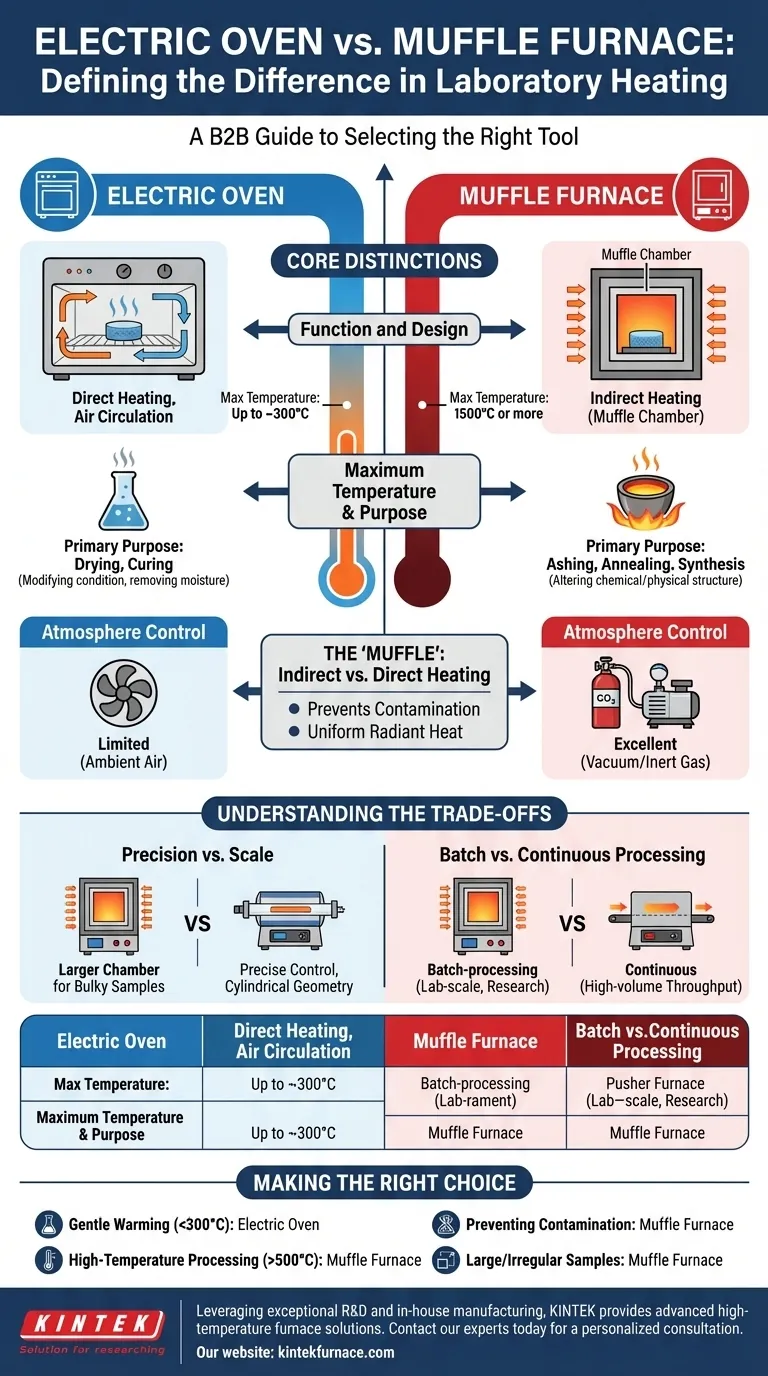
While both are common laboratory heating devices, the fundamental difference between a standard electric oven and a muffle furnace lies in their maximum temperature, heating mechanism, and intended purpose. An electric oven is a low-temperature device for processes like drying or curing, typically operating up to 300°C. A muffle furnace is a high-temperature tool, reaching 1500°C or more, designed for transforming materials through processes like ashing or heat treatment.
The choice is not about which is superior, but which is the correct tool for the task. An oven modifies a sample's condition, such as removing moisture, while a furnace is designed to fundamentally alter a material's chemical or physical structure.
