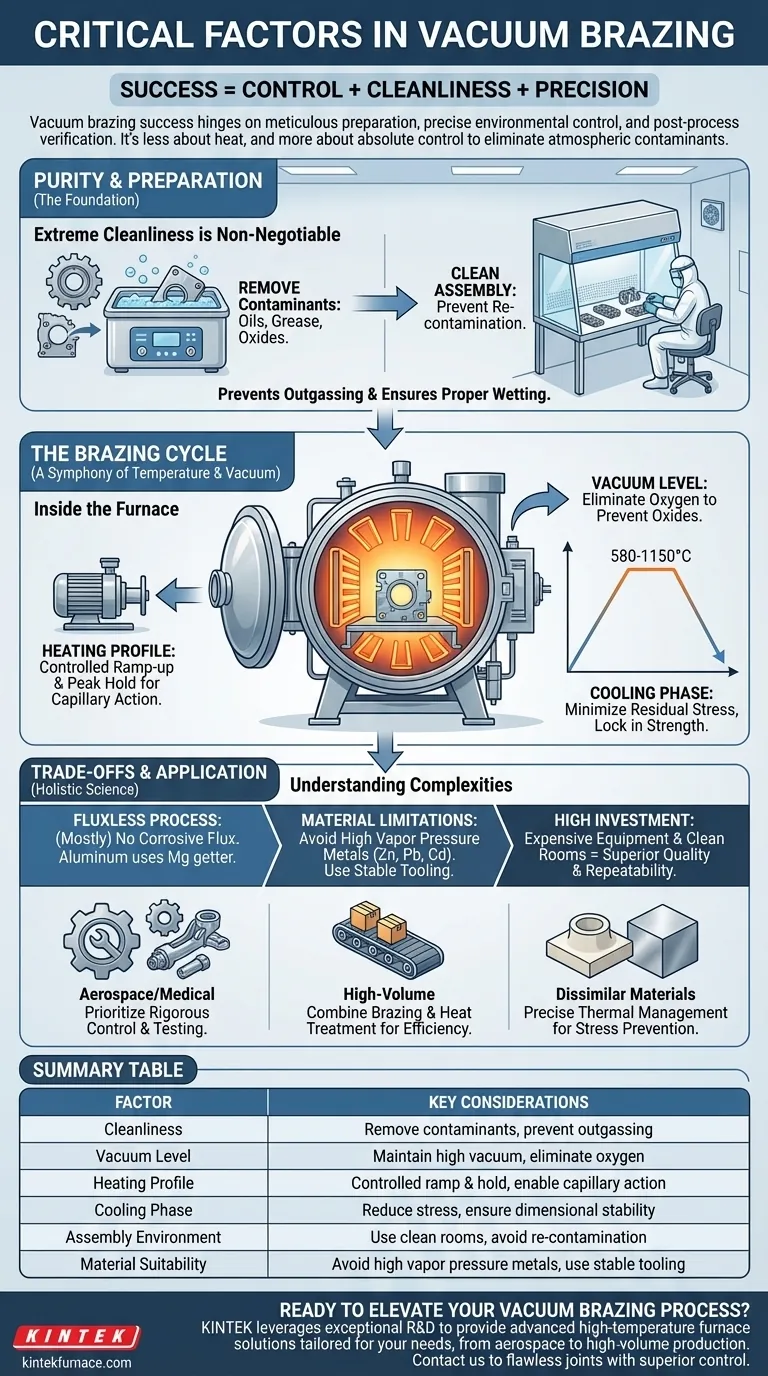
The most important factors in vacuum brazing are a combination of meticulous preparation, precise environmental control, and post-process verification. Success hinges on ensuring parts are perfectly clean before they enter a high-quality vacuum furnace, where a tightly controlled heating and cooling cycle is executed. The entire process, from assembly in a clean environment to the final testing of the joint, must be treated as a single, integrated system.
At its core, successful vacuum brazing is less about the heat and more about absolute control. The process creates a metallurgically perfect joint by eliminating atmospheric contaminants—primarily oxygen—that would otherwise weaken the bond, making pristine cleanliness and precise process control the true keys to success.

The Foundation: Purity and Preparation
The quality of the final brazed joint is determined long before the components enter the furnace. The initial preparation phase is the most common point of failure.
