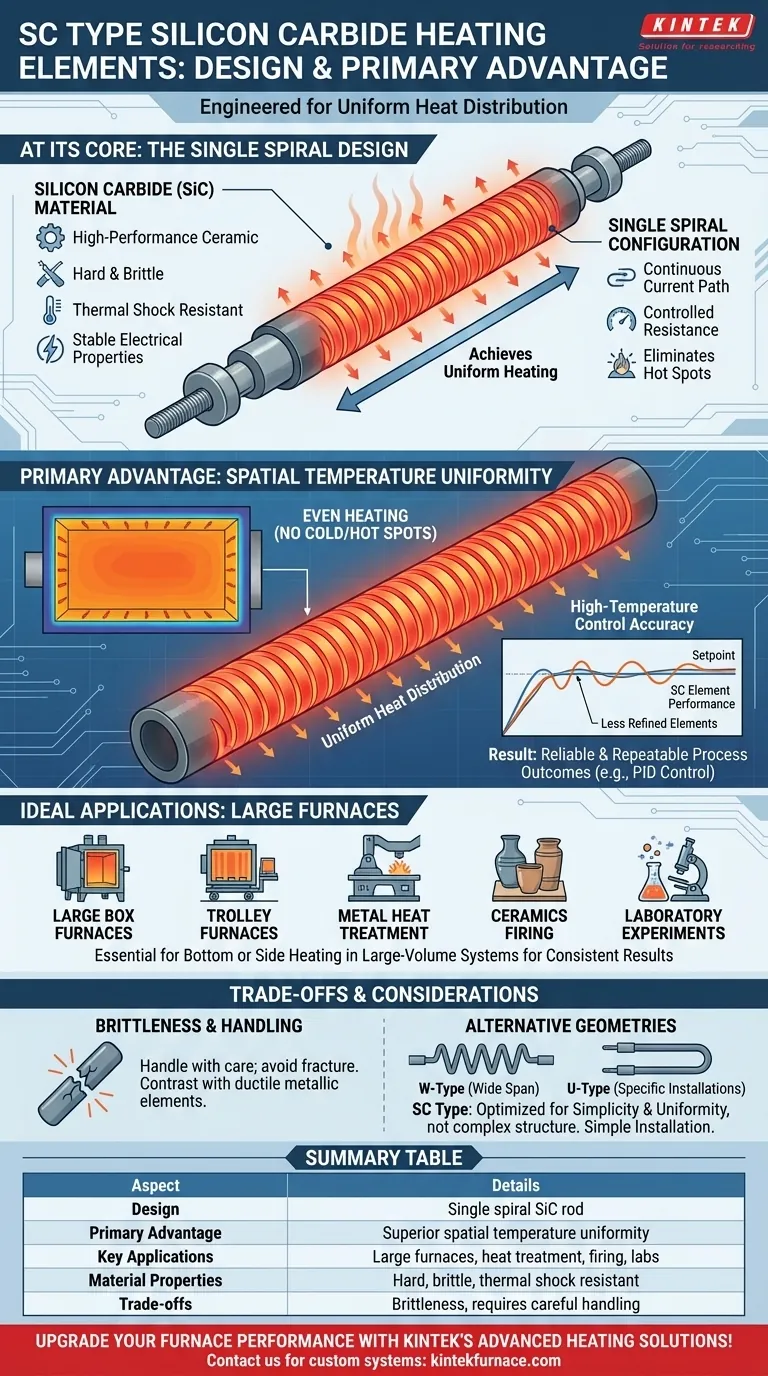
At its core, the SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating element is a ceramic rod distinguished by its single spiral construction. Its primary advantage is the ability to generate exceptionally uniform heat distribution, making it a definitive choice for applications where consistent temperature across a large area is critical.
The decision to use an SC Type element is driven by a need for thermal uniformity. While many elements can reach high temperatures, the single spiral design is specifically engineered to eliminate hot spots and ensure stable, even heating in large-volume furnaces.

Deconstructing the SC Type Design
To understand its advantages, we must first examine its fundamental components: the material and the geometry. These two aspects work in concert to define its performance.
The Silicon Carbide Material
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a high-performance ceramic known for its remarkable properties at extreme temperatures. It is inherently hard, brittle, and resistant to thermal shock, meaning it can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Crucially, it does not easily deform or degrade under high-temperature loads, ensuring long-term structural integrity and stable electrical properties within the furnace.
The Single Spiral Configuration
The "SC" designation refers directly to the Single Spiral cut of the element. This spiral pattern is machined into the rod to create a specific, continuous path for the electrical current.
This design is not arbitrary; it intentionally manipulates the element's resistance along its entire length. This controlled resistance is the key to its uniform heating capability.
The Core Advantage: Spatial Temperature Uniformity
The single spiral design directly translates into the SC Type's most important functional benefit: superior spatial temperature uniformity.
How the Design Achieves Even Heating
By creating a consistent resistance path, the single spiral ensures that heat is generated and dissipated evenly along the element's surface. This minimizes the "temperature difference" mentioned in technical specifications.
The result is a heating source that behaves predictably, free of the localized hot or cold spots that can plague less refined element designs.
Impact on Process Control
This inherent stability makes the entire heating system easier to manage. A furnace equipped with SC elements can achieve high-temperature control accuracy.
Control systems (like PID controllers) can more effectively maintain a setpoint because the heat source is consistent, leading to more reliable and repeatable process outcomes.
Ideal Applications: Large Furnaces
The SC Type is particularly effective for bottom or side heating in large-scale industrial systems.
Applications like large box furnaces, trolley furnaces, metal heat treatment, and ceramics firing all depend on subjecting a large product or batch to the exact same thermal conditions, making the SC element's uniformity indispensable. It's also a staple in laboratory settings where experimental reliability is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single component is perfect for every situation. Acknowledging the trade-offs of the SC Type is key to making an informed decision.
Brittleness and Handling
As a ceramic, SiC is hard but brittle. The elements must be handled with care during shipping, installation, and maintenance to avoid fracture. This contrasts with metallic elements, which are more ductile but often have lower temperature limits.
Context with Other Geometries
The SC Type is one of several available SiC geometries. Other designs, like the W-Type or U-Type, exist to solve different problems.
For example, a W-Type element is specifically designed for horizontal installation where support across a wide span is needed. The existence of these alternatives highlights that the SC Type's rod-like form is optimized for simplicity and uniformity, not complex structural challenges.
Installation and Wiring
The simple rod shape of the SC Type generally allows for convenient wiring and straightforward installation, either vertically or horizontally. This can simplify furnace design and reduce maintenance complexity compared to more intricate element shapes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating element requires aligning the component's strengths with your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity in a large furnace: The SC Type's single spiral design is engineered specifically for this and is your ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is accommodating specific installation constraints: You may need to consider alternative geometries like the W-Type for wide horizontal spans.
- If your primary focus is high-precision lab work: The stability and control accuracy afforded by SC elements make them a highly reliable option for repeatable experiments.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is about matching the technology to the thermal demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Design | Single spiral silicon carbide rod for even heat distribution |
| Primary Advantage | Superior spatial temperature uniformity in large volumes |
| Key Applications | Large box furnaces, trolley furnaces, metal heat treatment, ceramics firing, laboratory experiments |
| Material Properties | Hard, brittle, resistant to thermal shock, stable at high temperatures |
| Trade-offs | Brittleness requires careful handling; other geometries for specific installations |
Upgrade your furnace performance with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. For reliable, uniform heating and enhanced process control, contact us today to discuss how our SC Type SiC elements can optimize your thermal applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















