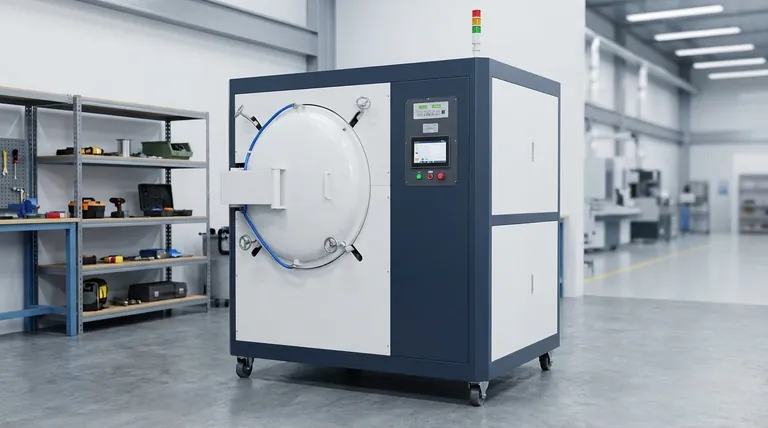
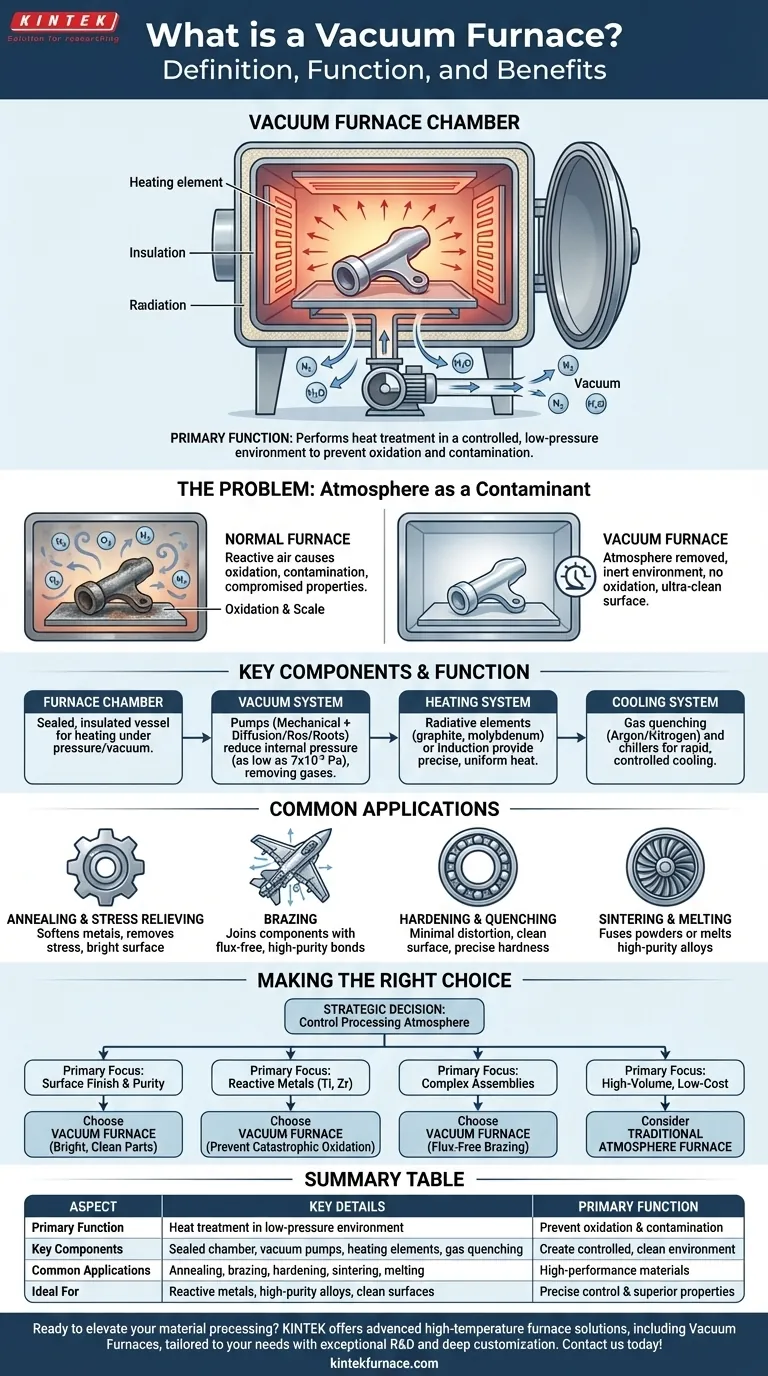
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized type of furnace that performs heat treatment in a controlled, low-pressure environment. Its primary function is to process materials at high temperatures without the interference of air or other gases. By pumping the atmosphere out of a sealed chamber, it prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and eliminates sources of contamination.
