Performing this process inside a vacuum chamber removes atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This prevents the formation of oxides and other impurities, which can degrade the metal's mechanical properties.
The vacuum also actively pulls dissolved gases out of the molten metal, resulting in a cleaner, denser, and stronger final product. This is essential for high-performance superalloys.
VIM vs. VIM&C: A Difference in Purpose
While they share a technological foundation, their application and output could not be more different. The choice between them depends entirely on whether you are producing a raw material or a finished component.
VIM: Creating a Refined Ingot
The goal of a standalone VIM process is to create a large, homogenous, and ultra-pure ingot of a specific alloy. The molten metal is simply poured into a basic mold to solidify.
This ingot is an intermediate product. It is not a finished part. It will later be removed from the VIM furnace and used as high-quality feedstock for other manufacturing processes, such as forging, rolling, or re-melting for other casting operations.
VIM&C: Manufacturing a Precision Casting
VIM&C integrates the casting process directly into the vacuum chamber. After the metal is melted and refined under vacuum, the entire crucible assembly is tilted to pour the molten metal directly into a pre-heated, complex mold.
This produces a near-net-shape casting. The part emerges from the process already in or very close to its final form, requiring minimal secondary machining. This is a complete manufacturing solution, not just a material refinement step.
Why Choose VIM&C? The Key Advantages
Opting for the integrated VIM&C process offers distinct advantages for manufacturing critical components, especially those made from superalloys used in demanding environments.
Superior Metallurgical Quality
By keeping the entire process from melt to solidification under vacuum, VIM&C minimizes any chance of re-introducing atmospheric contaminants. This results in castings with extremely low levels of porosity and inclusions, leading to enhanced strength and reliability.
Enhanced Geometric Precision
VIM&C is ideal for producing parts with intricate geometries, such as the complex blades and vanes used in aircraft engines. Creating these near-net-shape parts directly reduces the need for extensive and costly post-process machining.
Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs
While the equipment is sophisticated, VIM&C eliminates entire steps from the manufacturing chain. You no longer need to produce an ingot, ship it, re-melt it, and then cast it. This consolidation saves time, energy, and labor, reducing the overall cost per part for complex components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
VIM&C is a powerful process, but its specialization comes with clear trade-offs. It is not the correct solution for every application.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
A VIM&C furnace is inherently more complex than a standard VIM unit. It requires integrated tilt-pour mechanisms, mold handling systems, and pre-heating capabilities, all within the vacuum chamber. This results in a significantly higher capital investment.
Process Constraints
The size and complexity of the casting are limited by what can physically fit and be managed inside the vacuum chamber. This is a batch-oriented process, and its throughput may be lower than a traditional foundry that is continuously fed by raw ingots.
Application Specificity
Using VIM&C is only justified for applications that demand the highest level of metallurgical purity and geometric precision. For simpler components or materials where some impurities are acceptable, the process is overly complex and not cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision must be guided by the final application and your position in the supply chain.
- If your primary focus is creating a master alloy or raw material: VIM is the correct choice, delivering a pure, homogenous ingot for subsequent forging, rolling, or re-melting.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing a complex, high-performance component: VIM&C is superior, as it produces a near-net-shape part with exceptional purity and minimal defects in a single process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard components: A simpler process, such as standard investment casting (which may be fed by VIM ingots), is often more appropriate, as VIM&C is specialized for the most demanding applications.
Ultimately, understanding the distinction between refining a material and manufacturing a part is the key to selecting the right technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | VIM (Vacuum Induction Melting) | VIM&C (Vacuum Induction Melting & Casting) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Refining to produce pure ingots for further processing | Integrated melting and casting for near-net-shape parts |
| Final Product | Large, uniform ingots (intermediate product) | Complex, precision castings (finished or near-finished parts) |
| Key Advantages | High purity, homogeneity, suitable for raw material production | Superior metallurgical quality, geometric precision, efficiency in single-step manufacturing |
| Ideal Applications | Master alloys, feedstock for forging or rolling | High-performance components like aircraft engine parts, where minimal defects are critical |
Need expert guidance on high-temperature furnace solutions for your metal processing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Whether you're refining metals or creating complex components, contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















