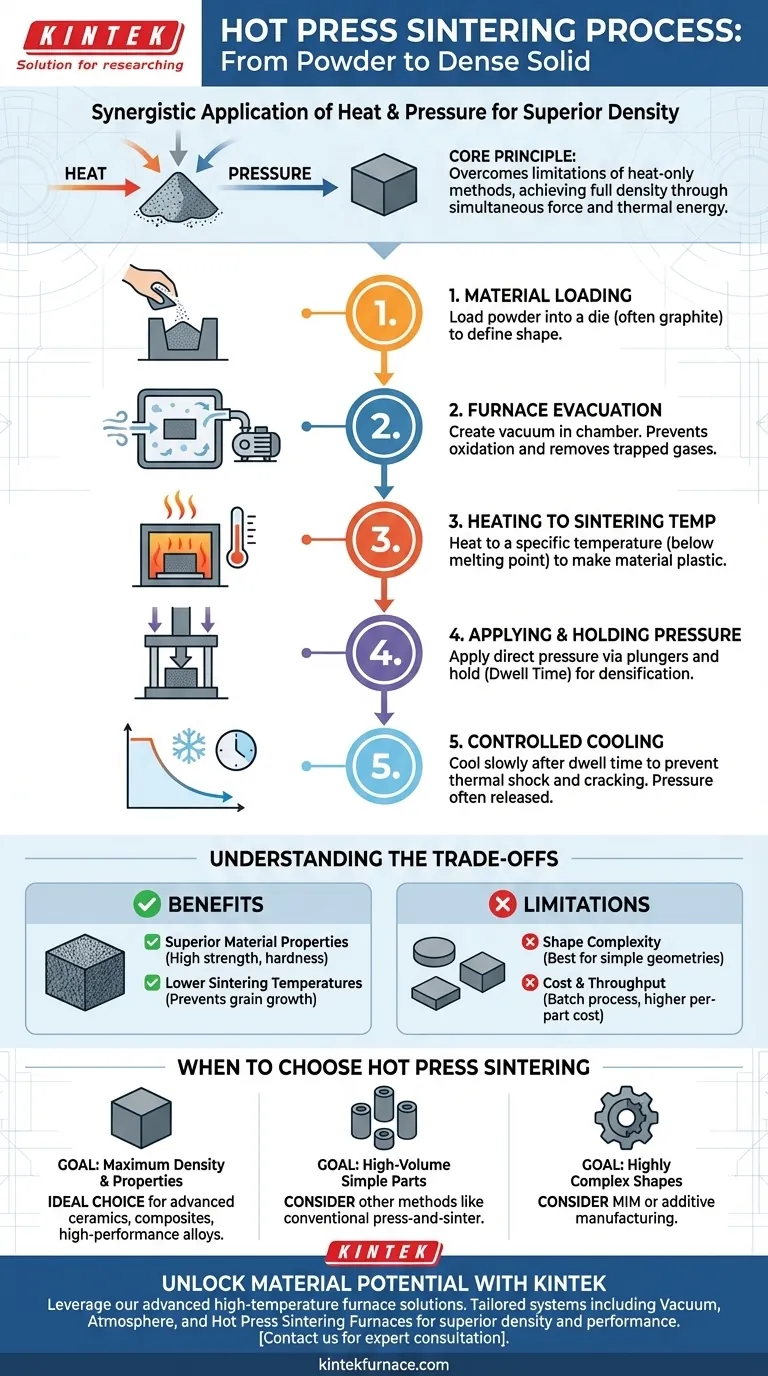
In essence, the hot press sintering process combines high temperature and mechanical pressure to transform a powder into a solid, dense object. The key steps are loading the material into a die, evacuating the furnace chamber to create a vacuum, heating the powder to a specific sintering temperature, applying uniaxial pressure, and finally, executing a controlled cooling sequence.
Hot press sintering is not merely a sequence of steps; it is a strategic application of simultaneous heat and pressure. This dual-action approach overcomes the limitations of heat-only methods, forcing particle rearrangement and diffusion to achieve superior density in advanced materials.

The Core Principle: Combining Heat and Mechanical Force
Hot press sintering is used when traditional, pressureless sintering cannot achieve the required density or mechanical properties. The process relies on the synergy between thermal and mechanical energy.
