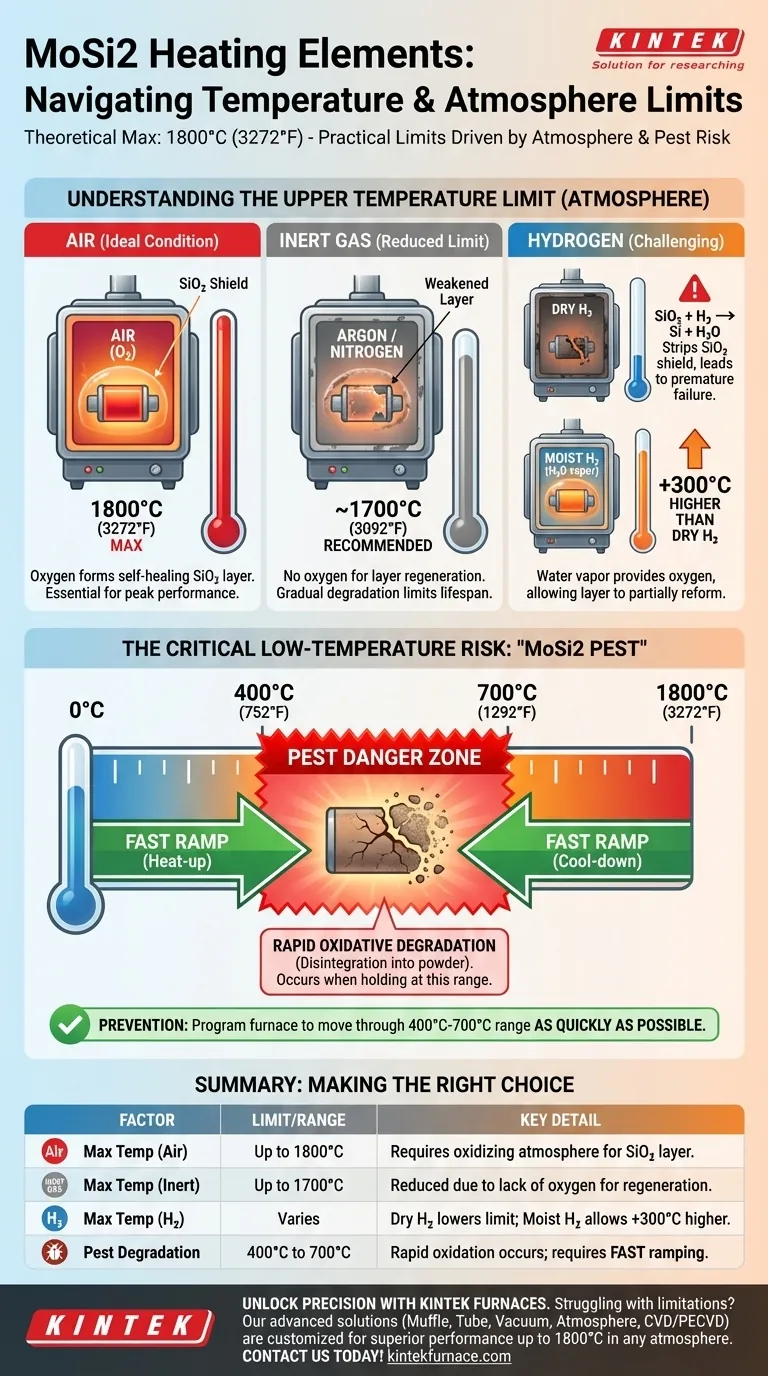
In ideal conditions, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements can operate at furnace temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). However, this absolute maximum is rarely achievable in practice. The true operating limit is dictated by the furnace atmosphere and a critical low-temperature failure mode that must be carefully managed.
The performance of MoSi2 elements is not defined by a single number, but by two critical boundaries. The upper limit is determined by the furnace atmosphere's ability to maintain a protective oxide layer, while a lower-temperature "pest" degradation dictates how the furnace must be heated and cooled.
