Future advancements in rotary furnace technology are focused on creating systems that are more intelligent, efficient, and versatile. The next generation of furnaces will integrate artificial intelligence for predictive process control, utilize advanced materials for better durability and heat management, and incorporate sophisticated energy recovery systems to drastically reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
The core evolution of the rotary furnace is its transformation from a simple, brute-force heating instrument into a precise, data-driven processing tool. Future advancements are not about a single breakthrough but a convergence of digital intelligence, material science, and sustainable engineering.

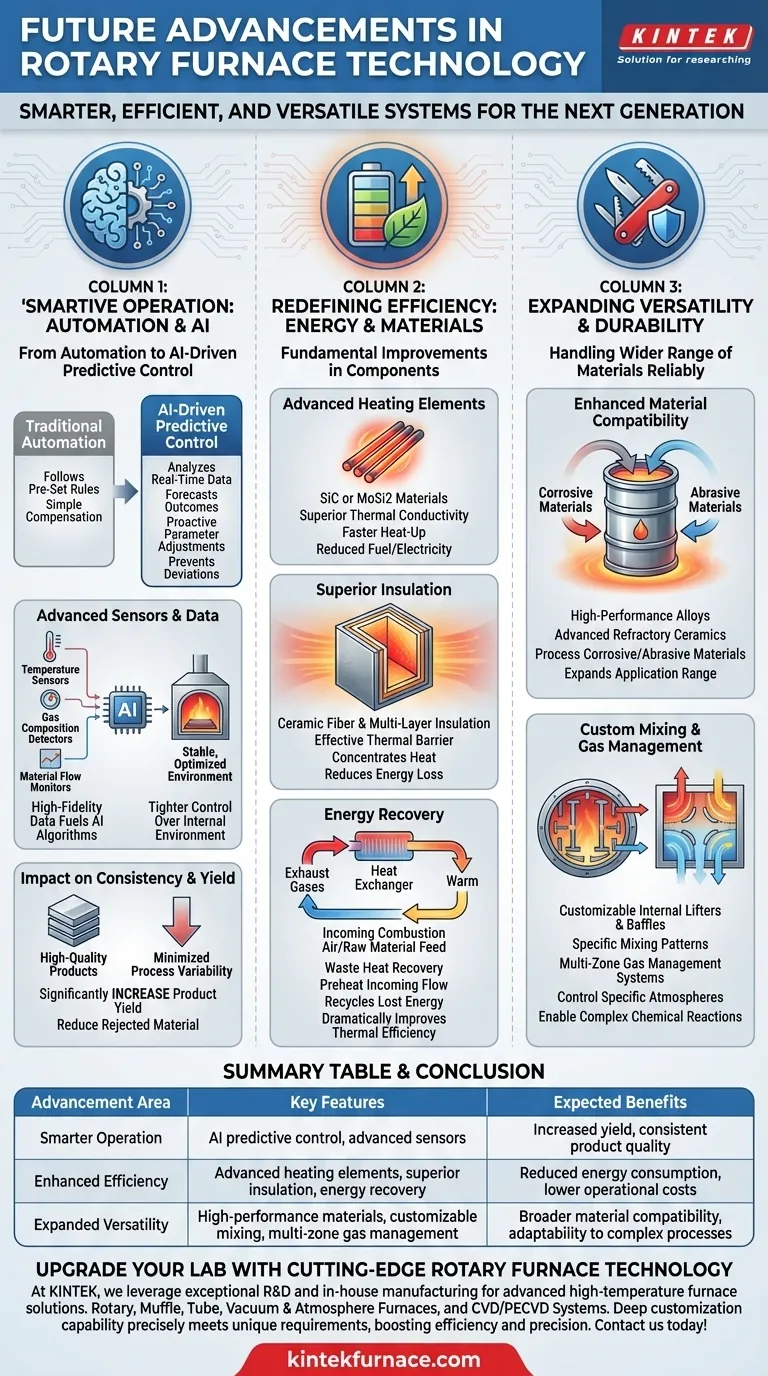
The Drive for "Smarter" Operation: Automation and AI
The most significant shift in furnace technology is the integration of intelligence. The goal is to move beyond simple automation to create a system that actively optimizes itself.