By removing air, a vacuum furnace creates an ultra-clean environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, enabling high-temperature processes that produce materials with superior purity, strength, and specific microstructures that would be impossible to achieve in a conventional furnace.

The Fundamental Problem: Atmosphere as a Contaminant
At elevated temperatures, most materials become highly reactive. The air around us, composed primarily of nitrogen, oxygen, and water vapor, becomes an aggressive agent that can damage or destroy the part being treated.
Why Normal Furnaces Fall Short
In a traditional furnace open to the atmosphere, heating a metal part causes the oxygen in the air to rapidly react with its surface. This process, known as oxidation, creates a layer of scale that compromises the part's dimensions, surface finish, and material properties.
The Vacuum Solution
A vacuum furnace solves this problem by physically removing the atmosphere from its sealed chamber. By pumping out these reactive gases, it creates a chemically inert environment. This ensures that the only changes to the material are those caused by the carefully controlled application of heat.
Beyond Oxidation Prevention
The vacuum offers two other significant advantages. First, it eliminates contamination from airborne dust or other particles. Second, it removes gas as a medium for heat transfer (convection), meaning heat is primarily transferred through radiation, which can allow for more precise and uniform temperature control under the right conditions.
Key Components and How They Function
A vacuum furnace is a complex system where each component plays a critical role in creating and maintaining the controlled environment.
The Furnace Chamber
This is the sealed, insulated vessel where the product is placed for heating. It is built to withstand both high temperatures internally and immense external atmospheric pressure when a vacuum is pulled inside.
The Vacuum System
This is the heart of the furnace. It typically uses a series of pumps to reduce the internal pressure. A mechanical "roughing" pump removes the bulk of the air, and then a diffusion or Roots pump takes over to achieve a high vacuum, often reaching pressures as low as 7 × 10⁻³ Pascals. Valves and gauges are used to control and monitor the vacuum level precisely.
The Heating System
Heating elements, often made of graphite or refractory metals like molybdenum, are arranged inside the chamber to radiate heat onto the product. In some advanced designs, like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnaces, magnetic fields are used to induce an electric current directly within the metal itself, causing it to heat and melt without contact.
The Cooling System
Controlling the cooling rate is just as critical as heating. Many vacuum furnaces include a gas quenching system that can rapidly backfill the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like argon or nitrogen. A powerful fan circulates this gas, removing heat quickly and controllably. External chillers are also used to cool the furnace walls and components.
Common Applications of Vacuum Heat Treatment
The unique capabilities of vacuum furnaces make them essential for a wide range of high-performance industrial processes.
Annealing and Stress Relieving
This process softens metals, enhances ductility, and removes internal stresses created during manufacturing. Performing it in a vacuum ensures the part emerges with a bright, clean surface free of discoloration.
Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a superior method for joining components. It allows filler metal to flow into joints cleanly without the need for corrosive fluxes, creating strong, high-purity bonds, especially in complex assemblies for aerospace and medical devices.
Hardening and Quenching
Hardening steel and other alloys in a vacuum results in minimal distortion and a clean surface. The controlled gas quench allows for precise cooling rates to achieve specific hardness levels and microstructures.
Sintering and Melting
Vacuum furnaces are used to fuse powdered metals into a solid mass (sintering) or to melt and produce extremely high-purity alloys. By preventing any reaction with air, the final material has enhanced properties ideal for critical applications like turbine blades or medical implants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the material requirements and desired outcome for the final part.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and purity: A vacuum furnace is the ideal choice to eliminate oxidation and achieve a bright, clean part that requires no secondary cleaning.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals: Materials like titanium, zirconium, and certain superalloys require a vacuum to prevent catastrophic oxidation at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies: Vacuum brazing provides unparalleled strength and cleanliness for intricate components, creating flux-free joints.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost treatment: A traditional atmosphere furnace may be more cost-effective if a perfectly clean surface and absolute material purity are not critical requirements.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to control the processing atmosphere, ensuring the final material meets the highest standards of integrity and performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Heat treatment in a low-pressure environment to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Key Components | Sealed chamber, vacuum system (pumps), heating elements (e.g., graphite), cooling system (gas quenching). |
| Common Applications | Annealing, brazing, hardening, sintering, and melting for high-performance materials. |
| Ideal For | Reactive metals, high-purity alloys, and processes requiring clean surfaces and precise control. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with reactive metals, complex assemblies, or demanding purity standards, our expertise ensures superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals with reliable, high-performance furnace technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















