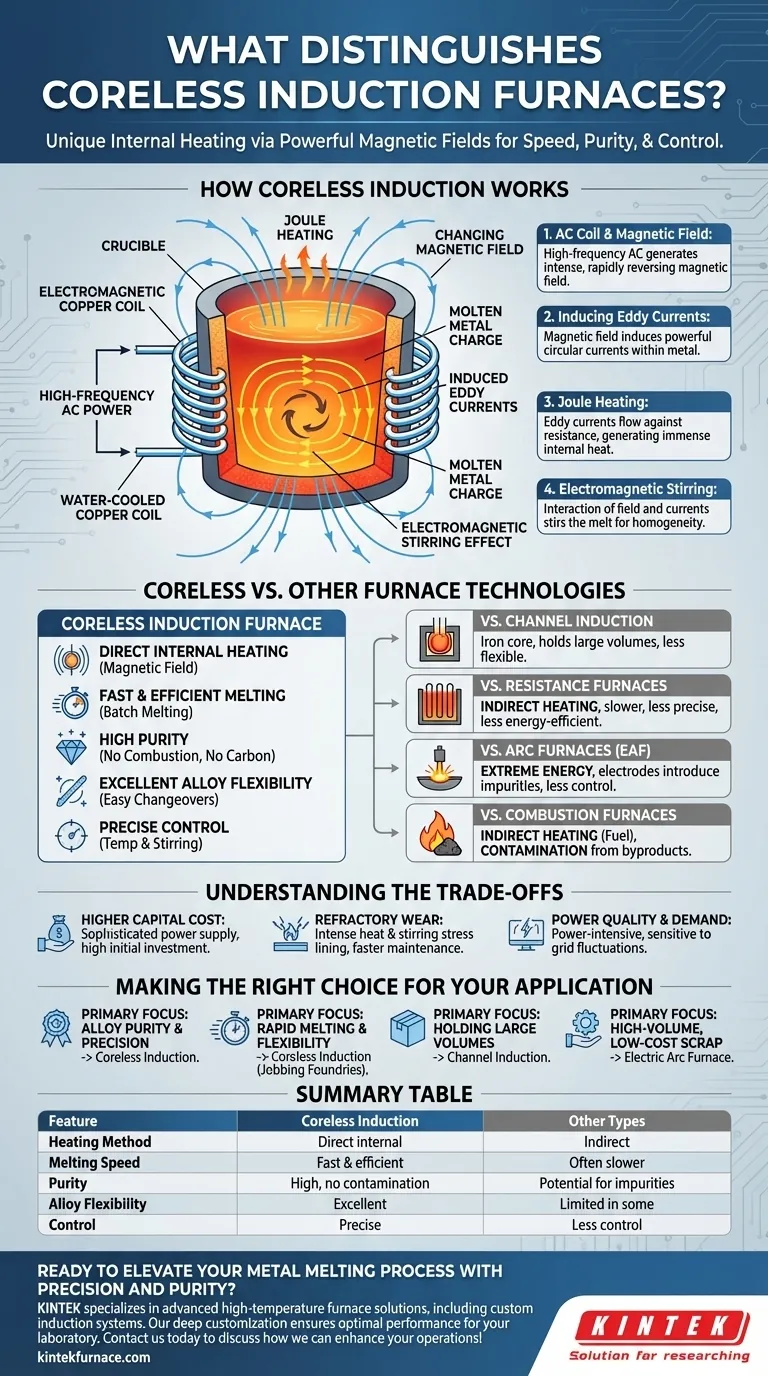
At its core, a coreless induction furnace is distinguished by its method of heating. Unlike other furnaces that heat metal using external flames or glowing electrical elements, a coreless furnace uses a powerful, changing magnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself, all without a central iron core to channel the magnetic flux. This fundamental difference enables unique levels of speed, purity, and control over the melting process.
The critical takeaway is that coreless induction furnaces are not just melting pots; they are active metallurgical tools. Their ability to heat the metal from the inside out while simultaneously stirring it provides a combination of speed, cleanliness, and alloy homogeneity that is difficult to achieve with other technologies.
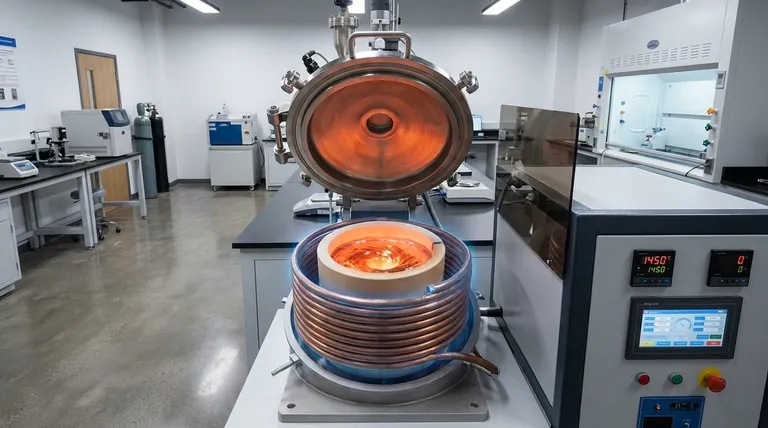

How Coreless Induction Works: The Principle of Direct Heating
The operation of a coreless induction furnace is based on fundamental principles of electromagnetism. It transforms electrical energy into thermal energy with remarkable efficiency by making the metal charge part of the electrical circuit.
