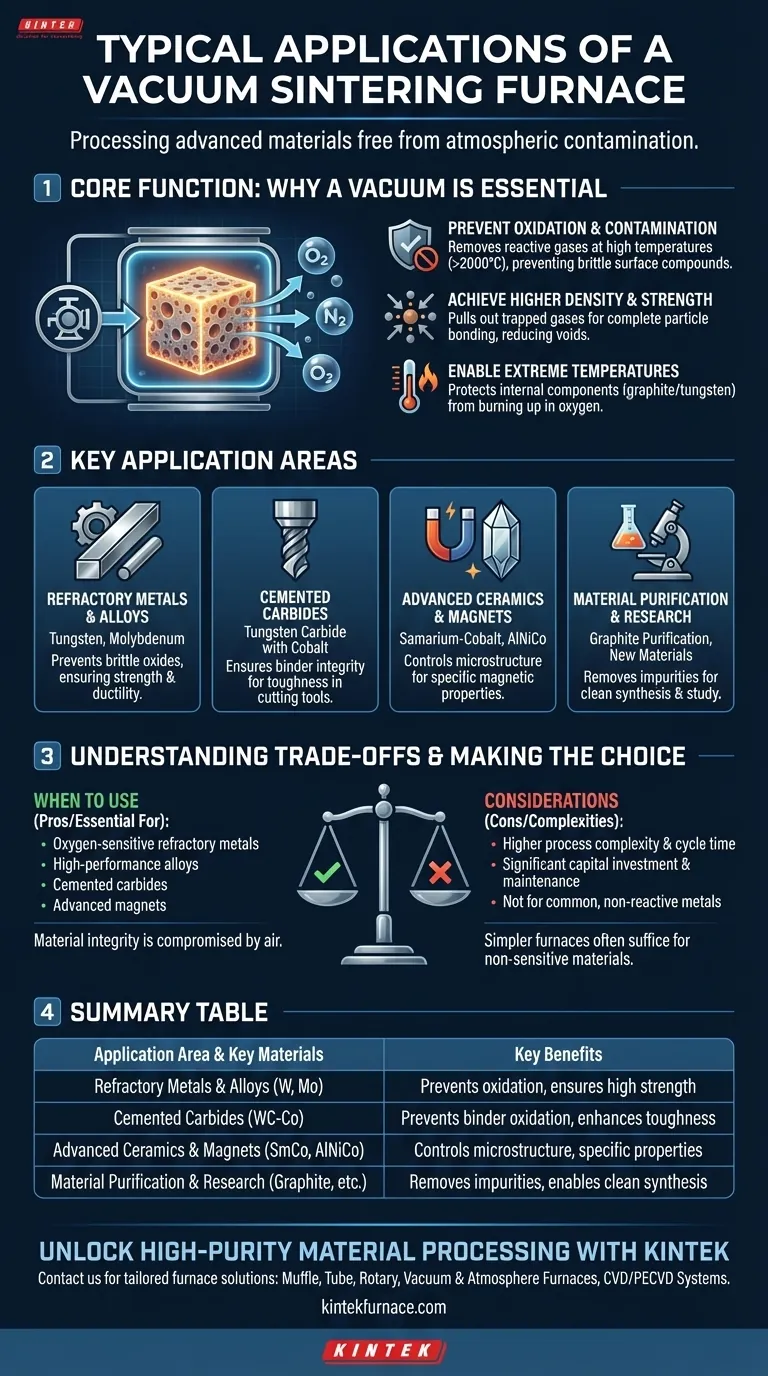
In essence, a vacuum sintering furnace is used to process advanced materials that cannot tolerate atmospheric contamination at high temperatures. Its typical applications include the sintering of refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum, cemented carbides for cutting tools, advanced ceramics, and high-performance magnetic materials such as samarium-cobalt. These furnaces are staples in scientific research, military, and industrial sectors where material purity and density are paramount.
A vacuum sintering furnace is not simply a high-temperature oven; it is a precision instrument for creating a controlled, oxygen-free environment. This core function—the removal of reactive gases—is what enables the fabrication of pure, dense, and high-strength components from some of the most advanced materials available.

The Core Function: Why a Vacuum is Essential
The defining feature of this furnace is its ability to create a vacuum. This controlled environment is not an optional feature but the fundamental reason for its existence, solving critical problems that arise during high-temperature processing.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At the extreme temperatures required for sintering (often exceeding 2000°C), most advanced materials will readily react with oxygen and other gases in the air. This oxidation can create brittle, undesirable compounds on the material's surface, ruining its structural integrity and performance.
