At the most fundamental level, a vacuum furnace is defined by two primary configurations: its thermal design, which is either hot wall or cold wall, and its physical orientation, which is either horizontal or vertical. While the orientation impacts logistics and part handling, the distinction between a hot wall and a cold wall design is the most critical factor, dictating the furnace's temperature range, vacuum capabilities, and ultimate process applications.
The choice between furnace configurations is not about which is "better," but which is the right tool for the job. Your decision is driven by the specific requirements of your process, balancing the need for high performance (temperature, vacuum level, purity) against operational simplicity and cost.

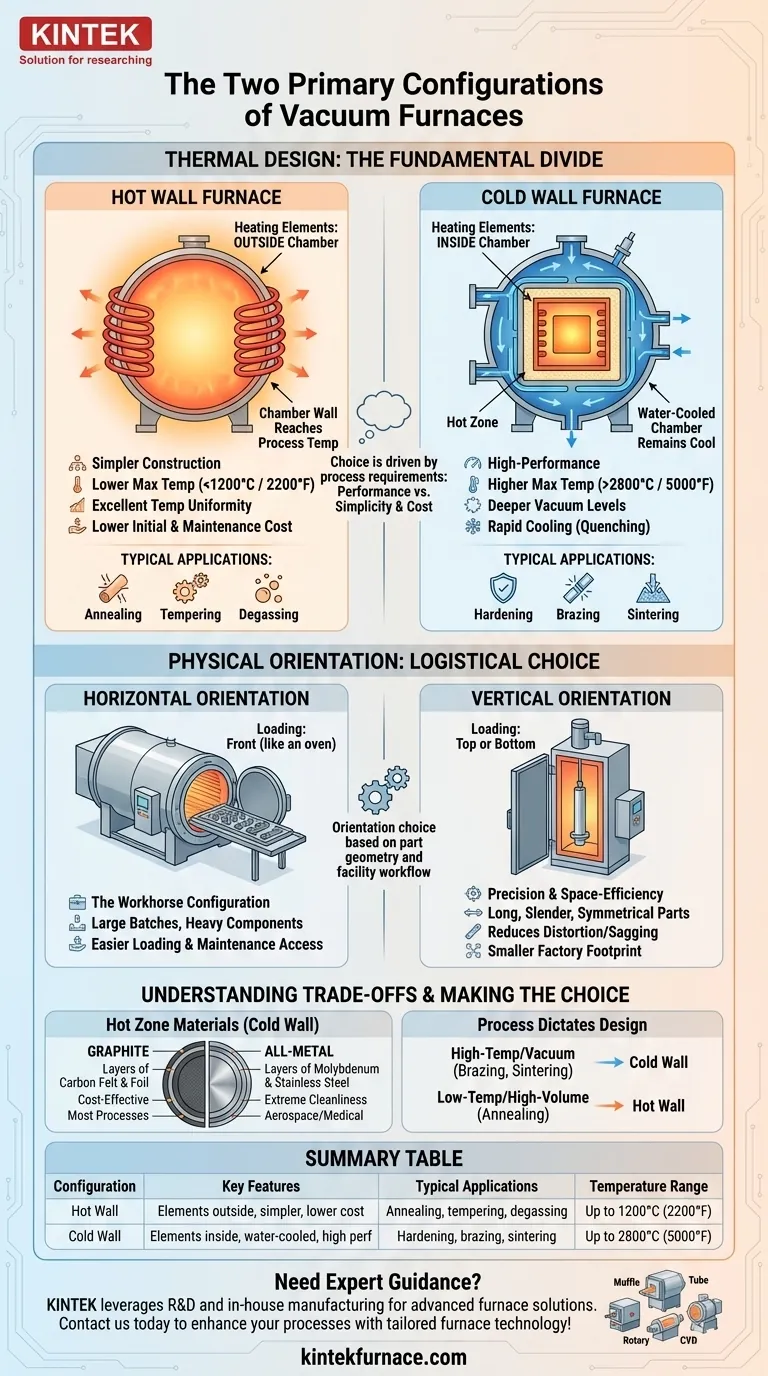
The Fundamental Divide: Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall
The most significant design difference in any vacuum furnace is how it contains and manages heat. This leads to the two core thermal designs: hot wall and cold wall.
What is a Hot Wall Furnace?
