In principle, vacuum heat treatment furnaces can process a range of advanced, non-oxide, and high-purity ceramics. These most commonly include transparent alumina ceramics, transparent ferroelectric ceramics, and various nitride ceramics, where precise atmospheric control is critical to achieving the desired material properties.
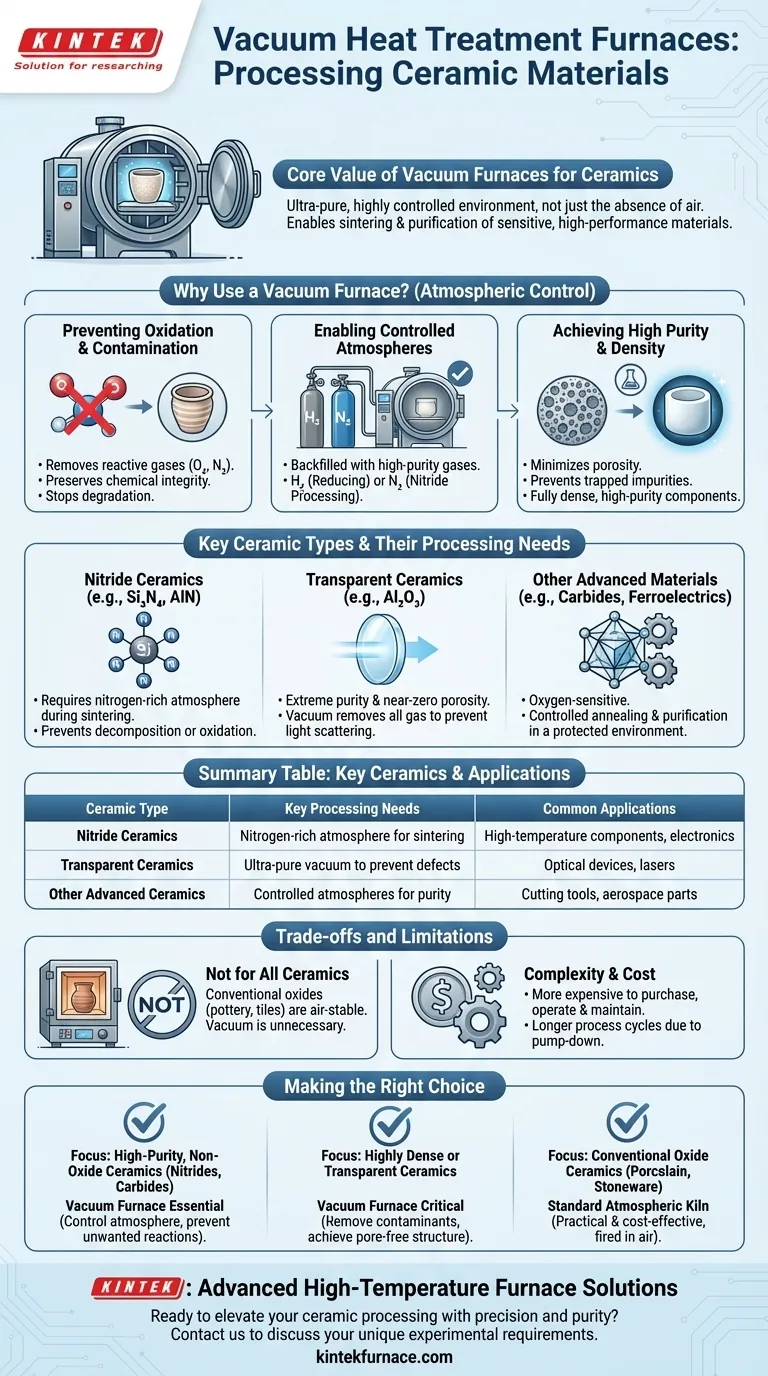
The primary value of a vacuum furnace for ceramics isn't just the absence of air, but the ability to create an ultra-pure, highly controlled environment. This prevents oxidation and contamination, enabling the sintering and purification of sensitive, high-performance materials that would be compromised if fired in a standard atmosphere.
