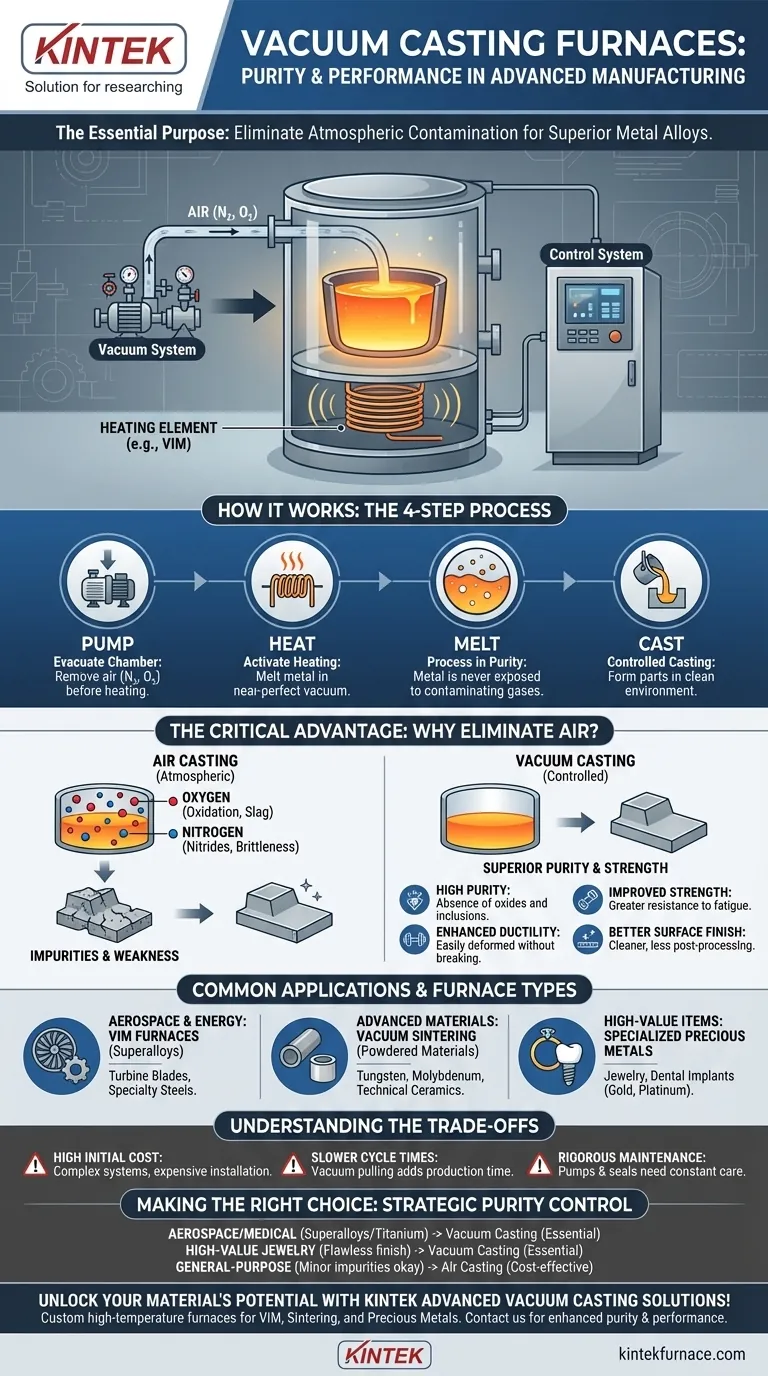
In advanced manufacturing, a vacuum casting furnace is a specialized system used to melt and cast metals inside a controlled, low-pressure chamber. Its primary purpose is to eliminate atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen during the melting process. This prevents contamination and allows for the creation of exceptionally pure, high-strength metal alloys with superior mechanical properties that cannot be achieved in a normal atmosphere.
The core value of a vacuum casting furnace is not simply melting metal. It is about creating an ultra-clean environment to control the material's fundamental chemistry, enabling the production of pristine alloys for the most demanding applications.

How a Vacuum Casting Furnace Works
A vacuum casting furnace is more than just a heater; it is a precisely controlled environment. Understanding its components and process reveals why it is so critical for high-performance materials.
The Core Principle: Removing the Atmosphere
The fundamental goal is to remove the air from the furnace chamber before and during heating. Air contains about 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen, both of which can react negatively with molten metal. By pumping out these gases, the metal melts in a near-perfect vacuum.
Key Components of the System
A typical furnace consists of several integrated parts:
- Furnace Body: A sealed, robust chamber designed to withstand both high temperatures and a high vacuum.
