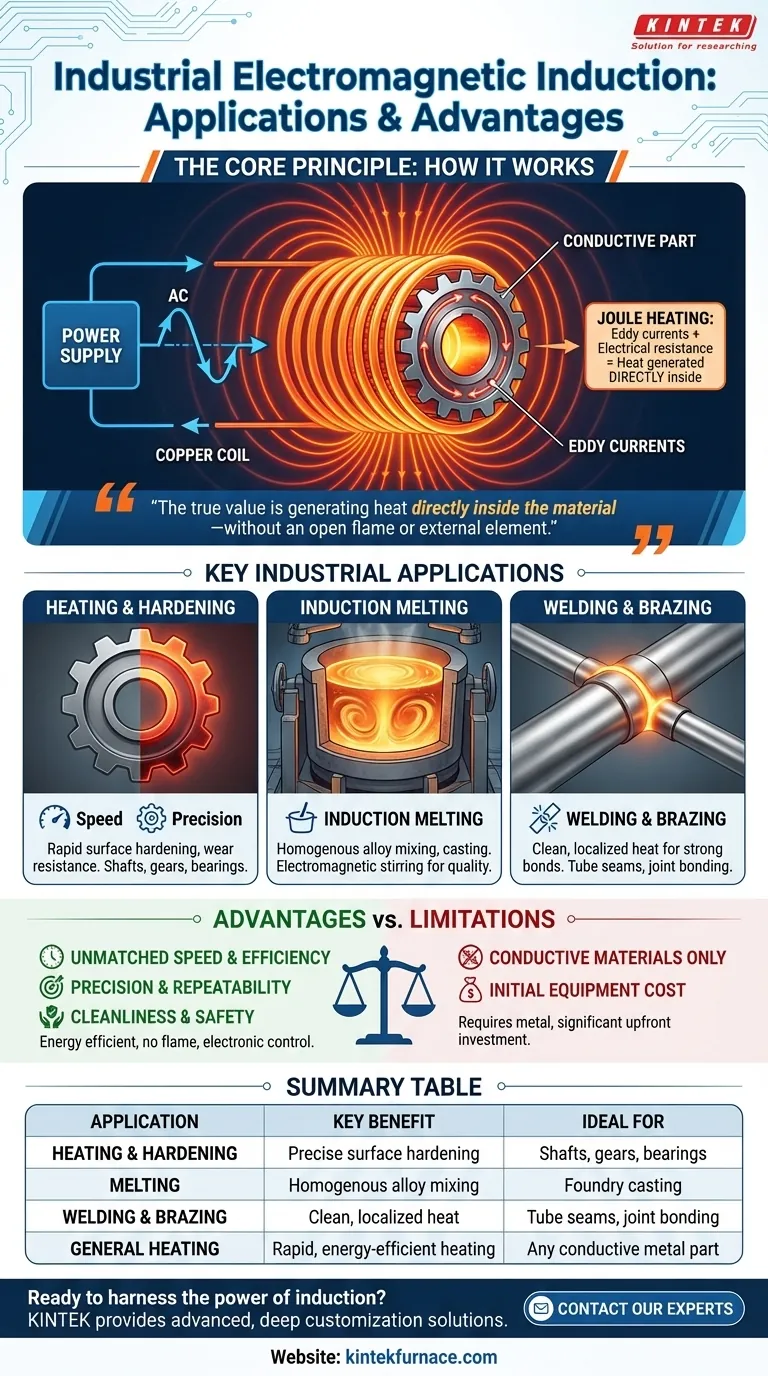
In industrial manufacturing, electromagnetic induction is a cornerstone technology for the non-contact heating of conductive materials. Its primary uses are for highly precise and rapid metal heating, surface hardening, melting, and welding or brazing applications where control and efficiency are paramount.
The true value of induction is not just what it does, but how it does it. By generating heat directly inside the material itself—without an open flame or external element—it provides a level of speed, precision, and cleanliness that traditional heating methods cannot match.
