At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized thermal processing system designed to heat materials to extremely high temperatures within a low-pressure environment. By systematically removing air and other reactive gases from a sealed chamber, it prevents oxidation and contamination, allowing for processes like brazing, sintering, and heat treatment that result in exceptionally high-quality and consistent material properties.
A vacuum furnace's primary function is not just heating; it's about achieving absolute environmental control. By creating a vacuum, you eliminate unwanted chemical reactions, enabling you to manipulate a material's structure with a level of precision that is impossible in a normal atmosphere.
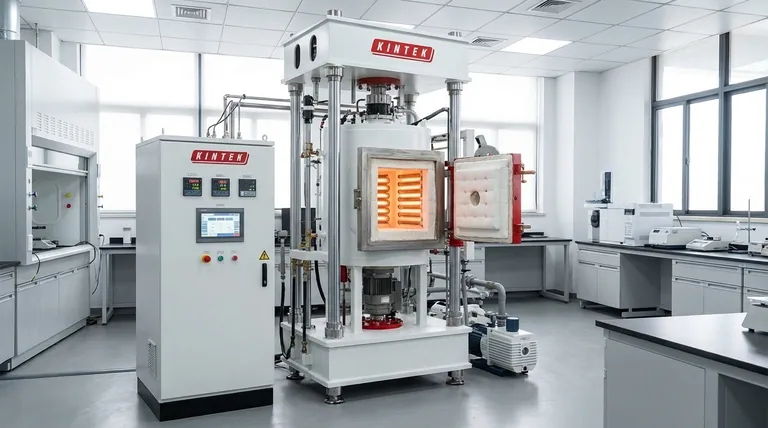

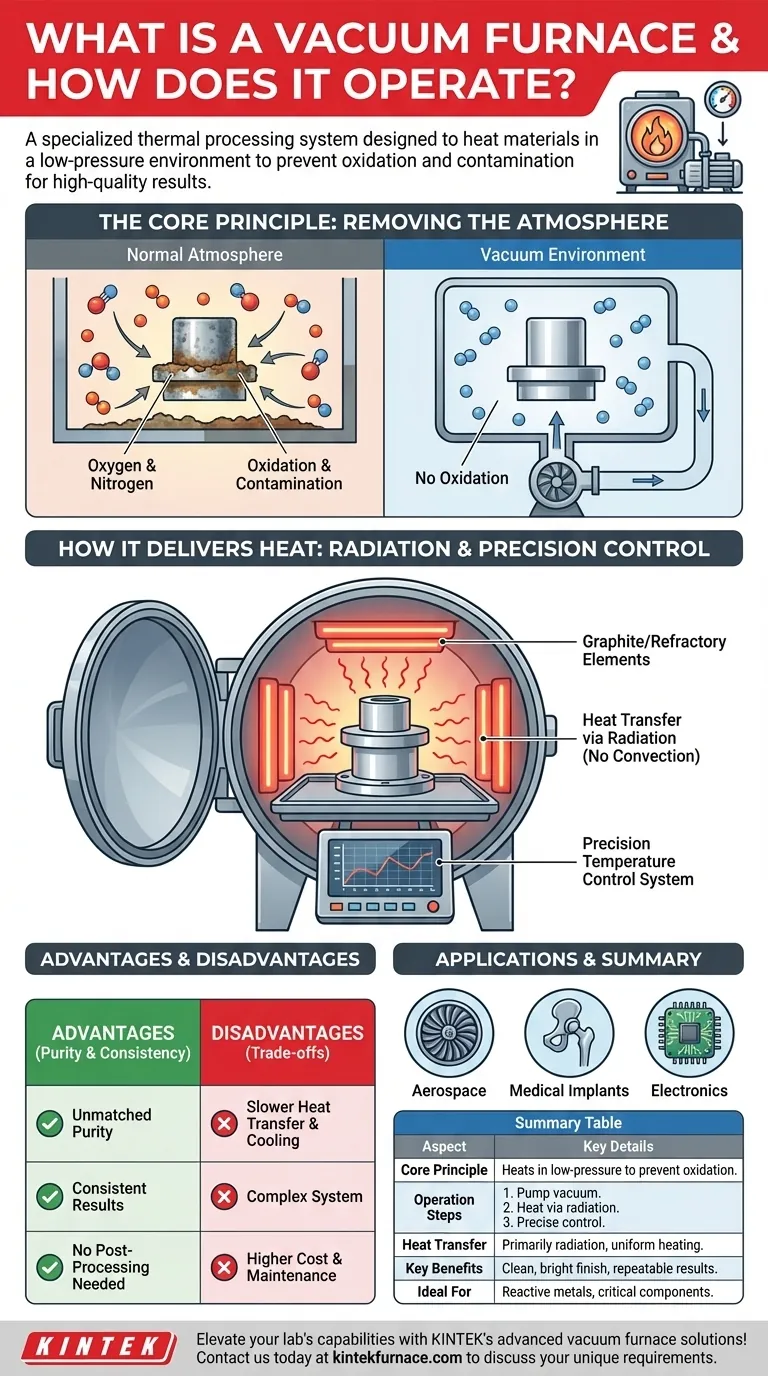
The Core Principle: Removing the Atmosphere
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create a chemically non-reactive environment. This is a fundamental departure from conventional furnaces that operate in the presence of air.