Why Extreme Cleanliness is Non-Negotiable
Parts must be thoroughly cleaned to remove all surface contaminants, such as oils, grease, and especially oxides. In the high heat and vacuum of the furnace, these contaminants will outgas, releasing vapors that can interfere with the braze alloy and prevent a strong, hermetic seal. A clean surface is essential for the molten filler metal to properly wet the parent materials.
The Role of the Clean Assembly Environment
Cleaning the parts is ineffective if they are re-contaminated during assembly. A dedicated, clean assembly room prevents dust, fibers, and other airborne particles from settling on the components or the filler material. This controlled environment is a critical link in the chain of purity.
The Brazing Cycle: A Symphony of Temperature and Vacuum
Inside the furnace, a carefully orchestrated sequence of events transforms separate components into a single, integrated assembly. This cycle is defined by vacuum level, temperature, and time.
The Furnace: Creating the Controlled Environment
A high-vacuum furnace is the heart of the operation. Its primary function is to pump out the atmosphere, especially oxygen, to prevent the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces during heating. Maintaining the correct vacuum level is critical for creating a clean, active surface for the braze alloy to bond with.
The Heating Profile: More Than Just Melting
The assembly is heated gradually to the specified brazing temperature. This controlled ramp-up minimizes thermal stress and prevents distortion, particularly in complex assemblies or those with dissimilar materials. The peak temperature, which varies by material (e.g., 580-620°C for aluminum, 800-1150°C for steel alloys), is held for a short period to allow the filler metal to melt and flow via capillary action into the joint.
The Cooling Phase: Locking in Strength
After brazing, the assembly is cooled in a controlled manner. Slow cooling is often used to minimize residual stress, ensuring the final part is strong and dimensionally stable. Some processes may also integrate rapid cooling or quenching with inert gas (like Argon) to achieve specific metallurgical properties, such as hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While vacuum brazing produces superior results, it demands a clear understanding of its inherent complexities and costs.
The Myth of "No Flux Required"
Vacuum brazing is often called a "fluxless" process, which is mostly true. The vacuum environment eliminates the need for the corrosive chemical fluxes used in other brazing methods. However, some materials, like aluminum, often rely on magnesium within the filler alloy to act as an "oxygen getter," effectively performing the function of a flux without leaving a residue.
Material and Fixture Limitations
Not all materials are suitable for vacuum brazing. Metals with high vapor pressures, like zinc, lead, and cadmium, can outgas and contaminate the furnace and the assembly. Furthermore, the fixtures, or tooling, used to hold parts in place must also be made of stable, low-outgassing materials (like graphite or molybdenum) that won't interfere with the process.
High Initial Investment
Achieving the necessary purity and control requires significant investment. High-quality vacuum furnaces, clean rooms, and robust testing facilities are expensive. This cost is a trade-off for the exceptional quality, repeatability, and reduced post-processing cleanup that the method provides.
Applying This to Your Project
The emphasis you place on each factor depends on your specific application and goals.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-value aerospace or medical components: Prioritize rigorous process control, certified clean room assembly, and comprehensive post-braze testing (e.g., helium leak tests, metallurgical analysis).
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for high-volume production: Leverage the ability to combine brazing with heat treatment or age hardening in a single furnace cycle to save significant time and energy.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (e.g., ceramic-to-metal): Concentrate on designing a precise heating and cooling profile to carefully manage the different thermal expansion rates and prevent stress fractures.
Ultimately, mastering vacuum brazing means treating it as a holistic science where every step, from initial cleaning to final inspection, is given critical importance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Cleanliness | Remove oils, grease, oxides; prevent outgassing for proper wetting |
| Vacuum Level | Maintain high vacuum to eliminate oxygen and prevent oxide formation |
| Heating Profile | Controlled ramp-up and hold to minimize stress and enable capillary action |
| Cooling Phase | Slow or rapid cooling to reduce residual stress and ensure dimensional stability |
| Assembly Environment | Use clean rooms to avoid re-contamination during part assembly |
| Material Suitability | Avoid high vapor pressure metals; use stable tooling materials |
Ready to elevate your vacuum brazing process? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or high-volume production, we help you achieve flawless joints with superior control and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your brazing outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the purpose of performing medium vacuum annealing on working ampoules? Ensure Pure High-Temp Diffusion
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