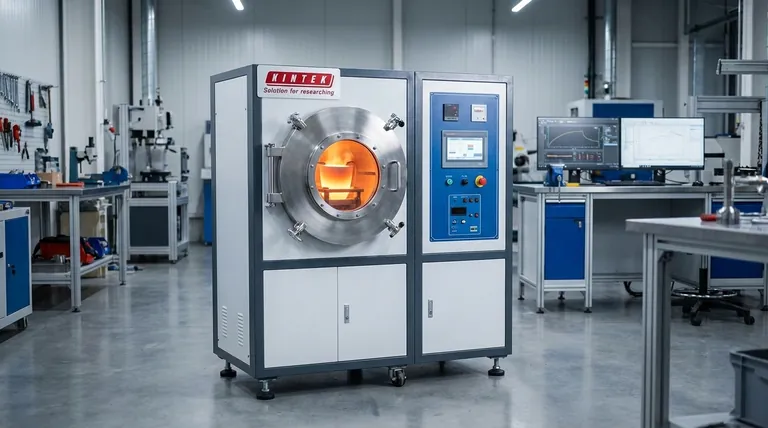

The Core Principle: How Induction Generates Heat
To understand induction's applications, we must first understand its fundamental mechanism. The process transforms electrical energy into a targeted magnetic field, which in turn generates heat within the workpiece.
Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with a specialized power supply that sends a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a copper coil. This coil, often shaped to fit the part being heated, generates an intense and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around it.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a conductive part, such as a steel gear or copper pipe, is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces small, circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
The Role of Resistance
All metals have some natural electrical resistance. As these powerful eddy currents flow against this resistance, they dissipate energy in the form of heat—a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This is what makes the part heat up, often in a matter of seconds. The material effectively becomes its own heating element.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The unique properties of induction heating make it ideal for processes that demand speed, consistency, and control.
Induction Heating & Hardening
This is one of the most common uses. A steel component, like a shaft or bearing race, is rapidly heated to a precise temperature and then quickly quenched. This process hardens a thin surface layer, making it highly resistant to wear, while leaving the inner core of the metal tough and ductile.
Induction Melting
In foundries, large induction furnaces are used to melt metals for casting. The magnetic field not only heats the metal but also creates a natural stirring action. This electromagnetic stirring ensures the molten metal is homogenous, which is critical for creating high-quality, uniform alloys.
Induction Welding & Brazing
Induction is used to join metal parts together. For welding, the edges of two components (like the seam of a steel tube) are rapidly heated to their melting point and fused. For brazing, the heat is used to melt a filler alloy into a joint, creating a strong bond between two parts without melting the parts themselves.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. Understanding the pros and cons of induction is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the part, the process is extremely fast and energy-efficient. There is very little wasted energy heating the surrounding air or furnace walls, unlike a conventional oven where heat must slowly soak in from the outside.
Advantage: Precision and Repeatability
The heating zone is defined by the shape and position of the coil. This allows heat to be applied to very specific areas of a part, leaving the rest unaffected. The process is electronically controlled, making it perfectly repeatable, which is essential for high-volume quality control.
Advantage: Cleanliness and Safety
Induction heating is a clean process. There is no open flame, no smoke, and no combustion by-products to contaminate the material or the workplace. This improves safety and the quality of the final product.
Limitation: Material Requirement
The fundamental principle of induction relies on electrical conductivity. Therefore, it works only on conductive materials like metals. It cannot be used to directly heat non-conductors such as plastics, wood, or most ceramics.
Limitation: Initial Equipment Cost
Induction heating systems, including the power supply and custom-designed coils, can require a significant upfront capital investment compared to simpler methods like a gas-fired forge or resistance oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use induction heating depends on balancing the need for performance against material constraints and budget.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable surface hardening: Induction is the definitive choice for its unmatched speed and precision.
- If your primary focus is melting high-purity alloys or ensuring a homogenous mix: An induction furnace provides a level of cleanliness and stirring that is superior to most combustion-based methods.
- If your primary focus is simple bulk heating or working with non-conductive materials: A conventional resistance or convection oven is a more practical and economical solution.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the right tool not just for the job, but for the specific quality and efficiency goals of your operation.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Heating & Hardening | Precise surface hardening | Shafts, gears, bearings |
| Melting | Homogenous alloy mixing | Foundry casting |
| Welding & Brazing | Clean, localized heat | Tube seams, joint bonding |
| General Heating | Rapid, energy-efficient heating | Any conductive metal part |
Ready to harness the power of electromagnetic induction for your manufacturing process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse industries with advanced induction heating solutions. Our product line, including custom-designed coils and power supplies, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique production requirements for hardening, melting, or brazing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction heating systems can enhance your efficiency, repeatability, and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















