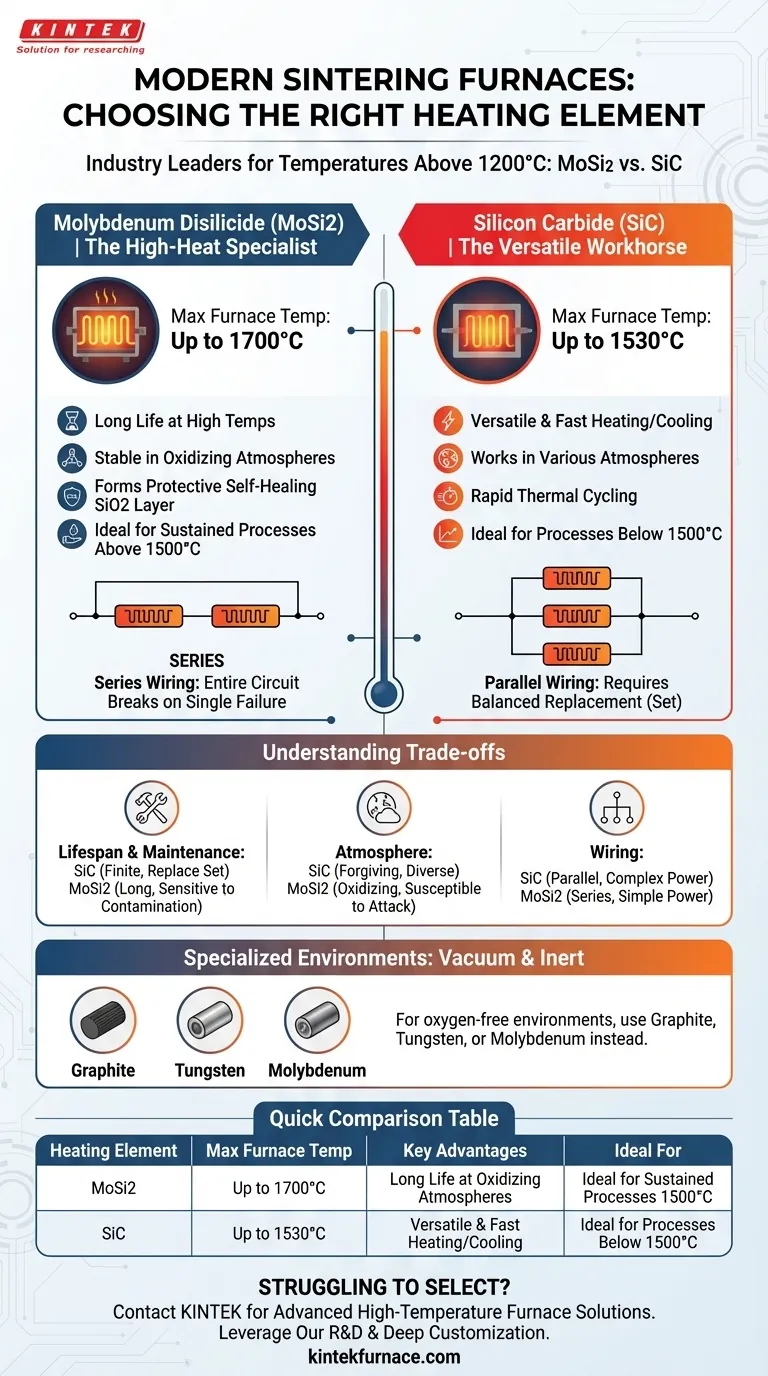
In modern high-temperature sintering furnaces, the two most prevalent heating elements are molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) and silicon carbide (SiC). These materials are the industry standard for furnaces operating above 1200°C due to their unique properties, but they are not interchangeable. The correct choice depends entirely on the specific temperature and atmospheric requirements of your process.
The decision between MoSi2 and SiC fundamentally hinges on your required operating temperature. MoSi2 is the superior choice for sustained processes above 1500°C, while SiC offers greater versatility and faster thermal cycling for applications operating at or below this critical threshold.

The Core Differentiator: Operating Temperature
The primary factor guiding selection is the maximum stable temperature each element can achieve and sustain within the furnace chamber.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): The High-Heat Specialist
MoSi2 elements are engineered for the most demanding high-temperature applications. They can reach surface temperatures of 1800°C to 1900°C, allowing for stable furnace operation up to 1700°C.
At high temperatures, MoSi2 forms a protective quartz-silica (SiO2) layer on its surface. This self-healing film prevents further oxidation, granting the element exceptional durability and a long service life, especially when operated consistently above 1500°C. This makes it ideal for processes requiring stable, uniform, and prolonged high-heat cycles.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The Versatile Workhorse
SiC elements are a robust and widely used option for a broad range of applications. Their maximum element temperature is around 1600°C, which translates to a maximum furnace operating temperature of approximately 1530°C.
The key advantages of SiC are its rapid heating and cooling speeds and its versatility. It performs well in both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres, making it a flexible choice for labs and production facilities that handle diverse materials and processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an element is not just about temperature; it involves balancing performance with operational realities like maintenance, atmosphere compatibility, and lifespan.
Lifespan and Maintenance
SiC elements have a finite lifespan and their electrical resistance increases with age. When one element fails, it is often necessary to replace the entire set to maintain balanced heating, as they are typically wired in parallel.
MoSi2 elements generally offer a longer service life, particularly when used for their intended high-temperature purpose. However, they are more sensitive to contamination from the process materials. Improper furnace maintenance can lead to premature failure.
Atmosphere and Contamination
SiC is known for its ability to perform reliably in a variety of furnace atmospheres. This makes it a more forgiving choice if process conditions vary.
MoSi2 elements deliver their best performance in clean, oxidizing environments. They are more susceptible to chemical attack, and care must be taken to prevent contaminants from binders or the product itself from degrading the protective silica layer.
Wiring and Power Control
The different wiring schemes impact the power supply and control systems. SiC's parallel wiring requires a system that can manage individual or grouped elements, while MoSi2's typical series wiring means a failure in one element can break the entire circuit.
What About Other Environments?
While MoSi2 and SiC dominate air-atmosphere furnaces, specialized environments require different solutions.
Metallic and Graphite Elements
For vacuum or controlled inert-gas sintering, different elements are required. The most common choices in these applications are graphite, tungsten, and molybdenum. These materials are suitable for oxygen-free environments where MoSi2 and SiC would not perform optimally.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be a direct reflection of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature capability (above 1500°C): MoSi2 is the definitive choice for its stability and long life at these temperatures.
- If your primary focus is versatility and rapid cycling below 1500°C: SiC provides excellent performance, faster heat-up and cool-down cycles, and superior adaptability to various atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is sintering in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: You must evaluate specialized elements such as graphite, tungsten, or pure molybdenum.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs ensures you select not just a heating element, but the right engine for your specific material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Max Furnace Temp | Key Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1700°C | Long life at high temps, stable in oxidizing atmospheres | Sustained processes above 1500°C |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1530°C | Versatile, fast heating/cooling, works in various atmospheres | Rapid cycling below 1500°C |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your sintering furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you need MoSi2 for extreme temperatures or SiC for versatility, we ensure precise performance to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