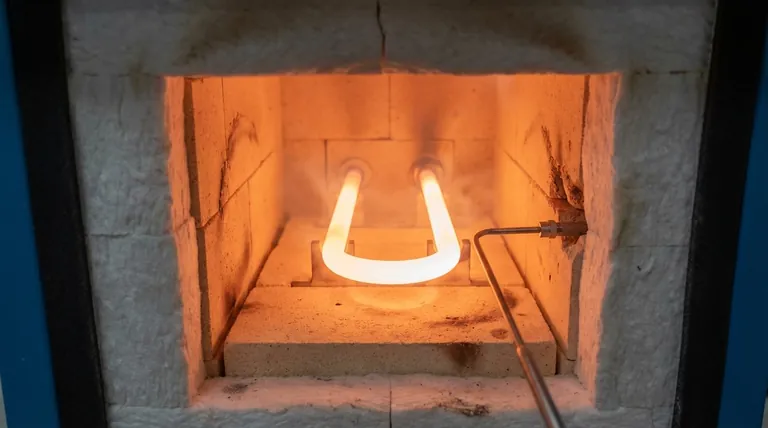

Understanding the Upper Temperature Limit
The maximum temperature of a MoSi2 element is entirely dependent on the presence of oxygen to form and maintain a protective surface layer of silica (SiO2).
The Ideal Condition: Air Atmosphere
In an oxidizing atmosphere like air, MoSi2 elements can reliably reach their peak temperature of 1800°C.
The oxygen in the air reacts with the element's surface to continuously form a thin, self-healing glass-like layer of silica. This layer protects the underlying material from further oxidation and is the key to its high-temperature capability.
The Impact of Inert Atmospheres
In inert atmospheres, such as argon or nitrogen, the maximum recommended operating temperature is reduced by approximately 100°C, to around 1700°C.
Without sufficient oxygen, the protective silica layer cannot regenerate if it becomes damaged or compromised at high temperatures. This gradual degradation limits the element's peak temperature and lifespan.
The Challenge of Hydrogen Atmospheres
Using MoSi2 elements in a dry hydrogen (H2) atmosphere severely reduces the maximum temperature.
Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, actively stripping the oxygen from the protective silica (SiO2) layer and converting it to silicon. This rapidly destroys the element's protective coating, leading to premature failure at much lower temperatures.
The Solution: Using Moist Hydrogen
The use of moist hydrogen can significantly improve performance, allowing for temperatures up to 300°C higher than in dry hydrogen.
The water vapor (H2O) in the moist gas provides a source of oxygen. This allows the protective silica layer to partially reform, counteracting the reducing effect of the hydrogen and enabling operation at higher temperatures.
The Critical Low-Temperature Risk: "MoSi2 Pest"
One of the most significant limitations of MoSi2 elements is a counterintuitive failure mode that occurs at low-to-moderate temperatures, known as "pest."
What is MoSi2 Pest?
MoSi2 pest is a form of rapid oxidative degradation that causes the element material to disintegrate into a fine powder.
This phenomenon is not a high-temperature failure but a specific chemical breakdown that occurs within a particular temperature window.
When Does It Occur?
Pest degradation occurs in a critical temperature range, typically between 400°C and 700°C (752°F and 1292°F).
Holding the elements within this temperature range for extended periods, or ramping through it too slowly, exposes them to accelerated decay.
How to Prevent It
Prevention requires programming the furnace controller to move through the 400°C-700°C range as quickly as possible during both heat-up and cool-down. This minimizes the element's exposure time to the conditions that cause pesting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your furnace's operating parameters must be set based on the specific requirements of your process while respecting the fundamental limitations of the heating elements.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum temperature (up to 1800°C): You must operate the furnace in an air atmosphere to ensure the protective silica layer is constantly maintained.
- If your primary focus is running a process in an inert or hydrogen atmosphere: You must accept a lower maximum operating temperature and carefully control gas moisture levels to protect the elements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: You must program furnace cycles to heat up and cool down rapidly through the 400°C-700°C range to avoid "MoSi2 pest" degradation.
By understanding these thermal and atmospheric boundaries, you can effectively harness the high-temperature capabilities of MoSi2 elements while ensuring reliable furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Temperature Limit / Range | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature in Air | Up to 1800°C | Requires oxidizing atmosphere for protective silica layer |
| Maximum Temperature in Inert Gas | Up to 1700°C | Reduced due to lack of oxygen for layer regeneration |
| Maximum Temperature in Hydrogen | Varies | Dry H2 lowers limit; moist H2 allows up to 300°C higher |
| Pest Degradation Range | 400°C to 700°C | Rapid oxidation occurs; requires fast heating/cooling |
Unlock Precision and Reliability with KINTEK's High-Temperature Furnaces
Struggling with temperature limitations or element degradation in your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed for superior performance up to 1800°C. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working in air, inert, or hydrogen atmospheres.
Don't let heating element failures hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency, extend equipment lifespan, and deliver consistent results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















