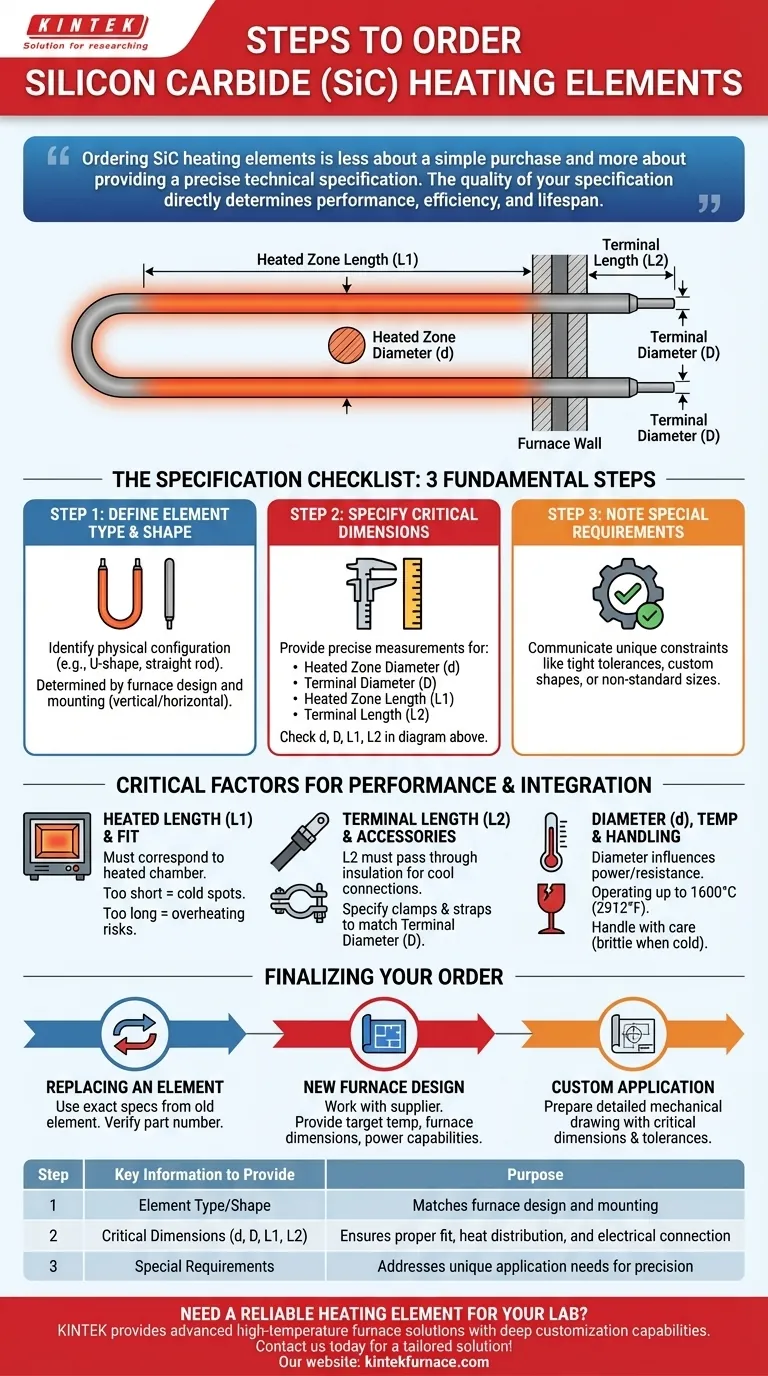
To order silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements, you must provide three key pieces of information to your supplier. This includes the element type or shape, the critical dimensions of the heated and terminal sections, and any special tolerances required for your specific furnace design.
Ordering SiC heating elements is less about a simple purchase and more about providing a precise technical specification. The quality of your specification—including element type, dimensions, and intended operating conditions—directly determines the performance, efficiency, and lifespan of your heating system.