Why Heat Alone Isn't Always Enough
In conventional sintering, heat is the sole driver. It gives atoms enough energy to diffuse across the boundaries of powder particles, slowly bonding them together and reducing porosity. For many high-strength materials, this process can be slow, require extremely high temperatures, or fail to eliminate all pores.
The Role of Mechanical Pressure
Applying external pressure physically forces the powder particles into intimate contact. This action breaks down surface contaminants, promotes plastic deformation at contact points, and provides a powerful driving force for densification that complements thermal diffusion.
The Synergistic Effect
When heat and pressure are applied simultaneously, the material becomes soft and malleable enough for the pressure to be highly effective. This combination dramatically accelerates the densification process, allowing for full density to be achieved at lower temperatures or in shorter times compared to pressureless methods.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Each stage of the hot pressing cycle is critical for achieving a high-quality, fully dense final product.
Step 1: Material Loading
The process begins by loading the raw material, typically in powder form, into a die. This die, often made of high-temperature graphite, defines the basic shape of the final component.
Step 2: Furnace Evacuation (The Vacuum Advantage)
The loaded die is placed inside a sealed furnace chamber. Air and other atmospheric gases are then pumped out to create a vacuum. This crucial step prevents oxidation of the material at high temperatures and helps remove gases that could otherwise become trapped as pores in the final part.
Step 3: Heating to Sintering Temperature
The furnace heats the material and die according to a pre-defined profile. The target temperature is below the material's melting point but high enough to make it sufficiently plastic. This temperature is one of the most critical process parameters.
Step 4: Applying and Holding Pressure
Once the target temperature is reached, a hydraulic or mechanical ram applies direct, uniaxial (single-direction) pressure to the powder via plungers. This pressure is held for a specific duration, known as the dwell time, allowing densification to complete through diffusion and material flow.
Step 5: Controlled Cooling
After the dwell time, the heating is turned off and the component is cooled in a controlled manner. Slow, controlled cooling is vital to prevent thermal shock, which can cause cracking, especially in brittle materials like ceramics. The pressure is typically released before or during the cooling phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. It involves a clear set of benefits and limitations that define its ideal applications.
Limitation: Shape Complexity
Because the pressure is applied in one direction (uniaxially), hot pressing is best suited for producing parts with relatively simple geometries, such as discs, blocks, and cylinders.
Limitation: Cost and Throughput
Hot pressing is a batch process, meaning parts are made one at a time or in small groups. This results in lower throughput and higher per-part costs compared to continuous, high-volume methods.
Benefit: Superior Material Properties
The primary advantage is the result. Hot pressing produces parts with near-full theoretical density, minimal porosity, and excellent mechanical properties like strength and hardness, which are often unattainable with other methods.
Benefit: Lower Sintering Temperatures
The addition of pressure allows for successful densification at lower temperatures. This helps prevent undesirable grain growth, which can weaken a material, resulting in a fine-grained microstructure that enhances mechanical performance.
When to Choose Hot Press Sintering
Selecting this process depends entirely on your final goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties: Hot press sintering is an ideal choice, especially for advanced ceramics, composites, and high-performance alloys.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple metal parts: A different method like conventional press-and-sinter is likely more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is creating highly complex shapes: You may need to consider alternative processes like metal injection molding (MIM) or additive manufacturing.
Ultimately, understanding this process empowers you to select the right manufacturing path to achieve your material performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Step | Description | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Loading | Load powder into a die | Defines shape; uses graphite dies |
| 2. Furnace Evacuation | Create vacuum in chamber | Prevents oxidation, removes gases |
| 3. Heating | Heat to sintering temperature | Below melting point, critical parameter |
| 4. Pressure Application | Apply uniaxial pressure | Held during dwell time for densification |
| 5. Controlled Cooling | Cool slowly after process | Prevents cracking, pressure released |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored hot press sintering systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior density, enhanced mechanical properties, and optimized performance for ceramics, composites, and alloys. Ready to elevate your sintering process? Contact us today for expert consultation and customized solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing



