A vacuum system actively removes these reactive gases from the chamber, preserving the chemical purity of the material being processed.
Achieving Higher Density and Strength
Sintering involves fusing powder particles together into a solid mass. Air and other gases trapped between these particles can inhibit this process, resulting in a porous and weaker final product.
The vacuum helps pull these trapped gases out of the powder compact before and during heating, allowing the particles to bond more completely. This results in a final component with higher density, fewer internal voids, and superior mechanical strength.
Enabling Extreme Temperatures
The heating elements used in these furnaces, often made of graphite or tungsten, can reach temperatures up to 2400°C. These elements would instantly burn up and fail if operated in an oxygen-rich atmosphere.
The vacuum protects the furnace's internal components, allowing it to achieve and sustain the ultra-high temperatures needed to sinter refractory materials.
Key Application Areas
The need for a pure, high-temperature environment makes vacuum sintering furnaces indispensable for a specific class of materials.
Refractory Metals and Alloys
Materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and their alloys have exceptionally high melting points. A vacuum furnace provides the necessary heat while preventing the formation of brittle oxides that would otherwise compromise their strength and ductility.
Cemented Carbides
Cemented carbides, such as tungsten carbide bonded with cobalt, are used for high-performance cutting tools and wear-resistant parts. The vacuum ensures the metallic binder (cobalt) does not oxidize, allowing it to properly wet and bond the carbide grains, which is critical for achieving the required toughness and hardness.
Advanced Ceramics and Magnets
The production of high-performance ceramic materials and permanent magnets like samarium-cobalt (SmCo) and aluminum-nickel-cobalt (AlNiCo) requires precise atmospheric control. The vacuum environment prevents unwanted chemical reactions and helps achieve the specific microstructure and density needed for their unique magnetic or physical properties.
Material Purification and Research
Vacuum furnaces are also used for processes beyond sintering, such as graphite purification, where impurities are vaporized and removed under vacuum at high temperatures. In research settings, they provide a clean, controllable environment for synthesizing new materials and studying their behavior without atmospheric interference.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum sintering furnace is a specialized tool with inherent complexities and is not the right choice for every application.
Process Complexity and Cycle Time
Operating a vacuum furnace involves more than just setting a temperature. It requires managing vacuum pumps, leak checking, and executing precise heating and cooling profiles. The time required to pump the chamber down to the desired vacuum level and to cool the load under controlled conditions can result in significantly longer total cycle times compared to atmospheric furnaces.
Higher Initial Cost and Maintenance
The components required to achieve and hold a high vacuum—including robust chambers, high-capacity pumps, and sophisticated control systems—make these furnaces a significant capital investment. Vacuum systems also require regular maintenance to ensure reliable, leak-free operation.
When a Simpler Furnace Suffices
For many materials that are not sensitive to oxidation or that can be protected by a simple inert gas flow (like argon), a conventional atmospheric furnace is a far more practical and cost-effective solution. The complexity of a vacuum system is unnecessary overhead if the material does not demand it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace comes down to the chemical nature of your material and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive refractory metals or high-performance alloys: A vacuum sintering furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and achieve the required material density and strength.
- If your primary focus is producing cemented carbides or advanced magnetic materials: The controlled vacuum environment is non-negotiable for ensuring binder integrity and achieving specific functional characteristics.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of common, non-reactive metals: An atmospheric furnace is almost always a more efficient and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, you choose a vacuum furnace when the integrity of your material is fundamentally compromised by exposure to atmospheric gases at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Materials | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory Metals & Alloys | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Prevents oxidation, ensures high strength and ductility |
| Cemented Carbides | Tungsten carbide with cobalt | Prevents binder oxidation, enhances toughness and hardness |
| Advanced Ceramics & Magnets | Samarium-cobalt, AlNiCo | Controls microstructure, achieves specific magnetic properties |
| Material Purification & Research | Graphite, new materials | Removes impurities, enables clean synthesis and study |
Unlock the Power of High-Purity Material Processing with KINTEK
Are you working with oxygen-sensitive materials like refractory metals, cemented carbides, or advanced ceramics? KINTEK's vacuum sintering furnaces deliver the contamination-free, high-density results you need. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer advanced solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