From Automation to Predictive Control
Traditional automation follows pre-set rules. The future lies in AI-driven predictive control, where the system analyzes real-time data to forecast outcomes and adjust parameters proactively.
This allows the furnace to automatically compensate for variations in raw material, prevent process deviations before they occur, and ensure a highly consistent final product.
The Role of Advanced Sensors
An intelligent system is only as good as its data. Future furnaces will feature more sophisticated sensor suites to monitor temperature, gas composition, and material flow with extreme precision.
This high-fidelity data is the fuel for AI algorithms, enabling tighter control over the internal environment than ever before.
Impact on Consistency and Yield
The ultimate benefit of a "smarter" furnace is a direct improvement in operational metrics. By minimizing process variability and optimizing reaction conditions, these systems will significantly increase product yield and reduce the volume of rejected or out-of-spec material.
Redefining Efficiency: Energy and Materials
Alongside intelligence, there is a powerful push to reduce the immense energy consumption inherent in high-temperature processing. This is being achieved through fundamental improvements in the furnace's physical components.
Advanced Heating Elements
Modern designs are moving toward materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) for heating elements.
These materials offer superior thermal conductivity and higher operating temperatures, enabling faster heat-up times and more efficient transfer of energy to the payload, which directly reduces fuel or electricity consumption.
Superior Insulation and Thermal Management
A major source of inefficiency is heat loss to the surrounding environment. Advancements in ceramic fiber and multi-layer insulation create a much more effective thermal barrier.
This keeps the thermal energy concentrated within the furnace barrel, reducing the energy required to maintain a setpoint temperature.
Innovations in Energy Recovery
Future systems will place a heavy emphasis on waste heat recovery. This involves capturing high-temperature exhaust gases and using a heat exchanger to preheat the incoming combustion air or even the raw material feed.
This creates a closed-loop system that recycles energy that would otherwise be lost, dramatically improving overall thermal efficiency.
Expanding Versatility and Durability
The final frontier of advancement is in making rotary furnaces capable of handling a wider range of materials and processes more reliably.
Enhanced Material Compatibility
The rotating barrel and its internal lining are subject to extreme thermal and chemical stress. The use of new high-performance alloys and advanced refractory ceramics will allow furnaces to process more corrosive or abrasive materials.
This expands the application range of rotary furnaces into new and more demanding industrial processes.
Custom Mixing and Gas Management
The rotary action is critical for mixing. Future designs will feature more customizable internal lifters and baffles to create specific mixing patterns tailored to a process.
Combined with multi-zone gas management systems, this allows operators to create and control highly specific atmospheres in different parts of the furnace, enabling complex chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While these advancements offer significant benefits, they are not without challenges that require careful consideration.
The Upfront Cost of Innovation
Advanced systems integrating AI, specialized sensors, and premium materials carry a higher initial investment. The long-term return on investment from energy savings and improved yield must be carefully calculated against this capital expenditure.
Increased Complexity and Maintenance
A smarter, more complex furnace requires a more skilled workforce. Maintenance shifts from purely mechanical and electrical to include software and sensor calibration, necessitating specialized training for operators and technicians.
The Risk of Overspecialization
A furnace highly customized for a single, specific process may offer peak performance for that task but lack the flexibility to adapt to new products or changing production needs in the future.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
As you evaluate future furnace technology, your decision should be guided by your primary operational driver.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency and reducing costs: Prioritize systems with advanced energy recovery, superior insulation, and AI controls specifically designed to optimize fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is improving product quality and consistency: Look for furnaces with multi-zone heating, comprehensive sensor suites, and predictive AI algorithms that can maintain exceptionally tight process windows.
- If your primary focus is increasing process versatility: Emphasize furnaces built with robust materials for enhanced compatibility and designs that offer customizable mixing and gas management systems.
Ultimately, these advancements are elevating the rotary furnace into a strategic asset capable of delivering unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Advancement Area | Key Features | Expected Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Smarter Operation | AI predictive control, advanced sensors | Increased yield, consistent product quality |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Advanced heating elements, superior insulation, energy recovery | Reduced energy consumption, lower operational costs |
| Expanded Versatility | High-performance materials, customizable mixing, multi-zone gas management | Broader material compatibility, adaptability to complex processes |
Ready to upgrade your lab with cutting-edge rotary furnace technology? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, boosting efficiency and precision. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