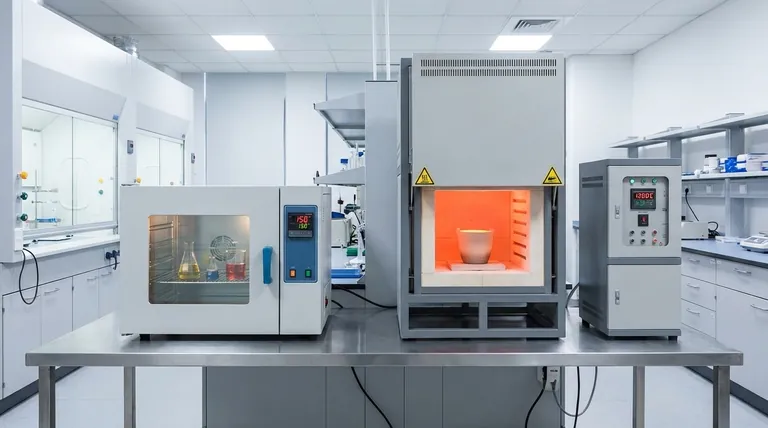

The Core Distinctions: Function and Design
The differences in application stem from critical variations in how these instruments are built and how they operate. Understanding these distinctions is key to selecting the right equipment.
Maximum Temperature and Purpose
A standard laboratory or electric oven is engineered for low-temperature applications. Its primary function is to gently and uniformly heat a sample, most often to drive off moisture for drying or to cure materials like epoxies.
A muffle furnace, by contrast, is built for high-heat material processing. Its capabilities are necessary for applications like determining the inorganic ash content of a sample, annealing metals to alter their properties, or synthesizing new materials at extreme temperatures.
The "Muffle"—Indirect vs. Direct Heating
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the muffle itself—a dedicated chamber that contains the sample and isolates it from the actual heating elements. This creates an indirect heating system.
This design ensures two critical outcomes. First, it prevents contamination, as byproducts from the heating elements cannot reach the sample. Second, it provides highly uniform radiant heat, eliminating hot spots that could occur with direct exposure to an element.
Atmosphere Control
Because the muffle creates a sealed chamber, it allows for precise atmosphere control. Air can be evacuated to create a vacuum, or the chamber can be filled with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation at high temperatures.
Most electric ovens simply circulate ambient air, making them unsuitable for processes where interaction with oxygen would compromise the results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A muffle furnace is a specialized tool, and its design comes with specific advantages and limitations compared to other types of furnaces.
Precision vs. Scale
Compared to a tube furnace, a muffle furnace offers a larger chamber, making it ideal for processing bulky or irregularly shaped samples that wouldn't fit in a narrow tube.
However, the cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace often allows for more precise control over temperature gradients and gas flow from one end to the other, which can be critical for certain synthesis or deposition processes.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
A muffle furnace is a batch-processing instrument. Samples are placed inside, the door is sealed, and the thermal cycle is run. This provides exceptional control over a stationary sample.
This contrasts with industrial pusher furnaces, which continuously move material through different heat zones. Muffle furnaces are therefore best for lab-scale work, research, and processes where absolute control over a single batch is paramount, not high-volume throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument requires a clear definition of your process goals, particularly regarding temperature, atmosphere, and sample purity.
- If your primary focus is drying, curing, or gentle warming (<300°C): An electric oven is the correct and most cost-effective tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing, annealing, or material synthesis (>500°C): A muffle furnace is necessary for its high-temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is preventing sample contamination or oxidation: The indirect heating and atmosphere control of a muffle furnace are essential.
- If your primary focus is processing large or irregularly shaped samples at high temperatures: A muffle furnace provides more usable chamber space than a tube furnace.
Ultimately, selecting the right equipment begins with a clear understanding of your required temperature, atmosphere, and sample integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to ~300°C | 1500°C or more |
| Primary Purpose | Drying, Curing | Ashing, Annealing, Synthesis |
| Heating Mechanism | Direct, Air Circulation | Indirect (Muffle Chamber) |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited (Ambient Air) | Excellent (Vacuum/Inert Gas) |
| Ideal For | Modifying sample condition (e.g., removing moisture) | Altering material's chemical/physical structure |
Still Unsure Which Heating Equipment is Right for Your Lab?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you need gentle drying or extreme heat treatment.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation to identify the perfect heating solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Mastering Thermal Polycondensation for Semiconductors
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity



















