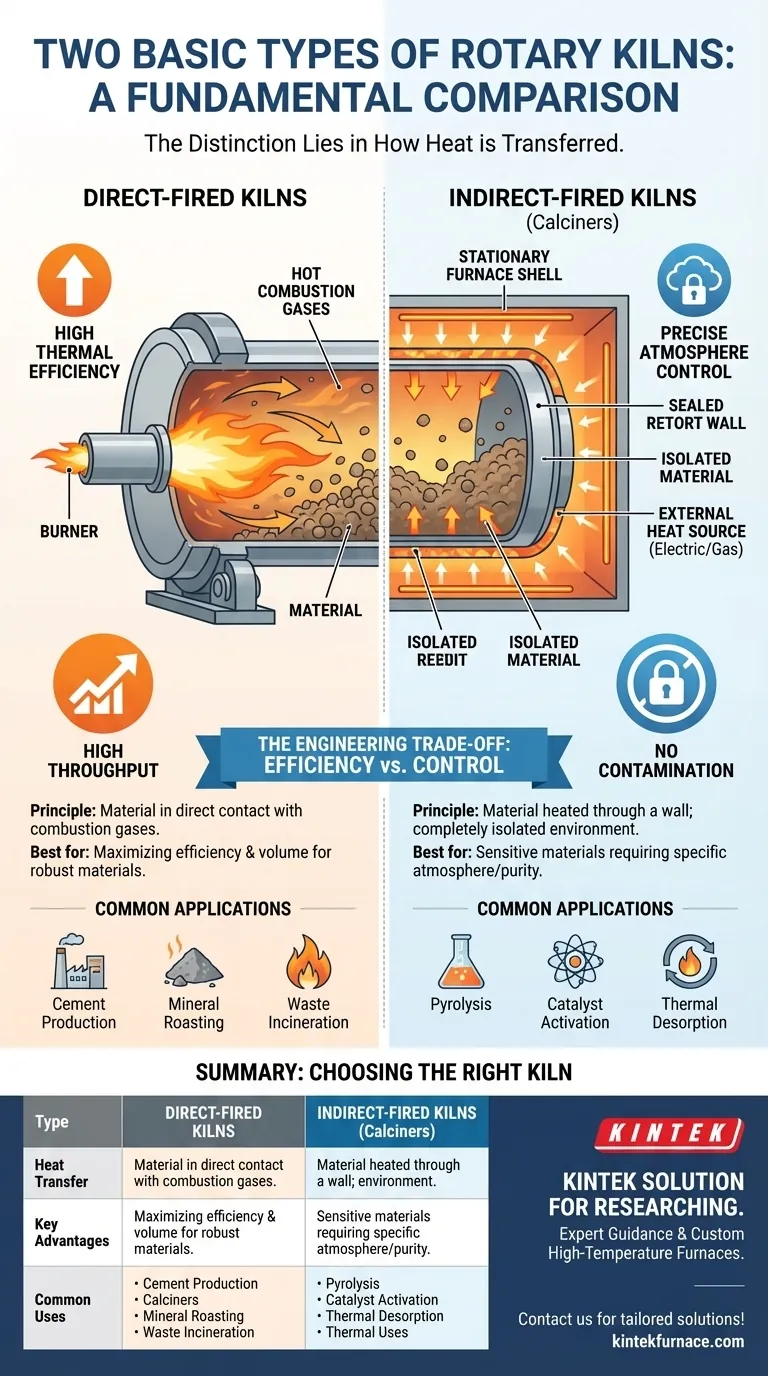
At their most fundamental level, the two basic types of rotary kilns are direct-fired and indirect-fired. The distinction lies entirely in how heat is transferred to the material being processed. In a direct-fired kiln, the material is in direct contact with the hot gases from combustion, while in an indirect-fired kiln, the material is heated through the wall of a rotating drum that is heated externally.
The choice between a direct and indirect rotary kiln is not about which is superior, but which is appropriate for the task. It represents a fundamental engineering trade-off between maximizing thermal efficiency and maintaining precise control over the processing atmosphere.

How Direct-Fired Kilns Work
Direct-fired kilns are the workhorses of many heavy industries, designed for high-volume and high-temperature processing where direct contact with combustion gases is acceptable or even beneficial.
The Principle of Direct Contact
In this design, a burner is located inside the kiln, typically at the discharge end. It fires a flame and hot process gas directly into the rotating chamber.
As material tumbles through the kiln, it comes into intimate contact with these hot gases, facilitating a rapid and efficient transfer of heat.
Key Advantage: Thermal Efficiency
Because the heat is generated and transferred directly to the material with no intermediary barrier, direct-fired kilns are more thermally efficient than their indirect counterparts.
This efficiency makes them ideal for processing large volumes of material, such as in the production of cement or the roasting of bulk minerals.
How Indirect-Fired Kilns Work
Indirect-fired kilns, sometimes called calciners, are engineered for processes that demand a controlled environment, completely isolated from the byproducts of combustion.
The Principle of External Heating
In an indirect kiln, the material is contained within a sealed rotating drum, or "retort." This retort is housed inside a larger insulated, stationary furnace.
Heat is applied to the outside of the rotating retort, and this thermal energy is conducted through the metal shell to the material tumbling inside. The material never touches the flame or combustion gases.
Preserving Atmosphere Integrity
The primary purpose of this design is to maintain absolute atmosphere control. The internal atmosphere can be tightly regulated—whether it needs to be inert (nitrogen), reducing (hydrogen), or oxidizing—without being contaminated by the heating source.
Common Heating Methods
The external heat source for an indirect kiln is often a series of electric heating elements or an external gas combustion chamber that envelops the rotating shell. Electric heating offers exceptionally precise temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct kiln type requires a clear understanding of your process priorities. The decision almost always comes down to efficiency versus control.
When to Prioritize Direct Firing
You should specify a direct-fired kiln when your process involves robust materials and the primary goal is high throughput and energy efficiency. Direct contact with combustion gas must be non-detrimental to the final product.
Common applications include cement manufacturing, aggregate drying, and waste incineration.
When to Demand Indirect Firing
An indirect-fired kiln is non-negotiable when the material is sensitive, could be contaminated by combustion gases, or requires a specific chemical reaction in a controlled atmosphere.
This is critical for processes like pyrolysis, thermal desorption of sensitive contaminants, catalyst activation, or the reduction of certain metal oxides where the gas chemistry is key.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your process requirements will dictate the correct kiln technology. Prioritize your primary objective to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency and throughput for a bulk material: A direct-fired kiln is almost always the correct and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control or preventing product contamination: An indirect-fired kiln is essential for maintaining process integrity.
- If your primary focus is ultra-precise temperature control with sensitive materials: An electrically heated indirect kiln offers the highest level of control available.
Understanding this core distinction between direct and indirect heating is the foundational step toward engineering a successful thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Type | Heat Transfer Method | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired | Material in direct contact with hot gases | High thermal efficiency, high throughput | Cement production, mineral roasting, waste incineration |
| Indirect-Fired | Material heated through external drum wall | Precise atmosphere control, no contamination | Pyrolysis, catalyst activation, thermal desorption |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect rotary kiln for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for thermal efficiency, atmosphere control, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your process and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