- Vacuum System: A series of pumps, valves, and gauges work together to evacuate the air from the chamber and maintain the desired low pressure.
- Heating Element: An electric heating system, often using induction currents (Vacuum Induction Melting - VIM) or resistance, melts the metal charge inside a crucible.
- Control System: This manages the entire process, from creating the vacuum to regulating the temperature and executing the final pour or cast.
The Process: Pump, Heat, Melt, Cast
The operational sequence is methodical. First, the metal is loaded into the furnace, and the chamber is sealed. The vacuum system then pumps the air out. Once the target vacuum level is reached, the heating system activates, melting the metal. This entire process ensures the molten metal is never exposed to contaminating gases.
The Critical Advantage: Eliminating Gas Contamination
Casting in the open air is sufficient for many applications, but it introduces unavoidable impurities that are unacceptable for high-performance components.
The Problem with Oxygen and Nitrogen
When metals are melted in the air, they react with atmospheric gases. Oxygen causes oxidation, forming slag and non-metallic inclusions that weaken the final product. Nitrogen can dissolve into certain alloys, forming nitrides that make the metal brittle. These reactions compromise the material's integrity.
The Result: Superior Purity and Properties
By eliminating these gases, vacuum casting produces alloys with:
- High Purity: The near-total absence of oxides and other inclusions.
- Improved Mechanical Strength: Materials are stronger and more resistant to fatigue and fracture.
- Enhanced Ductility: The metal can be deformed more easily without breaking.
- Better Surface Finish: Castings are often cleaner and require less post-processing.
Common Applications and Furnace Types
The need for purity dictates the application. Vacuum furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution and are specialized for particular tasks.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnaces
VIM furnaces are the workhorses for producing superalloys (e.g., for jet engine turbine blades) and high-quality specialty steels. The induction heating method is efficient and provides excellent stirring for a homogenous melt.
Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
These are designed to process powdered materials, such as tungsten, molybdenum, or technical ceramics. Instead of melting a solid block, the furnace heats the powder until the grains fuse together into a solid, dense part.
Specialized Furnaces for Precious Metals
The jewelry and dental industries use smaller vacuum casting furnaces to produce intricate, high-quality parts from gold, platinum, and palladium. The vacuum ensures a dense, pore-free casting with a brilliant finish, which is critical for high-value items.
Distinguishing Casting from Heat Treatment
It's important to note that while some vacuum furnaces are for casting (melting and pouring), others are solely for heat treatment. Processes like annealing (softening) or quenching (hardening) can also be performed in a vacuum to prevent surface oxidation on an already-formed part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum casting offers unparalleled quality, it comes with significant operational considerations.
High Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnace systems are far more expensive to purchase and install than their atmospheric counterparts. They are complex machines requiring specialized knowledge to operate and maintain.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pulling a vacuum before each melt adds considerable time to the production cycle. This makes vacuum casting a lower-throughput process compared to conventional methods.
Rigorous Maintenance Requirements
The vacuum pumps, seals, and internal components require constant monitoring and regular maintenance to ensure the system can achieve and hold the necessary low pressure. Any leak compromises the entire process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right process depends entirely on the required material properties and economic constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance superalloys for aerospace or medical implants: Vacuum casting, particularly VIM, is the only way to achieve the necessary purity and mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive metals like titanium: A vacuum environment is non-negotiable to prevent the metal from becoming brittle and unusable due to gas absorption.
- If your primary focus is creating flawless, high-value jewelry: A specialized vacuum casting furnace is essential for delivering a pore-free, brilliant surface finish.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose metal components where minor impurities are acceptable: Conventional air-melt casting is a far more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum casting is a strategic decision to control material purity at the atomic level, unlocking a new class of high-performance materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Eliminate atmospheric gases to prevent contamination and produce pure, high-strength metal alloys. |
| Key Components | Furnace body, vacuum system, heating element (e.g., VIM), control system. |
| Process Steps | Pump out air, heat and melt metal in vacuum, cast in controlled environment. |
| Main Advantages | High purity, improved mechanical strength, enhanced ductility, better surface finish. |
| Common Applications | Superalloys for aerospace, reactive metals like titanium, high-value jewelry, powdered materials sintering. |
| Trade-offs | High cost, slower cycle times, rigorous maintenance requirements. |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced vacuum casting solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnaces, Vacuum Sintering Furnaces, and specialized models for precious metals. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you're developing superalloys for aerospace, medical implants, or flawless jewelry. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material purity and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















