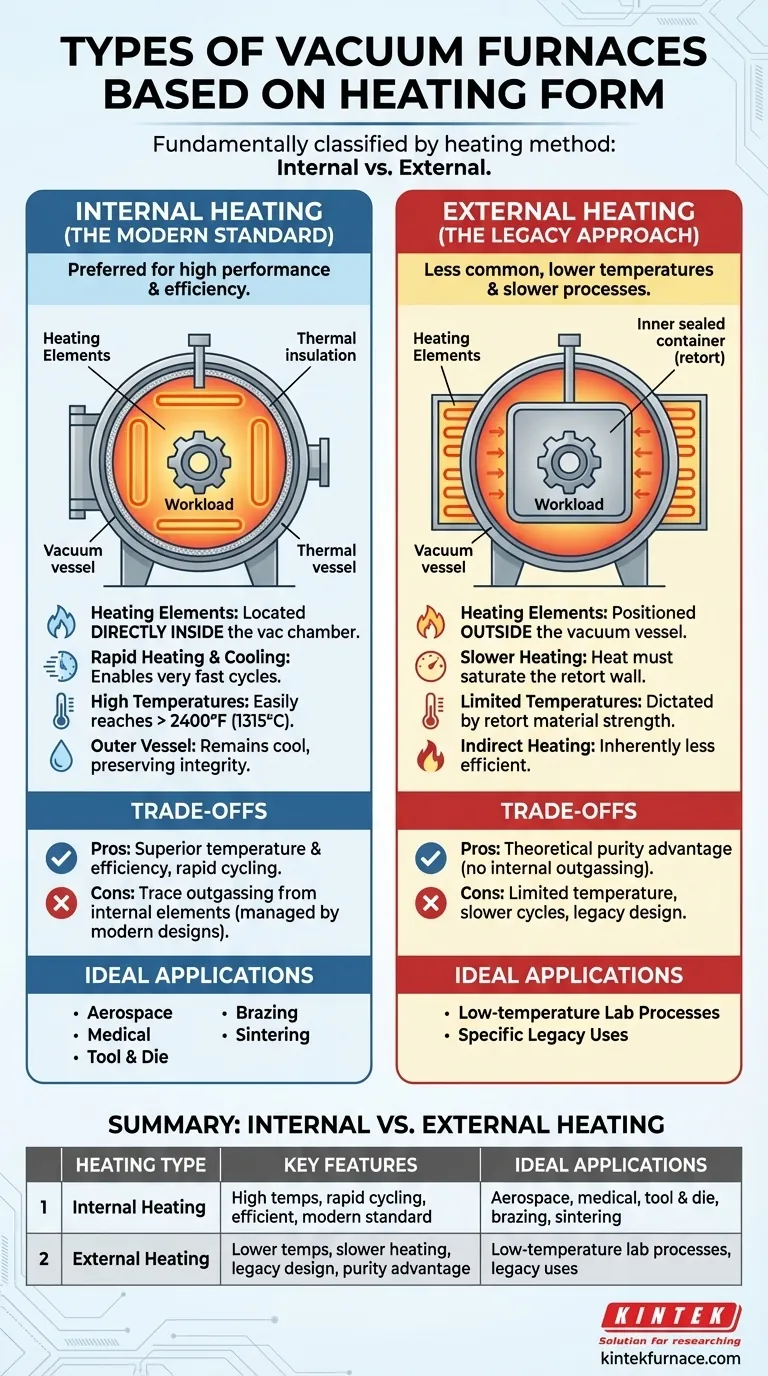
Fundamentally, vacuum furnaces are classified into two types based on their heating method: internal heating and external heating. The vast majority of modern, high-performance vacuum furnaces utilize an internal heating design, where the heating elements are located directly inside the vacuum chamber to maximize efficiency and temperature capabilities.
The core distinction is not just about the location of the heaters, but about a fundamental trade-off between performance and simplicity. Modern material processing demands the high temperatures and rapid cycling that only an internal heating architecture can reliably provide.

The Two Fundamental Heating Architectures
To understand any vacuum furnace, you must first understand how it generates and applies heat. The placement of the heating elements relative to the vacuum vessel dictates the furnace's performance, limitations, and ideal applications.
Internal Heating Furnaces (The Modern Standard)
In an internal heating furnace, the heating elements (typically made of graphite or refractory metals like molybdenum) and thermal insulation are located inside the vacuum chamber, surrounding the workload.
This design is the preferred standard for almost all modern industrial applications. Heat is generated directly within the vacuum environment, allowing for very rapid heating and cooling cycles and extremely high process temperatures.
Because the heat source is inside the chamber, the outer vacuum vessel remains cool, preserving its structural integrity.
External Heating Furnaces (The Legacy Approach)
In an external heating furnace, the heating elements are positioned outside the vacuum vessel. The workload is placed inside a sealed container, often called a "retort," which is then evacuated.
Heat must first saturate the wall of this retort before it can radiate to the workload inside. This indirect heating method is inherently slower and less efficient.
This design is far less common today, primarily found in older equipment or very specific, lower-temperature laboratory applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Internal vs. External Heating
The dominance of the internal heating design is a direct result of its significant performance advantages. However, understanding the trade-offs is key to appreciating why each design exists.
Temperature and Efficiency
Internal heating furnaces are vastly superior in this regard. They can easily reach temperatures above 2,400°F (1315°C) and do so with high energy efficiency, as the heat is generated exactly where it is needed.
External heating furnaces are severely limited. The maximum temperature is dictated by the material strength of the retort, which must contain the vacuum while being heated externally. This makes them unsuitable for high-temperature processes like brazing or sintering.
Purity and Contamination
This is the one area where external heating has a theoretical advantage. Because the heating elements are outside the vacuum, there is no risk of them "outgassing" and introducing contaminants into the workload environment.
In an internal heating furnace, the internal elements and insulation can release trace amounts of gas when heated, which must be managed by the vacuum pumping system. However, modern designs and materials have largely minimized this issue for most applications.
Application and Function
You will often see furnaces described by their function, such as vacuum hardening furnaces, brazing furnaces, or sintering furnaces.
These terms describe the process the furnace is designed for. Critically, nearly all of these high-performance functional types are built using an internal heating architecture to achieve the necessary temperature and control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will point directly to the necessary heating architecture.
- If your primary focus is high-performance material processing: You require an internal heating furnace for its high temperature capability, rapid cycling, and efficiency, making it standard for aerospace, medical, and tool & die industries.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity in a low-temperature process: An external heating furnace could be considered, but it is largely a legacy design with significant performance limitations.
Understanding this core design principle empowers you to look past marketing terms and evaluate a vacuum furnace based on its fundamental capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Heating Type | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Heating | High temperatures (>2400°F), rapid cycling, efficient, modern standard | Aerospace, medical, tool & die industries, brazing, sintering |
| External Heating | Lower temperatures, slower heating, legacy design, theoretical purity advantage | Low-temperature lab processes, specific legacy uses |
Need a high-performance vacuum furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your material processing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















