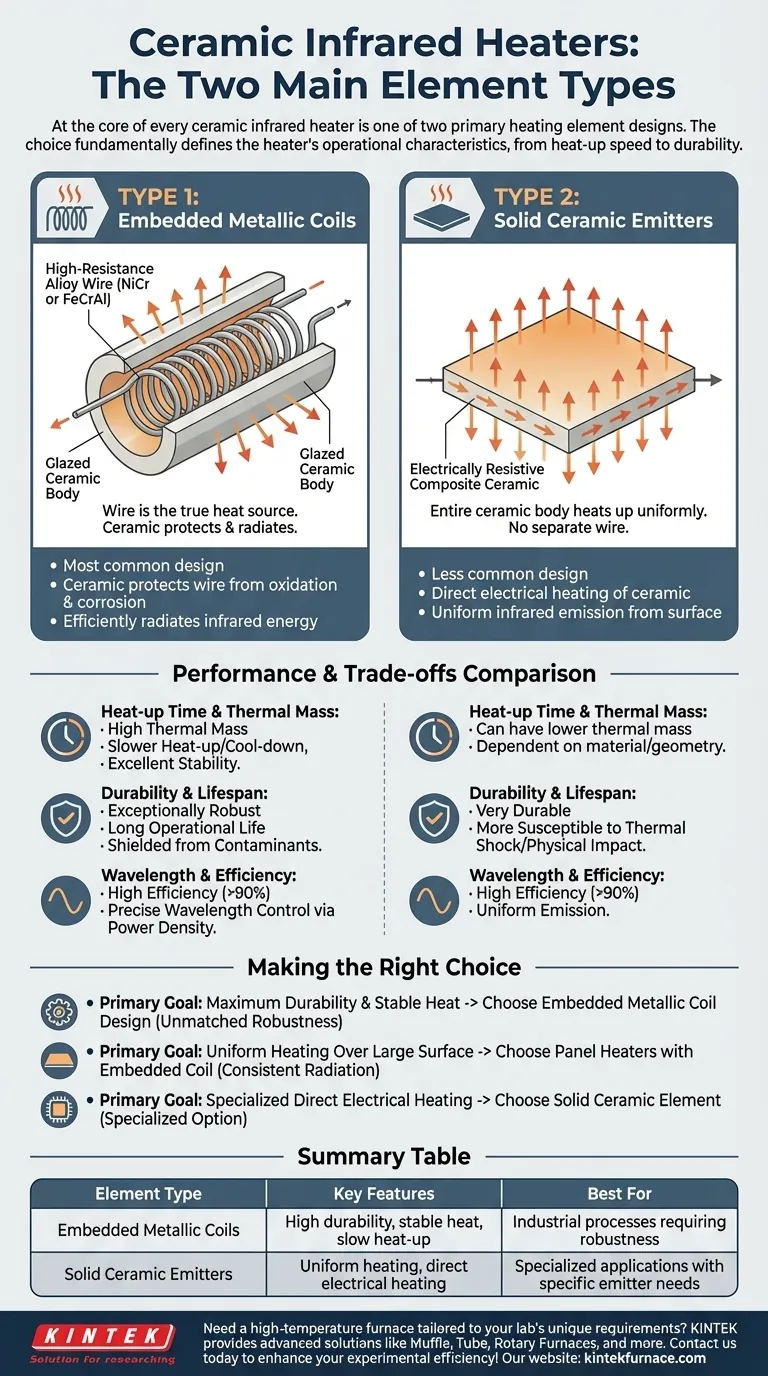
At the core of every ceramic infrared heater is one of two primary heating element designs. The main types are a solid ceramic element that functions as both the heater and emitter, or a metallic resistance wire that is embedded within a ceramic body, which then radiates the heat.
The choice between a solid ceramic element and an embedded metallic coil is not just about the material used. It fundamentally defines the heater's core operational characteristics, influencing everything from heat-up speed and durability to the type of infrared energy it produces.

Understanding the Core Element Designs
To select the right technology, you must first understand how each element type is constructed and how that design generates heat.
Type 1: Embedded Metallic Coils
This is the most common design for industrial and high-performance ceramic heaters.
A high-resistance alloy wire, often a nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy, is coiled or formed into a ribbon. This metallic element is then cast and fired inside a glazed ceramic body.
In this design, the wire is the true heat source. The surrounding ceramic serves two critical functions: it protects the wire from oxidation and corrosion, and it absorbs the wire's heat and efficiently radiates it outward as infrared energy.
Type 2: Solid Ceramic Emitters
In this less common design, the ceramic material itself is the heating element.
These are typically made from a composite ceramic material that becomes electrically resistive when heated. An electric current is passed directly through the ceramic rod or plate.
The entire ceramic body heats up uniformly and emits infrared radiation from its surface. This design avoids the use of a separate metallic element altogether.
How Element Type Influences Heater Performance
The physical construction of the element directly impacts how the heater behaves in a real-world application.
Heat-up Time and Thermal Mass
Embedded coil heaters generally have a higher thermal mass because the entire ceramic body must be heated. This results in slower heat-up and cool-down times, which provides excellent temperature stability once operational.
Solid ceramic emitters can sometimes be designed with lower thermal mass, but this is highly dependent on the specific material and geometry.
Durability and Lifespan
The embedded coil design is exceptionally robust. By encasing the metallic wire within the ceramic, it is shielded from atmospheric contaminants, moisture, and vibration, leading to a very long operational life.
Solid ceramic elements are also very durable but can be more susceptible to failure from thermal shock (rapid temperature changes) or direct physical impact.
Wavelength and Efficiency
Both designs are highly efficient at converting electricity into infrared energy, often exceeding 90%.
The specific wavelength of infrared energy produced (long-wave, medium-wave) is determined by the element's surface temperature, not the element type itself. However, the embedded coil design gives manufacturers precise control over the wire's power density, allowing them to engineer heaters for very specific target temperatures and wavelengths.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single design is universally superior. The optimal choice depends entirely on the application's specific requirements.
Heater Function vs. Element Type
You may see heaters categorized as "radiant" or "convective." This describes how the heater transfers energy to its environment, which is a result of its design, not the element type itself.
Heaters with high surface temperatures are almost purely radiant. Heaters designed with lower surface temperatures will transfer a larger portion of their energy through natural convection, warming the air around them.
Stability vs. Responsiveness
The high thermal mass of embedded coil ceramic heaters makes them ideal for processes requiring unwavering, consistent heat over long periods.
For applications needing rapid on-off cycling, the slower response time of a high-mass ceramic heater is a significant drawback. A different technology, like a quartz heater, may be more suitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and stable heat for an industrial process: An embedded metallic coil design provides unmatched robustness and temperature stability.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating over a large surface area: Panel heaters using embedded coil technology are the standard for providing consistent, even infrared radiation.
- If your primary focus is a specialized application requiring direct electrical heating of the emitter: A solid ceramic element may be necessary, though it is a less common and more specialized option.
Understanding the element's construction is the key to selecting a heater that delivers the precise performance your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Element Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Embedded Metallic Coils | High durability, stable heat, slow heat-up | Industrial processes requiring robustness |
| Solid Ceramic Emitters | Uniform heating, direct electrical heating | Specialized applications with specific emitter needs |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for diverse laboratories. Contact us today to enhance your experimental efficiency with the right furnace technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What ceramic materials are commonly used for heating elements? Discover the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision
- What are the key differences between SiC and MoSi2 heating elements in sintering furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the primary applications of MoSi2 heating elements in research? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Control for Material Synthesis
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications



