Why Use a Vacuum Furnace for Ceramics?
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the chemical sensitivity of the ceramic material at high temperatures. The core benefits revolve around atmospheric control.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At the extreme temperatures required for sintering, many advanced ceramic materials can react with oxygen in the air. This oxidation can degrade the material's properties, alter its composition, or prevent it from reaching full density.
A vacuum furnace removes reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen, creating a clean environment that preserves the material's chemical integrity.
Enabling Controlled Atmospheres
After pulling a vacuum to remove contaminants, the furnace can be backfilled with a specific, high-purity gas. This creates a precisely controlled atmosphere tailored to the material's needs.
Commonly used atmospheres include hydrogen (H₂), which acts as a reducing agent, and high-purity nitrogen (N₂), which is essential for processing nitride ceramics.
Achieving High Purity and Density
The combination of a clean vacuum and a controlled gas atmosphere minimizes porosity and prevents impurities from becoming trapped in the ceramic's structure. This is essential for producing fully dense, high-purity components for demanding applications.
Key Ceramic Types and Their Processing Needs
Different ceramics leverage vacuum furnace technology for specific reasons. The main process for forming these materials is high-temperature vacuum sintering, which bonds the ceramic particles together.
Nitride Ceramics
Materials like silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) or aluminum nitride (AlN) require a nitrogen-rich atmosphere during sintering. Firing them in air would cause them to decompose or oxidize.
A vacuum furnace first removes the air, then introduces a precise partial pressure of high-purity nitrogen to create the ideal processing conditions.
Transparent Ceramics
Transparent alumina (Al₂O₃) and other optical ceramics demand extreme purity and near-zero porosity. Any tiny impurity or pore will scatter light, making the material translucent or opaque.
The vacuum environment is critical for removing all gas and contaminants that could cause these light-scattering defects, often followed by sintering in a hydrogen or vacuum environment to achieve full transparency.
Other Advanced Materials
The principles also apply to other oxygen-sensitive materials like carbides or certain ferroelectric compositions. The furnace allows for critical processes like high-temperature annealing and purification in a protected environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is a specialized tool and not the solution for all ceramic processing.
Not for All Ceramics
Conventional oxide ceramics, such as those used for pottery, tiles, or basic insulators, are stable when fired in air. Using a vacuum furnace for these materials would be unnecessarily complex and expensive.
Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric kilns. The process cycles are often longer due to the need to pump down the vacuum and carefully control the atmosphere.
Material and Gas Compatibility
The furnace's internal components, such as heating elements (e.g., graphite, molybdenum) and insulation, must be compatible with the process gases used. For example, introducing oxygen at high temperatures can damage graphite elements, requiring different furnace construction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Ceramic Process
Your choice of furnace technology must align directly with your material's chemical requirements and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, non-oxide ceramics (like nitrides or carbides): A vacuum furnace is essential to control the atmosphere and prevent unwanted reactions with oxygen.
- If your primary focus is creating highly dense or transparent ceramics: The vacuum environment is critical for removing contaminants and achieving the pore-free microstructure required for optical or high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is processing conventional oxide ceramics (like porcelain or stoneware): A standard atmospheric kiln is the more practical and cost-effective choice, as these materials are designed to be fired in air.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision driven by the unique chemical and physical requirements of the advanced material you intend to create.

Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Key Processing Needs | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nitride Ceramics (e.g., Si₃N₄, AlN) | Nitrogen-rich atmosphere for sintering | High-temperature components, electronics |
| Transparent Ceramics (e.g., Al₂O₃) | Ultra-pure vacuum to prevent defects | Optical devices, lasers |
| Other Advanced Ceramics (e.g., carbides) | Controlled atmospheres for purity | Cutting tools, aerospace parts |
Ready to elevate your ceramic processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can help you achieve superior results in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















