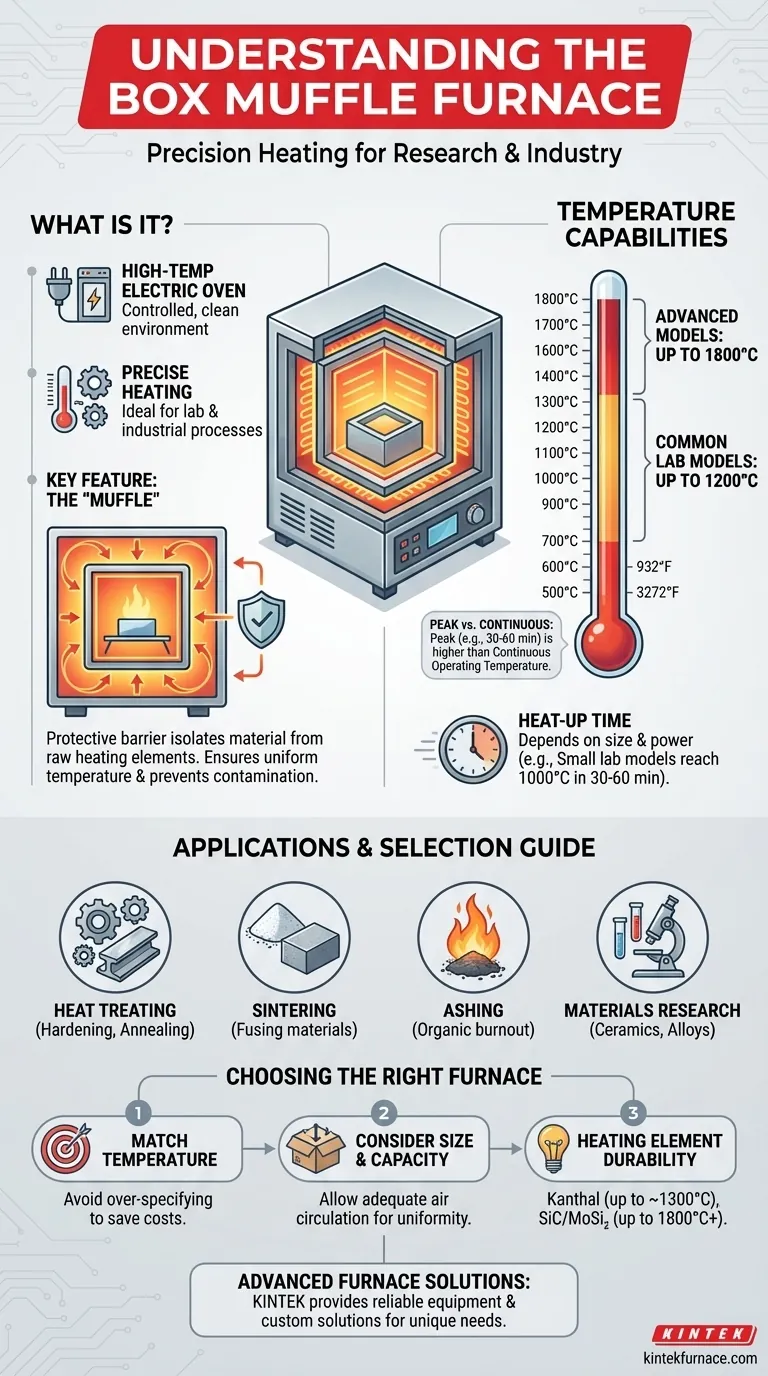
In essence, a box muffle furnace is a high-temperature electric oven used for laboratory and industrial processes that require a precisely controlled, clean heating environment. While specific models vary, they can typically reach temperatures ranging from 500°C to 1800°C (932°F to 3272°F), with many standard laboratory models operating up to 1200°C.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is not just its high temperature, but its design. A protective barrier, or "muffle," isolates the material being heated from the raw heating elements, ensuring uniform temperature and preventing contamination.

What Defines a Box Muffle Furnace?
A box muffle furnace is a fundamental tool for processes like sintering, melting, heat treatment, and materials purification. Its design is optimized for precision and thermal isolation.
The Box-Shaped Heating Chamber
The core of the unit is a chamber made of highly heat-resistant materials, such as ceramic fiber or firebrick. This design provides excellent thermal insulation, allowing the furnace to achieve and maintain extreme temperatures efficiently.
The Critical Role of the "Muffle"
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber or liner that separates the workload from the heating elements. This separation is the furnace's key advantage.
It ensures that the sample is heated uniformly through radiation and convection, rather than direct contact with the elements. More importantly, it protects the sample from any contaminants that might be emitted from the heating elements at high temperatures.
Common Applications
These furnaces are indispensable in fields requiring high-temperature processing. Common uses include:
- Heat Treating: Hardening or annealing metals and alloys.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials together below their melting point.
- Ashing: Burning off organic material to determine the inorganic content of a sample.
- Materials Research: Developing and testing new ceramics, alloys, and composites.
Understanding Temperature Capabilities
The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace is not a single number but a function of its design, materials, and intended purpose.
A Wide Operational Range
The temperature capabilities of muffle furnaces vary significantly by model. General-purpose laboratory units often have a maximum temperature of 1100°C or 1200°C.
More advanced models designed for specialized materials science or ceramics can reach 1700°C, 1800°C, or even higher.
Peak vs. Continuous Operating Temperature
It is critical to distinguish between a furnace's maximum peak temperature and its continuous operating temperature. Many models can only hold their absolute maximum temperature for a short period (e.g., 30-60 minutes).
For extended processes, the continuous operating temperature, typically 50°C to 100°C lower than the peak, is the more important specification to consider. Exceeding this for long durations can reduce the lifespan of the heating elements and insulation.
Heat-Up Time Considerations
The time it takes to reach the target temperature depends on the furnace's size and power. Small laboratory models might reach 1000°C in 30 to 60 minutes.
Larger industrial furnaces with greater thermal mass will naturally require a longer time to heat up and stabilize.
Key Considerations Before Choosing
Selecting the right furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and the specific needs of your process. Simply choosing the model with the highest temperature is often a mistake.
Matching Temperature to Your Material
Identify the actual temperature your process requires. A furnace rated for 1800°C is significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than a 1200°C model. Over-specifying temperature capabilities leads to unnecessary costs.
Chamber Size and Capacity
Ensure the internal chamber dimensions can accommodate your largest sample or batch. A tightly packed chamber can suffer from poor temperature uniformity, so allow for adequate air circulation around the workload.
Heating Element Durability
The type of heating element dictates the furnace's maximum temperature and longevity. Common Kanthal (FeCrAl) elements are used up to ~1300°C, while silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are required for higher temperatures up to 1800°C and beyond.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the demands of your specific application, not just by raw specifications.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or basic heat treatment: A reliable furnace with a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C is typically sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or sintering technical ceramics: You will need a high-temperature model capable of reaching 1700°C to 1800°C, likely with advanced programming controls.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and throughput: Pay close attention to the furnace's heat-up and cool-down rates, as this directly impacts your cycle times.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently select a furnace that serves as a precise and reliable tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 500°C to 1800°C (932°F to 3272°F), with common lab models up to 1200°C |
| Key Features | Protective muffle for uniform heating and contamination prevention, precise temperature control |
| Common Applications | Heat treating, sintering, ashing, materials research |
| Selection Tips | Match temperature to material needs, consider chamber size, and heating element durability |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















