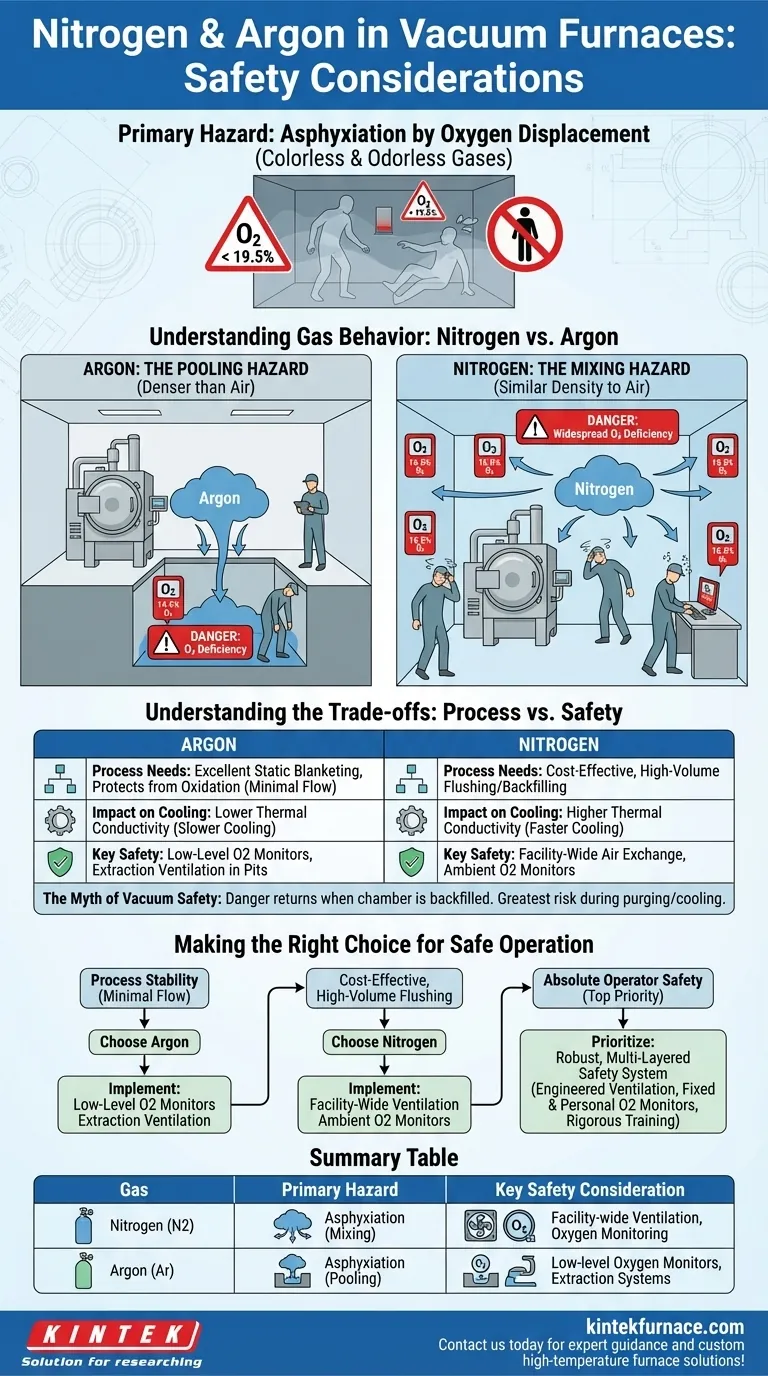
When operating vacuum furnaces, the primary safety consideration for using nitrogen and argon is the risk of asphyxiation. Both gases are non-toxic but can displace oxygen in the workspace to dangerously low levels. Understanding their different physical properties is critical, as argon is denser than air and pools in low areas, while nitrogen mixes readily with air, creating a more widespread hazard if ventilation is inadequate.
The core safety principle is not that these gases are inherently dangerous, but that they are dangerous in the absence of oxygen. Safe operation depends entirely on engineered controls like ventilation and oxygen monitoring, which must be designed to account for the specific behavior of the gas being used.

The Primary Hazard: Asphyxiation by Oxygen Displacement
Why Inert Gases Are a Risk
Nitrogen and argon are used in vacuum furnaces precisely because they are inert, meaning they prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation at high temperatures.
However, this same property means they do not support life. When released, they dilute the concentration of breathable oxygen in the air.
The Silent Danger
These gases are colorless and odorless, making human senses completely ineffective at detecting a hazardous situation.
A person entering an oxygen-deficient environment may experience dizziness, confusion, and loss of consciousness within seconds, leaving no time to escape. This is why relying on procedural safeguards and monitoring is non-negotiable.
Understanding Gas Behavior: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Argon: The Pooling Hazard
Argon is approximately 40% denser than air. When a leak or release occurs, it will flow downwards and accumulate in low-lying, unventilated areas.
This creates a serious, concentrated risk in basements, maintenance pits, or any confined space below the furnace level. An operator could unknowingly walk into an invisible pool of argon and be overcome immediately.
Nitrogen: The Mixing Hazard
Nitrogen has a density very similar to that of air. Because of this, it does not pool but instead mixes easily and thoroughly with the ambient air in a room.
This makes it a more insidious hazard. A slow, unnoticed leak can gradually lower the oxygen level in an entire workspace, posing a threat to everyone in the area, not just those in low-lying spots.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Needs vs. Physical Risk
Argon's high density makes it excellent for creating a static "blanket" over a workpiece, effectively protecting it from oxidation with minimal gas flow.
Nitrogen is significantly less expensive and is often preferred for processes requiring continuous, high-volume flushing or backfilling. This cost benefit must be weighed against its more challenging ventilation requirements.
Impact on Cooling Rates
The choice of gas also affects the material properties. Argon has a lower thermal conductivity than nitrogen, meaning parts will cool more slowly inside the furnace.
This is a critical process variable but not a direct safety concern. However, the decision on which gas to use for process reasons dictates the specific safety protocols that must be followed.
The Myth of Vacuum Safety
While operating under a vacuum eliminates the risk of fire by removing oxygen, the danger returns the moment the chamber is backfilled with an inert gas. The greatest risk occurs during the purging and cooling cycles or in the event of a system leak.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Safe operation is achieved by designing safety systems that directly counter the physical properties of your chosen gas.
- If your primary focus is process stability with minimal gas flow: Argon's blanketing effect is ideal, but you must install and maintain oxygen monitors and extraction ventilation in all low-lying areas.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume flushing: Nitrogen is the standard choice, but your primary safety investment must be in powerful, facility-wide air exchange systems and ambient O2 monitors.
- If your top priority is absolute operator safety: The gas choice is secondary to implementing a robust, multi-layered safety system that includes engineered ventilation, fixed and personal oxygen monitors, and rigorous operator training.
Ultimately, safe furnace operation is achieved not by avoiding these gases, but by respecting their properties with rigorous engineering and procedural discipline.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Hazard | Key Safety Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Asphyxiation due to mixing with air | Requires facility-wide ventilation and oxygen monitoring |
| Argon | Asphyxiation due to pooling in low areas | Needs low-level oxygen monitors and extraction systems |
Ensure your lab's safety with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today for expert guidance and reliable equipment tailored to your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing



