In a hot wall design, the heating elements are located on the outside of the vacuum chamber (often called a retort). The entire chamber is heated, meaning the vessel wall itself reaches the process temperature while holding the vacuum.
These furnaces are generally simpler in construction. Because the vessel wall gets hot, they are typically limited to lower maximum temperatures, often below 1200°C (2200°F), to protect the structural integrity of the material under vacuum.
The Case for Hot Wall: Simplicity and Uniformity
Hot wall furnaces excel in processes where absolute temperature uniformity is critical and cycle times are less demanding. Their primary application is for lower-temperature processes like annealing, tempering, and degassing.
Their simpler design often translates to lower initial and maintenance costs compared to their cold wall counterparts.
What is a Cold Wall Furnace?
In a cold wall design, the heating elements are located inside the vacuum chamber. The chamber itself is a water-cooled vessel that remains cool during operation. A "hot zone" made of insulating materials like graphite or metal shields is built inside the chamber to contain the heat.
This design allows for much higher operating temperatures, often exceeding 2800°C (5000°F), and enables the furnace to reach deeper vacuum levels because outgassing from the chamber walls is minimized.
The Case for Cold Wall: Performance and Versatility
Cold wall furnaces are the industry standard for high-performance applications. The water-cooled chamber allows for very rapid cooling (quenching), which is essential for processes like hardening, brazing, and sintering.
Their ability to achieve higher temperatures and higher vacuum levels makes them far more versatile, capable of handling a wider range of advanced materials and processes.
The Logistical Choice: Horizontal vs. Vertical Orientation
Once the thermal design is established, the furnace's physical orientation is chosen based on the parts being processed and the workflow of the facility.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Workhorse Configuration
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration. They are loaded from the front, similar to a conventional oven, making them ideal for processing large batches, heavy components, or parts loaded on trays and fixtures.
This orientation generally provides easier access for loading, unloading, and internal maintenance.
Vertical Furnaces: Precision and Space-Efficiency
Vertical furnaces are loaded from the top or bottom. This design is preferred for parts that are long, slender, or rotationally symmetrical (e.g., shafts, tubes, or gears).
Suspending or supporting a part vertically can significantly reduce the risk of distortion or sagging at high temperatures. Vertical furnaces also typically have a smaller factory floor footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding the compromises inherent in each design.
Hot Zone Materials: Graphite vs. All-Metal
Within cold wall furnaces, a critical decision is the material used for the hot zone insulation.
- Graphite-based hot zones use layers of carbon felt and graphite foil. This is a robust, cost-effective solution suitable for the vast majority of heat-treating processes.
- All-metal hot zones use layers of molybdenum and stainless steel. This design is specified for applications demanding extreme cleanliness and purity, such as in the medical, aerospace, or nuclear industries, where carbon contamination is unacceptable.
Process Application Dictates Design
The furnace's function is the ultimate guide. High-temperature processes like vacuum brazing (joining metals) and sintering (fusing powders) almost exclusively require a cold wall design for its performance capabilities.
Lower-temperature processes like annealing (softening metal) can be performed effectively and more economically in a hot wall furnace.
Temperature and Vacuum Level Limitations
A hot wall furnace's maximum temperature and vacuum level are limited by the material strength of the heated retort. A cold wall furnace, free from this constraint, can achieve extreme temperatures and create an ultra-high vacuum environment, enabling the removal of impurities and ensuring product purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace begins with a clear understanding of your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, lower-temperature processes like annealing or tempering: A hot wall furnace is often the most cost-effective and energy-efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is high-performance applications like brazing, sintering, or quenching: A cold wall furnace is essential for its high-temperature range, deep vacuum capability, and rapid cooling.
- If your primary focus is processing large, heavy, or batch-loaded parts: A horizontal configuration offers the most practical solution for material handling and maintenance.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in long or symmetrical parts: A vertical configuration provides the best part support and thermal stability for specific geometries.
By understanding these fundamental design choices, you are empowered to select the precise tool required to achieve your material processing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Configuration | Key Features | Typical Applications | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Wall | Heating elements outside chamber, simpler design, lower cost | Annealing, tempering, degassing | Up to 1200°C (2200°F) |
| Cold Wall | Heating elements inside chamber, water-cooled, high performance | Hardening, brazing, sintering | Up to 2800°C (5000°F) |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect vacuum furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with tailored furnace technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















