In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the generation and subsequent decomposition of precursor molecules are governed by the fundamental principles of thermodynamics and kinetics. Your ability to manipulate process parameters like temperature, pressure, and concentration allows you to control the interplay between these two forces, which directly determines the quality, structure, and growth rate of your final film.
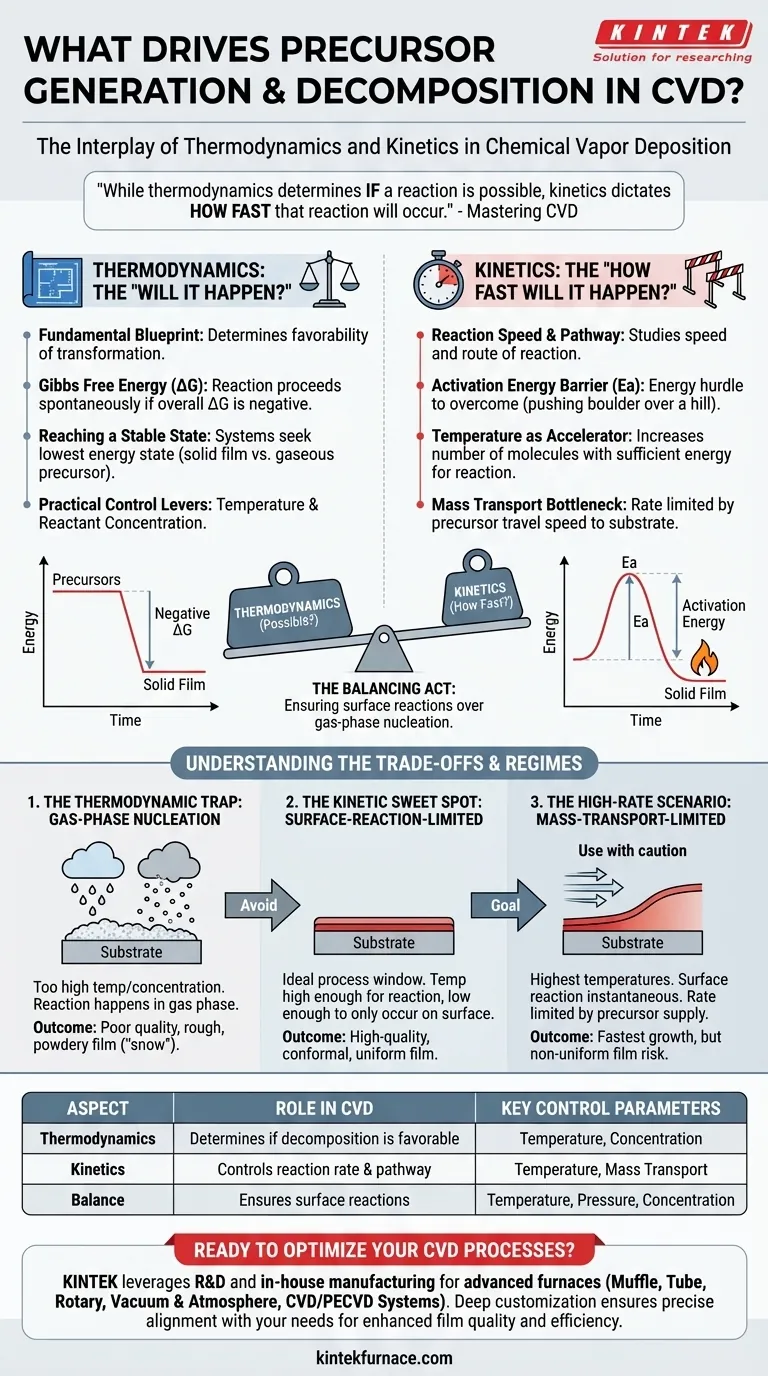
While thermodynamics determines if a reaction is possible and what its most stable outcome is, kinetics dictates how fast that reaction will occur. Mastering CVD is a process of finding the kinetic sweet spot where reactions happen controllably on the substrate surface, not chaotically in the gas phase.
The Role of Thermodynamics: The "Will It Happen?"
