In short, vacuum technology is fundamental to nearly every advanced manufacturing sector. It is utilized across industries including aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, nuclear, and energy. This technology is not a niche process but a critical enabler for producing the high-performance components that define modern engineering.
The core reason vacuum thermal processing is so widespread is its ability to create a perfectly controlled, contaminant-free environment. This allows manufacturers to manipulate material properties at a molecular level, achieving levels of purity, strength, and complexity that are simply impossible in the open atmosphere.

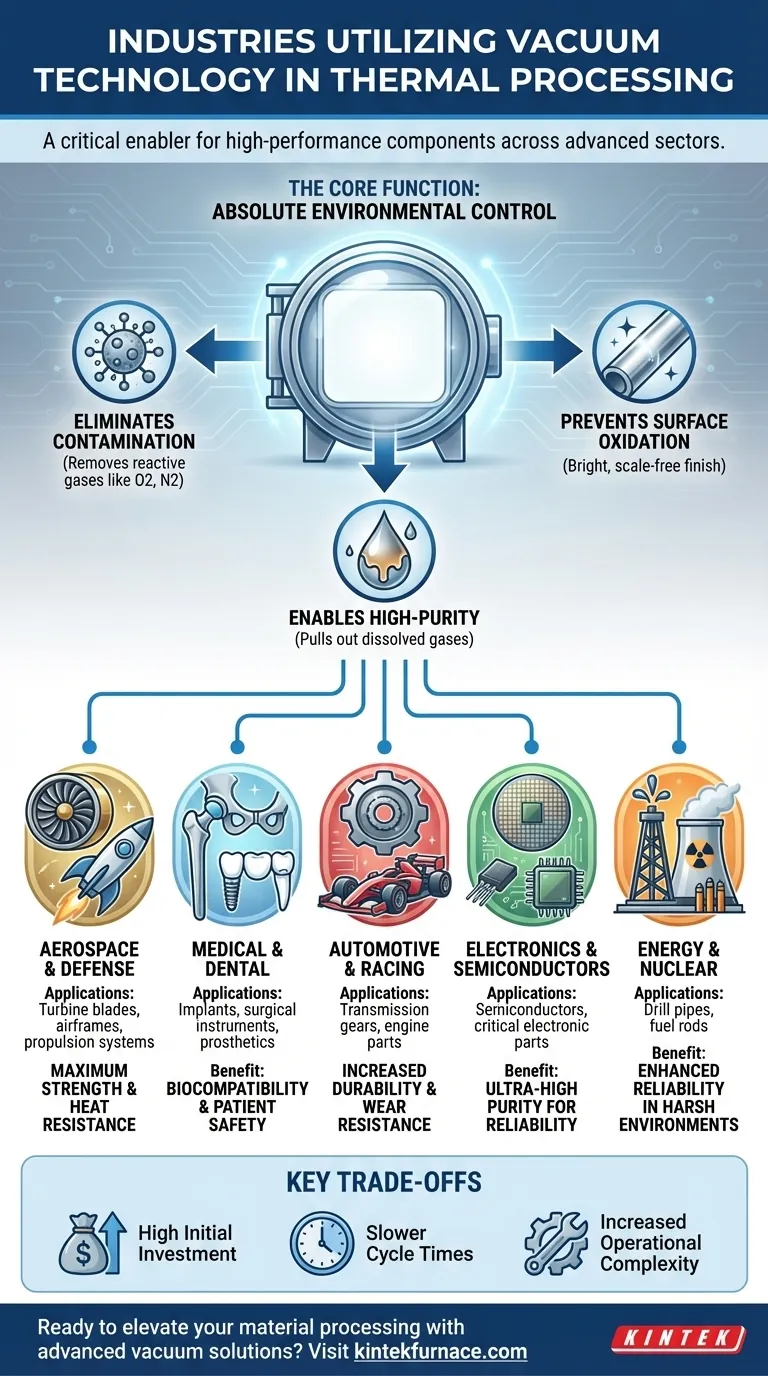
The Core Function of Vacuum in Thermal Processing
To understand why so many industries rely on this technology, you must first understand what it accomplishes. A vacuum isn't just empty space; it's a tool for absolute environmental control.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
The air around us contains oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor, and other elements. At high temperatures, these elements eagerly react with metals, forming oxides and nitrides that degrade a material's integrity.
