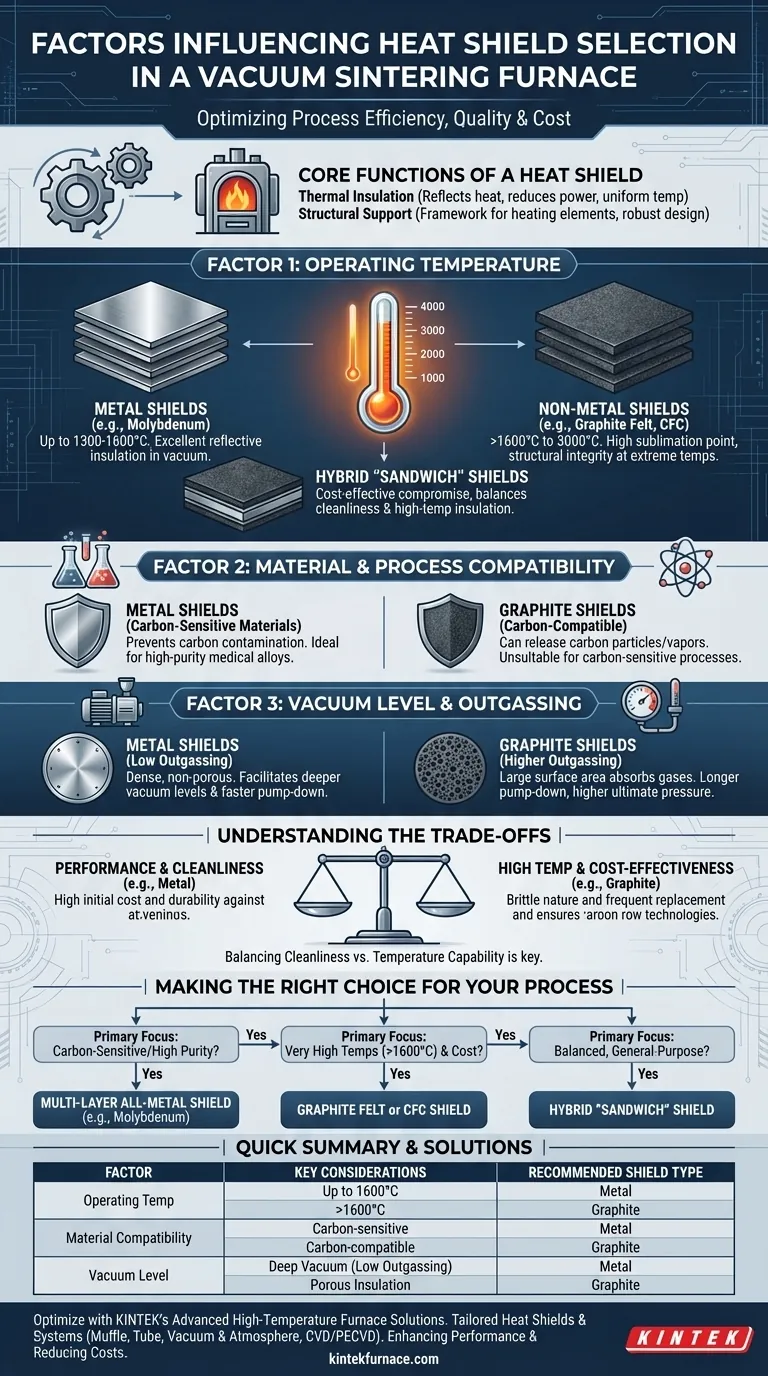
Choosing the right heat shield for a vacuum sintering furnace is a critical decision that directly impacts process efficiency, product quality, and operational cost. The selection is primarily driven by three core factors: the required sintering temperature, the chemical compatibility with the materials being processed, and the necessary vacuum level. Each factor dictates whether a metal, non-metal, or hybrid shield design is the most appropriate solution.
The selection of a heat shield is not a simple choice between metal and non-metal. It is a calculated trade-off between high-temperature performance, chemical reactivity, and long-term operating costs. Understanding these trade-offs is essential to optimizing your specific sintering process.

The Core Functions of a Heat Shield
Before diving into selection criteria, it's crucial to understand the dual roles a heat shield plays within the furnace's hot zone.