Thermodynamics provides the fundamental blueprint for any chemical reaction, including those in a CVD process. It tells you whether a desired transformation from a gaseous precursor to a solid film is favorable under your set conditions.
The Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG)
The primary indicator of thermodynamic favorability is the change in Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG). A reaction can proceed spontaneously only when its overall ΔG is negative.
In CVD, this means the system must favor the state where precursors have decomposed into a stable solid film and gaseous byproducts over the state where they remain as intact precursor molecules.
Reaching a Stable State
All systems naturally seek their lowest energy state. By introducing energy (usually heat) into the CVD reactor, you enable the precursor molecules to overcome barriers and rearrange themselves into the more stable solid film configuration on the substrate.
Practical Control Levers
You can influence the thermodynamics of your system primarily through temperature and reactant concentration. Increasing temperature often makes decomposition reactions more favorable (more negative ΔG), pushing the equilibrium towards product formation.
The Role of Kinetics: The "How Fast Will It Happen?"
A reaction being thermodynamically possible does not mean it will happen at a useful rate. Kinetics is the study of reaction speed and the pathway a reaction takes.
The Activation Energy Barrier (Ea)
For a precursor to decompose, it must overcome an energy hurdle known as the activation energy (Ea). Think of it as needing to push a boulder over a small hill before it can roll down into a deep valley.
Even if the valley (the solid film) is a much lower energy state, no reaction will occur without sufficient energy to get over that initial hill.
Temperature as the Accelerator
Temperature is the most powerful tool for controlling kinetics. Increasing the temperature gives more molecules the energy needed to surpass the activation energy barrier, dramatically increasing the rate of reaction.
The Mass Transport Bottleneck
Kinetics isn't just about the chemical reaction itself. The overall rate can also be limited by mass transport—the speed at which precursor molecules can travel through the gas phase to reach the substrate surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The success of a CVD process hinges on balancing thermodynamics and kinetics to favor surface reactions over gas-phase reactions. This balance defines the operating regime of your process.
The Thermodynamic Trap: Gas-Phase Nucleation
If the temperature or concentration is too high, the reaction becomes too fast and thermodynamically favorable everywhere. Precursors will react in the hot gas phase before ever reaching the substrate.
This gas-phase nucleation forms tiny solid particles ("snow" or powder) that may rain down on your substrate, resulting in a rough, poorly adhered, and low-quality film.
The Kinetic Sweet Spot: The Surface-Reaction-Limited Regime
The ideal process window is often the surface-reaction-limited regime. Here, the temperature is high enough for reactions to occur but low enough that they only happen on the catalytically active substrate surface.
In this kinetically controlled state, film growth is uniform and orderly because the chemical reaction rate on the surface is the slowest step in the process.
The High-Rate Scenario: The Mass-Transport-Limited Regime
At even higher temperatures, the surface reaction becomes instantaneous. The growth rate is now limited only by how fast new precursor molecules can be supplied to the surface.
This mass-transport-limited regime provides the fastest possible growth but risks creating non-uniform films, as areas with better gas flow (like the leading edge of the wafer) will grow thicker layers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process parameters should be set based on the desired outcome for your film.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality, conformal, and uniform film: Operate in the surface-reaction-limited regime by carefully controlling temperature to ensure reactions occur on the substrate, not in the gas.
- If your primary focus is maximum deposition rate: You will need to push the temperature into the mass-transport-limited regime, but you must accept the inherent risk of non-uniformity.
- If you are observing particle formation or hazy films: Your process is likely too aggressive. Reduce the temperature or precursor concentration to move out of the gas-phase nucleation regime.
Ultimately, mastering the balance between what is possible (thermodynamics) and what happens at a controlled rate (kinetics) is the key to successful Chemical Vapor Deposition.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in CVD | Key Control Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Thermodynamics | Determines if precursor decomposition is favorable | Temperature, Concentration |
| Kinetics | Controls the rate of reaction and pathway | Temperature, Mass Transport |
| Balance | Ensures surface reactions over gas-phase nucleation | Temperature, Pressure, Concentration |
Ready to optimize your CVD processes with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing film quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















