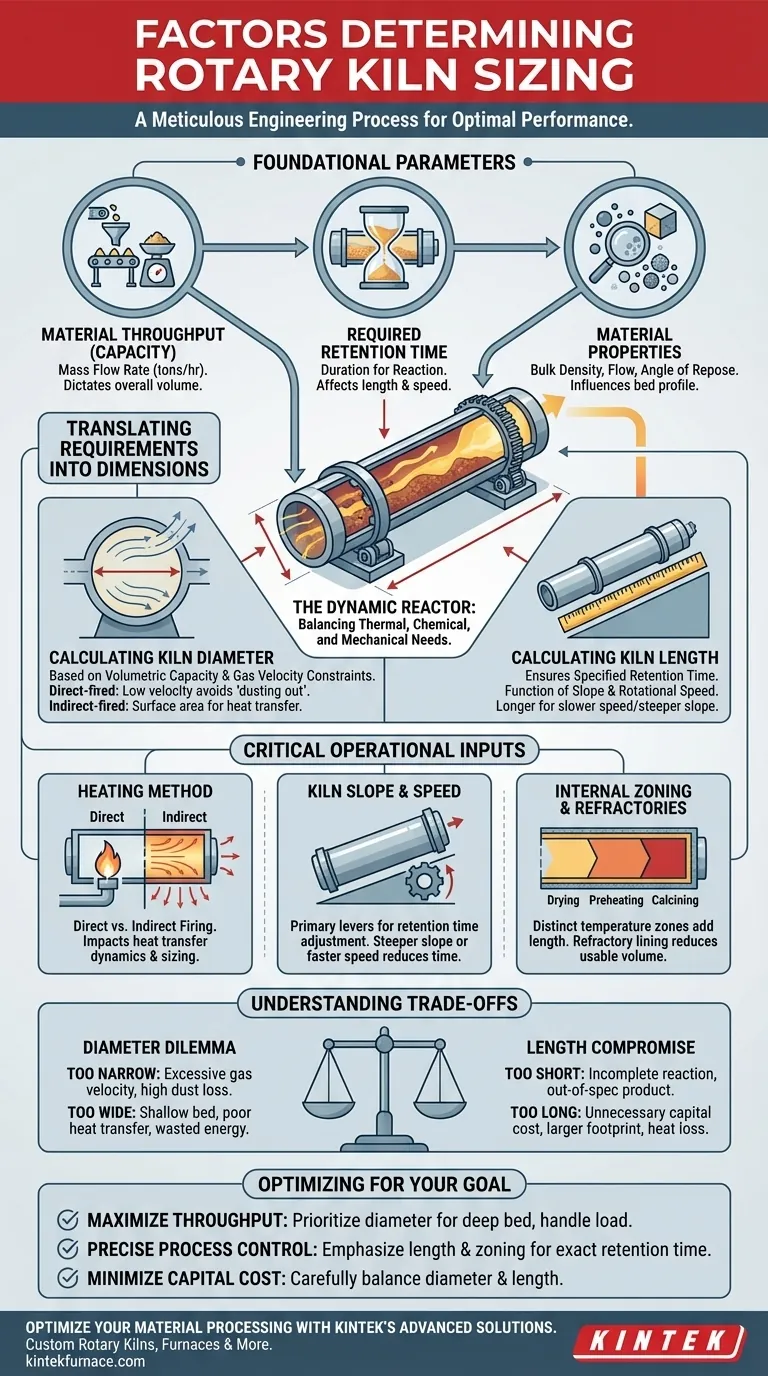
At its core, sizing a rotary kiln is a meticulous engineering process that balances the thermal and chemical requirements of your material with the physical mechanics of the kiln itself. The primary factors that determine its dimensions are the required material capacity (throughput), the necessary retention time to achieve the desired reaction, and the physical properties of the material being processed. These inputs directly inform the two final outputs: kiln diameter and length.
A rotary kiln is not just a container; it is a dynamic reactor. Its size is dictated by the need to expose a specific volume of material to a precise temperature profile for a specific duration, all while ensuring efficient and continuous movement from inlet to discharge.

Foundational Sizing Parameters
The entire design process begins with a deep understanding of the material you intend to process. These properties form the non-negotiable foundation of any sizing calculation.
Material Throughput (Capacity)
The most fundamental parameter is the mass flow rate of the material, typically measured in tons per hour. This dictates the overall volume the kiln must be able to handle at any given moment.