The AC Coil and the Magnetic Field
The furnace is built around a crucible, which is a refractory-lined vessel designed to contain molten metal. This crucible is encircled by a heavy, water-cooled copper coil.
When a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly reversing magnetic field in the space occupied by the crucible.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This intense magnetic field penetrates the conductive metal placed inside the crucible. According to Faraday's law of induction, the changing magnetic field induces powerful circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Joule Heating: The Source of Heat
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow through this resistance, they generate immense heat according to the principle of Joule heating (P = I²R).
This process effectively turns the metal charge into its own heating element, causing it to melt rapidly and uniformly from within.
The Electromagnetic Stirring Effect
A key secondary benefit of this process is a strong stirring action. The interaction of the magnetic field and the eddy currents creates forces within the molten bath that cause it to circulate vigorously.
This natural stirring ensures the melt is chemically and thermally homogenous, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Coreless Induction vs. Other Furnace Technologies
Understanding the coreless furnace requires comparing it to alternative technologies, as each is suited for different applications.
vs. Channel Induction Furnaces
A channel furnace also uses induction but features an iron core that passes through a "channel" of molten metal, functioning much like a transformer. This makes it highly efficient for holding large volumes of a single metal type at temperature but far less flexible for starting from cold or frequently changing alloys.
The coreless design excels at batch melting and offers superior alloy flexibility.
vs. Resistance Furnaces
Resistance furnaces use heating elements (like nichrome wire) that are heated by electricity. These elements then radiate heat to the crucible and the charge.
This is an indirect heating method. It is often slower, less energy-efficient, and offers less precise temperature control compared to the direct, internal heating of a coreless induction furnace.
vs. Arc Furnaces
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) melt metal using an extremely high-energy electric arc struck between graphite electrodes and the metal charge.
EAFs are exceptionally powerful and ideal for melting massive quantities of scrap steel. However, they are less controlled, and the carbon electrodes can introduce impurities into the melt, making them less suitable for high-purity or specialty alloys.
vs. Combustion Furnaces
Combustion furnaces (like cupolas or reverberatory furnaces) burn fuel such as coke, natural gas, or oil. The hot gases from this combustion transfer heat to the metal.
The primary disadvantage is contamination. The byproducts of combustion can be absorbed by the molten metal, altering its chemistry and purity. The coreless induction process is inherently cleaner as there is no combustion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the coreless induction furnace is not without its specific challenges and considerations.
Higher Capital Cost
The sophisticated power supply, including the high-frequency inverter and capacitor bank, makes the initial investment for a coreless induction system significantly higher than for simpler combustion or resistance furnaces.
Refractory Wear
The combination of intense, direct heat and the vigorous electromagnetic stirring action places considerable stress on the refractory lining of the crucible. This leads to faster wear and necessitates a disciplined maintenance and relining schedule.
Power Quality and Demand
These furnaces are power-intensive and can be sensitive to fluctuations in the electrical grid. A stable, high-capacity power infrastructure is a prerequisite for their reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your operational goals for quality, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is alloy purity and precise composition: The clean, contained, and self-stirring nature of the coreless induction furnace makes it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting and production flexibility: The ability to start quickly from a cold state and easily switch between different alloys makes the coreless furnace ideal for jobbing foundries.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of a single, consistent alloy: A channel induction furnace may prove more energy-efficient for maintaining temperature over long periods.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost melting of ferrous scrap: An Electric Arc Furnace is likely the more economical and powerful tool for the job.
Ultimately, the coreless induction furnace is the definitive choice when the metallurgical quality of the final product is the most critical factor.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Other Furnace Types |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct internal heating via magnetic field | Indirect heating (e.g., flames, elements) |
| Melting Speed | Fast and efficient | Often slower |
| Purity | High, no combustion contamination | Potential for impurities |
| Alloy Flexibility | Excellent for batch melting and changes | Limited in some types (e.g., channel furnaces) |
| Control | Precise temperature and stirring | Less control in some cases |
Ready to elevate your metal melting process with precision and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom induction systems. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures optimal performance for your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