Thermal Insulation and Efficiency
The primary function of the heat shield is to reflect thermal energy back into the hot zone. This minimizes heat loss, reduces power consumption, and ensures uniform temperature distribution across the product load.
Structural Support
Beyond insulation, the heat shield assembly often serves as the structural framework for mounting the heating elements. Its design must be robust enough to support these components without warping or failing at high temperatures.
Factor 1: Operating Temperature
The maximum required sintering temperature is the first and most important filter in the selection process.
Molybdenum and Metal Shields
All-metal heat shields, typically constructed from multiple layers of molybdenum (and sometimes tungsten for hotter zones), are excellent for processes up to approximately 1300-1600°C. Their reflective surfaces provide highly efficient insulation in a vacuum.
Graphite and Non-Metal Shields
For very high temperatures, often exceeding 1600°C and going up to 3000°C, graphite felt or rigid carbon-fiber composite (CFC) shields are the industry standard. Graphite has a very high sublimation point and maintains its structural integrity at extreme temperatures where metals would fail.
Hybrid or "Sandwich" Shields
These designs combine an inner layer of metal (like molybdenum) with outer layers of graphite felt. This approach attempts to balance the cleanliness of a metal shield with the superior high-temperature insulation of graphite, often serving as a cost-effective compromise.
Factor 2: Material and Process Compatibility
The chemical interaction between the heat shield, the processing atmosphere, and the product itself is a critical consideration.
Metal Shields for High-Purity Environments
Metal shields are the definitive choice when processing carbon-sensitive materials, such as certain medical alloys or high-purity metals. Because they do not contain carbon, they prevent contamination of the product.
Graphite Shields and Carbon Reactivity
Graphite shields can release fine carbon particles or hydrocarbon vapors (outgassing), which can react with or contaminate the product load. This makes them unsuitable for processes where carbon is considered a contaminant.
Impact on Vacuum Level
The material and construction of the shield directly influence the furnace's vacuum performance. Porous materials like graphite felt have a large surface area and can absorb moisture and other gases, leading to longer pump-down times and a higher ultimate pressure due to outgassing. Dense metal shields offer a cleaner environment and facilitate achieving deeper vacuum levels more quickly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every heat shield choice involves balancing competing priorities. An objective analysis of these trade-offs is essential for making an informed decision.
Performance vs. Cost
All-metal shields have a high initial purchase price but are often more durable and can be cleaned, offering a longer service life in the right applications. Graphite shields are less expensive initially but can be brittle and may require more frequent replacement, especially if subjected to mechanical shock.
Cleanliness vs. Temperature Capability
This is the classic dilemma. If your process requires extreme purity and the lowest possible outgassing, a metal shield is superior. If your process requires the absolute highest temperatures, graphite is often the only viable option.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Loss
A multi-layer metal shield is a highly effective insulator through radiation reflection. A thick graphite felt package is an effective insulator through low thermal conductivity. The choice impacts the furnace's power curve and overall energy consumption, a key factor in long-term operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision should be guided by a clear understanding of your primary process objective.
- If your primary focus is processing carbon-sensitive materials or achieving the highest vacuum purity: A multi-layer all-metal shield (typically molybdenum) is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is reaching very high temperatures (>1600°C) and cost-effectiveness is a major concern: A graphite felt or carbon-fiber composite (CFC) shield is the standard industry solution.
- If your primary focus is a balanced, general-purpose application at moderate temperatures: A "sandwich" or mixed-felt shield combining metal and non-metal layers can offer a practical compromise between performance and cost.
By aligning your heat shield choice with your specific process requirements, you ensure optimal performance and long-term reliability for your furnace.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations | Recommended Shield Type |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1600°C: High efficiency; Above 1600°C: Extreme heat resistance | Metal (e.g., Molybdenum) for lower temps; Graphite for higher temps |
| Material Compatibility | Carbon-sensitive materials require purity; Risk of contamination | Metal for purity; Graphite may cause carbon reactivity |
| Vacuum Level | Outgassing affects pump-down and pressure; Cleanliness for deep vacuum | Metal for low outgassing; Graphite for porous insulation |
Optimize your lab's sintering efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored heat shields and systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and reducing costs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance



