The Specification Checklist: What to Provide Your Supplier
A clear and complete specification prevents errors and ensures you receive an element that fits and performs as expected. The process can be broken down into three fundamental steps.
Step 1: Define the Element Type and Shape
Your first step is to identify the physical configuration of the element you need. The most common type is a "U" shape, but straight rods and other custom forms are also available.
The element's shape is determined by your furnace's design, including how the element will be mounted (vertically or horizontally) and how power connections are made.
Step 2: Specify the Critical Dimensions
This is the most critical part of your order. You must provide precise measurements for four distinct areas of the element. Element diameters are normally specified in millimeters (mm), but lengths may be given in either millimeters or inches.
- Heated Zone Diameter (d): The diameter of the main body of the element that will radiate heat inside the furnace.
- Terminal Diameter (D): The diameter of the "cold ends" that pass through the furnace wall.
- Heated Zone Length (L1): The length of the section that will reach the target operating temperature.
- Terminal Length (L2): The length of the cold ends, which must be sufficient to pass through the furnace insulation for external power connection.
Step 3: Note Any Special Requirements
If your application has unique constraints, you must communicate them. This includes any tight dimensional tolerances or requirements for custom shapes or sizes.
Suppliers can often produce elements outside of standard dimensions, from small 0.5-inch diameter rods to large elements up to 3 inches in diameter and 10 feet in length.
Why These Specifications Matter
Each dimension you provide directly impacts the element's integration and performance within your heating system. Understanding the function of each measurement helps you create a better specification.
The Role of Heated Length (L1)
The heated length (L1) must correspond precisely to the heated chamber of your furnace. If L1 is too short, you will have cold spots; if it's too long, you risk overheating the furnace walls or terminal connections.
The Importance of Terminal Length (L2)
The terminal length (L2) must be long enough for the ends to pass completely through the furnace's refractory and insulation layers. This ensures the electrical connections are made in a cooler, ambient environment, preventing damage to the connection hardware.
The Impact of Element Diameter (d)
The diameter of the heated zone influences the element's electrical resistance and its power density (watts per square inch). This parameter is critical for matching the element to your power supply and achieving the desired heat output.
Understanding the Operational Context
Beyond the physical dimensions, the operating environment is a key factor in selecting the right element.
Operating Temperature and Atmosphere
SiC elements are an excellent choice for high-temperature applications, capable of operating at up to 1600°C (2912°F).
They are known for being particularly robust in reducing atmospheres, where they often outperform Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements.
Physical Properties and Handling
Silicon carbide is an extremely hard and strong material, even at high temperatures. However, like most ceramics, it can be brittle at room temperature and must be handled with care to prevent fracture.
Don't Forget the Accessories
Proper installation requires accessories like mounting clamps and high-current electrical straps. When ordering, ensure these accessories are specified to match the terminal diameter (D) of your heating elements for a secure and reliable electrical connection.
Finalizing Your Order
Use your specific goal to guide your final specification process.
- If your primary focus is replacing an existing element: Use the exact specifications from the old element. If possible, verify the part number with the original furnace or element manufacturer.
- If your primary focus is designing a new furnace: Work directly with the element supplier. Provide them with your target temperature, furnace dimensions, and power supply capabilities to get a tailored recommendation.
- If your primary focus is a custom application: Prepare a detailed mechanical drawing with all critical dimensions and tolerances clearly marked to ensure the manufacturer can produce exactly what you need.
A precise and detailed order is the first step toward a reliable and efficient high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Information to Provide | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Element Type/Shape (e.g., U-shape, straight rod) | Matches furnace design and mounting |
| 2 | Critical Dimensions (Heated Zone Diameter, Terminal Diameter, Heated Zone Length, Terminal Length) | Ensures proper fit, heat distribution, and electrical connection |
| 3 | Special Requirements (e.g., tolerances, custom shapes) | Addresses unique application needs for precision |
Need a reliable heating element for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements—ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specifications and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