A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, ensuring the material remains in its intended, pure state throughout the heating and cooling process.
Enabling High-Purity Material Production
For sectors like electronics and medicine, even parts-per-million contamination can be catastrophic. Vacuum melting and refining processes are used to pull dissolved gases like oxygen and hydrogen out of molten metal.
This results in an ultra-pure material with superior electrical, mechanical, and biocompatible properties, which is essential for semiconductors and medical implants.
Preventing Oxidation on the Surface
Vacuum processing delivers a bright, clean, scale-free surface finish. Because there is no oxygen to cause oxidation (rust or scale), parts emerge from the furnace without needing aggressive secondary cleaning operations like blasting or chemical pickling.
Key Industrial Applications and Their Drivers
The decision to use vacuum processing is always driven by the need for a specific, high-stakes outcome that atmospheric processing cannot deliver.
Aerospace & Defense: The Quest for Performance
This sector relies on vacuum technology to create high-performance superalloys for critical components like turbine blades, airframes, and propulsion systems. These parts must withstand extreme temperatures and stresses without failing.
The controlled vacuum environment ensures the metallurgical properties of these alloys are perfected, delivering maximum strength and heat resistance.
Medical & Dental: The Mandate for Biocompatibility
For medical implants, surgical instruments, and dental prosthetics, material purity is a matter of patient safety. Vacuum processing is essential for creating components that are strong, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible.
By preventing contamination, the vacuum process guarantees that implants will not react adversely with the human body. It is also used in additive manufacturing to create patient-specific implants from reactive metals like titanium.
Automotive & Racing: The Push for Durability
In the automotive industry, vacuum heat treatment is used to increase the strength and wear resistance of critical components like transmission gears, engine parts, and high-performance drivetrain components.
This leads to longer-lasting parts that can handle higher loads, which is crucial for both consumer vehicle reliability and the extreme demands of off-road and racing applications.
Electronics & Semiconductors: The Requirement for Purity
The electronics industry requires materials of the highest possible purity for semiconductors and other critical electronic components.
Vacuum melting is the only way to produce materials pure enough to meet these specifications. Any impurities would alter the material's electrical properties and render the final component useless.
Energy & Nuclear: The Demand for Reliability
Components used in oil and gas drilling (drill pipes) and nuclear power generation (fuel rods) operate in some of the harshest environments imaginable.
Vacuum processing ensures these parts have the necessary strength and corrosion resistance to function reliably and safely under extreme pressure and temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Vacuum Processing
While powerful, vacuum thermal processing is not the solution for every application. It involves specific trade-offs that must be considered.
High Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces and their associated pumping systems represent a significant capital expense compared to conventional atmospheric furnaces. This technology requires a clear business case based on high-value parts.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping a furnace chamber down to a deep vacuum level takes time. This can result in longer overall cycle times compared to atmospheric processes, impacting throughput.
Increased Operational Complexity
Operating and maintaining a vacuum system requires specialized knowledge. Issues with seals, pumps, or sensors can compromise the process, demanding a higher level of operator skill and a rigorous maintenance program.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum processing must be aligned with your component's specific performance requirements and material type.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and performance: Vacuum processing is non-negotiable for reactive metals (like titanium), superalloys, and medical-grade components.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective hardening of common steels: Conventional atmospheric heat treating is often sufficient, faster, and more economical.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, net-shape parts with superior surfaces: Vacuum-based processes like additive manufacturing or vacuum pressing offer unparalleled precision and finish.
Ultimately, mastering the vacuum environment is what separates the production of standard components from the creation of truly high-performance ones.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Turbine blades, airframes, propulsion systems | Maximum strength, heat resistance, and performance |
| Medical & Dental | Implants, surgical instruments, dental prosthetics | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and patient safety |
| Automotive & Racing | Transmission gears, engine parts, drivetrain components | Increased strength, wear resistance, and durability |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Semiconductors, electronic components | Ultra-high purity for reliable electrical properties |
| Energy & Nuclear | Drill pipes, fuel rods | Enhanced strength and corrosion resistance in harsh environments |
Ready to elevate your material processing with advanced vacuum solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, or energy, we can help you achieve superior purity, strength, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