The Problem with Air: Oxidation and Contamination
When metals are heated in the presence of air, the oxygen and nitrogen react with the material's surface. This process, known as oxidation, creates discoloration and scale, altering the part's dimensions and compromising its structural integrity. Other atmospheric gases can act as contaminants, weakening the final product.
Creating a Vacuum: The Role of the Pump
A vacuum furnace begins its cycle by using a powerful vacuum system to pump virtually all air and other gases out of the sealed heating chamber. This reduces the internal pressure to a level far below standard atmospheric pressure, creating the necessary vacuum state.
The Sealed Chamber: An Isolated Environment
The entire process takes place inside a robust, sealed vessel capable of withstanding both the intense internal heat and the external atmospheric pressure. This chamber isolates the material from the outside world, ensuring the purity of the vacuum environment is maintained throughout the heating cycle.
How a Vacuum Furnace Delivers Heat
Once the vacuum is established, the heating process can begin. However, heating in a vacuum presents unique challenges and requires a different approach to energy transfer.
The Heating Elements
Like a conventional oven, a vacuum furnace uses heating elements to generate thermal energy. These elements are typically made of graphite or refractory metals capable of reaching temperatures from 600°C to over 2000°C (1100°F to 3600°F) without degrading.
The Challenge of Heat Transfer in a Vacuum
In a normal furnace, heat is transferred by convection (movement of hot air), conduction, and radiation. By removing the air, a vacuum furnace eliminates convection entirely. Heat is transferred almost exclusively through radiation, where the hot elements emit thermal energy that is absorbed directly by the material.
This method results in extremely uniform heating, as all surfaces are exposed to the same level of radiant energy without interference from gas currents.
Precision Control: The Brains of the Operation
A sophisticated temperature control system precisely manages the power sent to the heating elements. This system monitors the temperature of the material and adjusts the output to follow a specific heating and cooling profile, ensuring the process is repeatable and achieves the desired metallurgical outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum furnaces offer significant advantages, they come with inherent trade-offs that make them suitable for specific, high-value applications.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Consistency
The primary benefit is a clean, bright, and uncontaminated final product. By preventing oxidation, parts emerge from the furnace without scale, often eliminating the need for subsequent cleaning or surface finishing operations.
Disadvantage: Slower Heat Transfer and Cooling
Because heat transfer relies solely on radiation, heating and cooling cycles can be slower compared to furnaces that use convection. Gaseous "backfilling" with inert gases like argon or nitrogen is often used to accelerate the cooling phase, but the process remains highly controlled.
Disadvantage: System Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines. The need for a sealed chamber, high-capacity vacuum pumps, and sophisticated control systems makes them significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Applying This to Your Process
Choosing a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the required quality and properties of your final product. It is an investment in process control and material perfection.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical purity: A vacuum furnace is essential for reactive metals or mission-critical components (like aerospace turbine blades) where any contamination is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is a bright, clean finish: Vacuum brazing and annealing produce parts that are immediately ready for use, avoiding costly and difficult post-processing steps.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: The precise control over both temperature and atmosphere ensures that every part in every batch receives the exact same treatment, crucial for medical implants and high-performance electronics.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace provides an unparalleled level of environmental control, enabling the creation of advanced materials with superior performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heats materials in a low-pressure, sealed chamber to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Operation Steps | 1. Pump air out to create vacuum. 2. Heat via radiation from elements. 3. Control temperature precisely. |
| Heat Transfer | Primarily through radiation, ensuring uniform heating without convection. |
| Advantages | Unmatched purity, consistent results, no post-processing needed for clean finishes. |
| Disadvantages | Slower heating/cooling, higher complexity and cost compared to standard furnaces. |
| Applications | Ideal for aerospace, medical implants, electronics, and reactive metals requiring high purity. |
Elevate your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior material processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and achieve unparalleled results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity



















