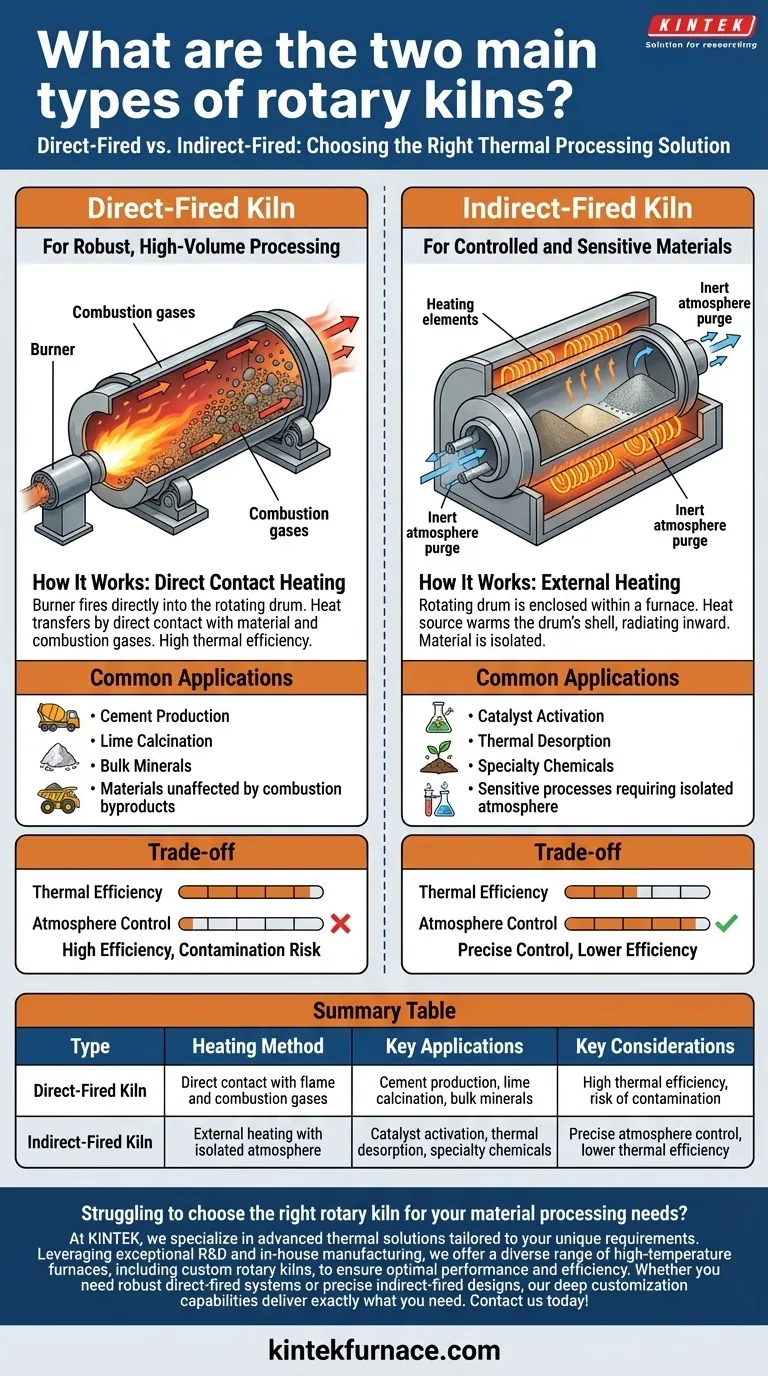
At their core, rotary kilns fall into two primary categories: direct-fired and indirect-fired. The fundamental difference lies in how heat is introduced to the material being processed. In a direct-fired kiln, the material is in direct contact with the flame and combustion gases, while an indirect-fired kiln heats the material by warming the exterior of the rotating drum, keeping the process atmosphere separate and controlled.
The decision between a direct-fired and an indirect-fired kiln is not about which is "better," but which is appropriate for your material. The central question is whether the material can tolerate direct contact with combustion byproducts or if it requires a strictly controlled, isolated atmosphere.

The Direct-Fired Kiln: For Robust, High-Volume Processing
A direct-fired kiln is the workhorse of heavy industry, designed for maximum thermal transfer and high throughput.
How It Works: Direct Contact Heating
In this design, a burner fires directly into the rotating drum. The hot combustion gases flow through the kiln, transferring heat by making direct contact with the material bed as it tumbles.
This method is highly efficient because heat transfer is immediate and pervasive throughout the length of the kiln.
Common Applications
Direct-fired kilns are used when the process material is robust and unaffected by the chemical byproducts of combustion.
Classic examples include the production of cement, the calcination of lime, and the processing of various bulk minerals where slight atmospheric variations are not a concern.
The Indirect-Fired Kiln: For Controlled and Sensitive Materials
An indirect-fired kiln, often called a calciner, provides a highly controlled environment for materials that cannot be exposed to a raw flame or combustion gas.
How It Works: External Heating
Here, the rotating drum is enclosed within a furnace or lined with heating elements. The heat source warms the outside of the drum's shell, and this heat radiates inward to the material.
This design completely isolates the material from the heating source, allowing for precise control over the internal atmosphere. It can be purged with inert gases, run with a reducing atmosphere, or even held under a vacuum.
Common Applications
This method is essential for sensitive processes. This includes activating catalysts, performing thermal desorption to remove soil contaminants, upgrading phosphate ores, and processing specialty chemicals or plastics that could be damaged or contaminated by direct firing.
Understanding the Core Trade-off: Atmosphere Control vs. Thermal Efficiency
Choosing the right kiln requires understanding the fundamental compromise between these two designs.
The Efficiency of Direct Firing
Direct-fired kilns are more thermally efficient. By bringing the heat source directly to the material, less energy is lost to the environment. This generally results in lower operational costs and higher processing volumes.
The risk, however, is potential product contamination or unwanted side reactions caused by exposure to the combustion gases.
The Precision of Indirect Firing
Indirect-fired kilns offer unparalleled process control. Because the internal atmosphere is separate from the combustion environment, you can create the exact conditions needed for a specific chemical reaction or phase change without risk of contamination.
This control comes at the cost of thermal efficiency. Heating the shell and radiating that heat inward is a less direct, and therefore less efficient, method of energy transfer. This often translates to higher capital and operational costs for a given throughput.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your material and process goals will dictate the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of inert materials like cement or minerals: A direct-fired kiln is the standard due to its superior thermal efficiency and throughput.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials that require a specific atmosphere or must not be contaminated: An indirect-fired kiln is the only viable option for its precise process control.
- If your primary focus is thermal desorption or treating contaminated soils: An indirect-fired design is necessary to capture and treat volatile compounds without them mixing with combustion gases.
Understanding how heat is delivered is the first and most critical step in selecting the right thermal processing technology.
Summary Table:
| Type | Heating Method | Key Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired Kiln | Direct contact with flame and combustion gases | Cement production, lime calcination, bulk minerals | High thermal efficiency, risk of contamination |
| Indirect-Fired Kiln | External heating with isolated atmosphere | Catalyst activation, thermal desorption, specialty chemicals | Precise atmosphere control, lower thermal efficiency |
Struggling to choose the right rotary kiln for your material processing needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse range of high-temperature furnaces, including custom rotary kilns, to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Whether you need robust direct-fired systems for high-volume production or precise indirect-fired designs for sensitive materials, our deep customization capabilities deliver exactly what you need. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your process with reliable, high-performance kiln solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