All subsequent calculations are based on meeting this primary capacity requirement.
Required Retention Time
Retention time is the duration a particle of material must spend inside the kiln to undergo the desired physical change or chemical reaction.
This is determined through laboratory testing or pilot-scale trials. A process requiring a long retention time will necessitate a longer kiln or a slower material transport speed.
Material Properties & Bed Profile
The characteristics of the material—such as its bulk density, particle size distribution, and angle of repose—are critical.
These properties influence how the material tumbles and flows, which determines the optimal bed profile, or the percentage of the kiln's cross-section that is filled with material. A typical fill level is between 10-20%.
Translating Requirements into Dimensions
Once the foundational parameters are set, they are used to calculate the physical dimensions of the kiln. Diameter and length are interconnected but are driven by different primary factors.
Calculating Kiln Diameter
The kiln diameter is primarily a function of the required volumetric capacity and constraints on internal gas velocity.
In a direct-fired kiln, the diameter must be large enough to keep the counter-flow gas velocity low. Excessively high velocity can blow fine material out of the kiln, a phenomenon known as "dusting out."
For indirectly-fired kilns, diameter is more closely tied to achieving the necessary surface area for heat transfer into the material bed.
Calculating Kiln Length
The kiln length is calculated to ensure the specified retention time is met. It is a direct function of the kiln's slope and its rotational speed.
Material advances through the kiln with each rotation. Therefore, a longer kiln is required to achieve a given retention time if the slope is steeper or the rotation speed is higher.
Critical Operational Inputs
The final dimensions are refined by a set of operational variables that you control. These settings are determined during the design phase and have a major impact on the kiln's final size and efficiency.
Heating Method (Direct vs. Indirect)
Whether the kiln is direct-fired (burner flame and gases are in contact with the material) or indirectly-fired (heat is applied to the outside of the shell) fundamentally changes the sizing calculations.
Direct-fired designs are dominated by thermal efficiency and gas flow dynamics, while indirect designs prioritize conductive heat transfer through the kiln shell.
Kiln Slope and Rotation Speed
The slope, or inclination, of the kiln (typically 1% to 4%) and its rotational speed (0.2 to 5 RPM) work together to control the rate at which material travels.
These two parameters are the primary levers for adjusting retention time. A steeper slope or faster rotation moves material through more quickly, reducing retention time for a given length.
Internal Zoning & Refractories
Most processes require distinct temperature zones (e.g., drying, preheating, calcining). The length of each zone must be calculated to meet the process requirements, which contributes to the total kiln length.
Furthermore, the refractory lining, which protects the steel shell, reduces the internal usable volume. Its thickness must be factored into the diameter calculation to ensure the required capacity is met.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sizing a kiln involves balancing competing factors. An error in one direction creates inefficiency, while an error in the other leads to process failure.
The Diameter Dilemma
A kiln that is too narrow can lead to excessive gas velocities in direct-fired systems, causing high dust loss and reducing yield.
Conversely, a kiln that is too wide for the required throughput may result in a shallow material bed, leading to poor heat transfer, wasted energy, and a higher capital cost.
The Length Compromise
A kiln that is too short is a critical failure. It will not provide the necessary retention time, meaning the material will exit before the reaction is complete, resulting in an out-of-spec product.
A kiln that is unnecessarily long represents a significant and needless capital expense. It also increases the physical footprint, structural support costs, and potential for heat loss over its surface area.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final kiln design should be optimized for your most critical operational priority.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Prioritize a diameter that allows for a deep material bed without creating excessive gas velocity, and ensure the drive system can handle the load.
- If your primary focus is precise process control: Emphasize the calculation of kiln length and zoning to guarantee the required retention time and temperature profile are achieved without compromise.
- If your primary focus is minimizing capital cost: Carefully balance diameter and length; a shorter, wider kiln may have a similar volume to a longer, narrower one, but the structural, installation, and operational costs will differ.
Ultimately, proper kiln sizing is the blueprint for predictable, efficient, and successful material processing.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Influence on Sizing |
|---|---|
| Material Throughput | Determines kiln volume and capacity requirements |
| Retention Time | Affects kiln length for complete reactions |
| Material Properties | Influences bed profile and flow dynamics |
| Heating Method | Dictates diameter based on gas velocity or heat transfer |
| Kiln Slope & Speed | Controls material travel rate and retention time |
| Internal Zoning | Adds to total length for distinct temperature stages |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and control. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















