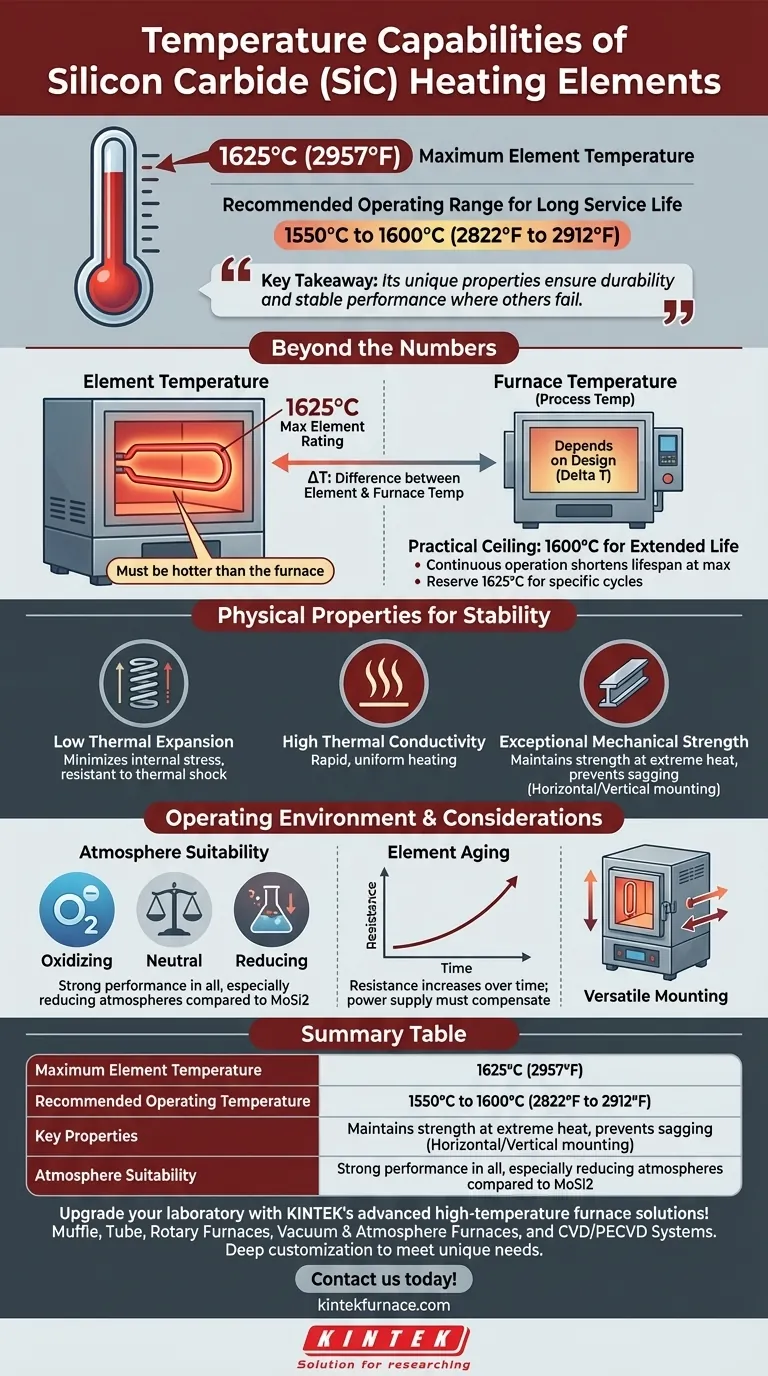
In short, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements can achieve element temperatures as high as 1625°C (2957°F). However, for most industrial applications requiring long service life and stability, the practical and recommended maximum operating temperature is typically between 1550°C and 1600°C.
The key takeaway is not just the maximum temperature, but why SiC can reliably sustain these temperatures. Its value comes from a unique combination of physical properties that ensures durability and stable performance where other materials would fail.

Beyond the Maximum Temperature: What the Numbers Mean
Understanding the difference between an element's peak rating and its practical operating limit is critical for designing a reliable high-temperature process. The datasheet value is only part of the story.
Element Temperature vs. Furnace Temperature
A heating element must always be hotter than the furnace chamber it is heating to drive heat transfer effectively. A rating of 1625°C refers to the maximum temperature the element itself can withstand, not the temperature your process or furnace will reach.
The difference between element and furnace temperature, known as the delta T, depends on furnace design, insulation, and the workload. This must be factored into your design calculations.
The Practical Operating Ceiling
For extended service life and predictable performance, most engineers design systems around a continuous operating temperature of 1600°C (2912°F) or slightly below. Running an element constantly at its absolute maximum rating will shorten its operational lifespan.
Pushing to the 1625°C limit is possible but should be reserved for specific, demanding process cycles rather than continuous operation.
The Physical Properties Behind High-Temperature Stability
Silicon carbide isn't just notable for its heat tolerance; it's the combination of properties that makes it a superior choice for demanding thermal applications.
Low Thermal Expansion
SiC has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little during rapid temperature changes, dramatically reducing internal mechanical stress. This property is the primary reason SiC elements are so resistant to thermal shock and have a long service life.
High Thermal Conductivity
These elements conduct heat very efficiently. This allows for rapid heating of the furnace and helps maintain a uniform temperature throughout the heating chamber, which is critical for process consistency.
Exceptional Mechanical Strength
Unlike many materials that weaken significantly when hot, silicon carbide maintains high mechanical strength even at extreme temperatures. This prevents the elements from sagging, stretching, or deforming under their own weight when installed horizontally.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operating Environment
No heating element is perfect for every situation. Understanding the context of your application is essential for making the right choice.
Impact of Furnace Atmosphere
Silicon carbide elements perform exceptionally well in both oxidizing and neutral atmospheres. They are also notably stronger in reducing atmospheres compared to common alternatives like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements, making them a preferred choice for certain metallurgical processes.
Element Aging
It is a known characteristic that SiC elements "age" over their lifespan. This means their electrical resistance gradually increases with use at high temperatures. Your power supply system must be able to compensate for this change by delivering increased voltage to maintain the required power output.
Physical Versatility
SiC elements are robust and can be mounted in both vertical and horizontal orientations. This provides significant flexibility in furnace design and construction, allowing for easier electrical connections and replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific goals of your industrial process.
- If your primary focus is reaching peak process temperatures: You can design around a 1600°C operating ceiling, but ensure your power control system can manage the higher stress and eventual aging of the elements.
- If your primary focus is maximum service life and reliability: Design your system with a more conservative element temperature, operating closer to 1550°C, to minimize thermal stress and extend replacement intervals.
- If your primary focus is operation in a reducing atmosphere: Silicon carbide is an inherently stronger and more suitable choice than many common high-temperature alternatives.
By understanding these principles, you can select and operate silicon carbide heating elements to achieve both high performance and long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Element Temperature | Up to 1625°C (2957°F) |
| Recommended Operating Temperature | 1550°C to 1600°C for long life |
| Key Properties | Low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, mechanical strength |
| Atmosphere Suitability | Oxidizing, neutral, and reducing atmospheres |
| Orientation | Can be mounted vertically or horizontally |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable silicon carbide heating elements and more. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and achieve superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















