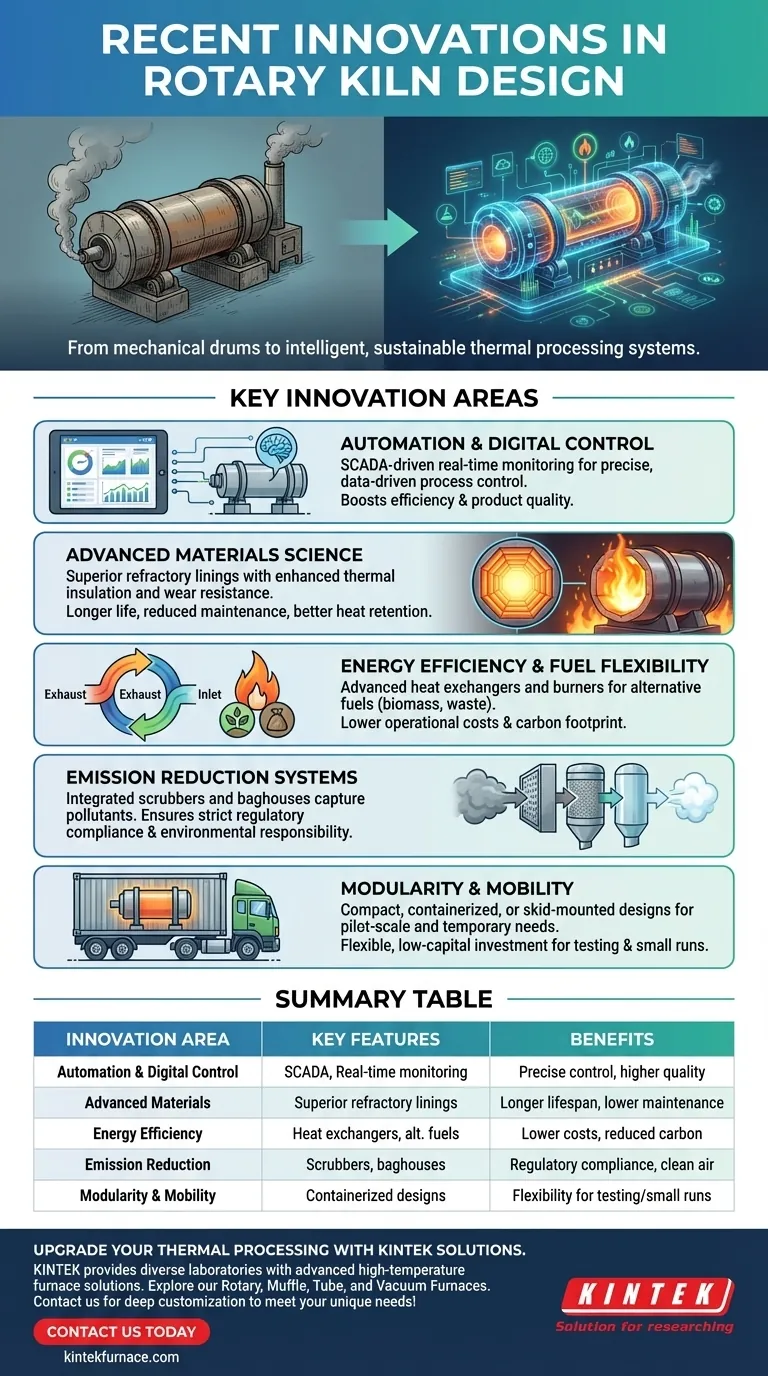
In recent years, rotary kiln design has evolved significantly beyond its traditional mechanical roots. The most impactful innovations center on automation and digital control, advanced materials for construction, energy efficiency, emission reduction, and new modular form factors. These changes work together to transform the kiln from a simple heating drum into a precise, data-driven thermal processing system.
The core challenge with traditional rotary kilns has always been their inefficiency, high operational costs, and environmental impact. Modern innovations are not merely incremental upgrades; they represent a fundamental shift towards making kilns smarter, more sustainable, and highly adaptable to specific material processing needs.

Why Traditional Kiln Design is Being Reimagined
A rotary kiln, at its heart, is a simple machine: a large, rotating steel cylinder lined with refractory brick, set at a slight angle. Material fed into the higher end travels through the kiln as it rotates, undergoing thermal and chemical changes.
For decades, the design focused on brute-force durability and scale, with some kilns reaching over 700 feet in length. However, this approach comes with inherent limitations: massive energy consumption, reliance on operator experience for control, significant maintenance downtime, and substantial environmental emissions.
Modern demands for process efficiency, cost optimization, and strict regulatory compliance have forced a complete rethinking of this traditional model.
Key Areas of Modern Innovation
Today's innovations target the core weaknesses of older designs, focusing on intelligence, efficiency, and sustainability.
Automation and Digital Control
The single biggest leap is the integration of digital control systems. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are now central to modern kiln operation.
These platforms provide real-time monitoring of critical variables like temperature profiles, retention time, feed rate, and gas flow. This allows for automated adjustments, moving from manual, experience-based operation to precise, data-driven process control that boosts efficiency and product quality.
Advanced Materials Science
The durability of a kiln is dictated by its refractory lining, which protects the steel shell from extreme heat and chemical attack.
Innovations in refractory materials have produced linings with superior thermal insulation and resistance to wear. This directly translates to longer campaign life, reduced maintenance downtime, and better heat retention, which lowers overall energy consumption.
Energy Efficiency and Fuel Flexibility
Energy is the primary operational cost of a rotary kiln. Modern designs prioritize efficiency through several means.
Advanced heat exchangers are used to recover waste heat from exhaust gases and preheat the incoming material or combustion air. Furthermore, burners and combustion systems are now designed to handle a wider range of alternative fuels, including biomass or waste-derived fuels, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering both costs and carbon footprint.
Emission Reduction Systems
Meeting environmental regulations is a non-negotiable aspect of modern industry. Kiln systems now integrate sophisticated emission reduction technologies.
These include high-efficiency scrubbers, baghouses, and other gas treatment systems that capture pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere. This ensures the entire thermal processing operation remains compliant with even the most stringent standards.
Modularity and Mobility
A significant innovation is the move away from exclusively massive, permanent installations. Modular and mobile rotary kilns offer new flexibility.
These compact, containerized, or skid-mounted systems are ideal for pilot-scale testing, smaller production runs, or temporary projects at remote sites. They allow companies to validate a process or fulfill a specific contract without the massive capital investment of a permanent kiln.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While these innovations offer clear advantages, they are not without their own set of challenges and considerations.
The Cost of Added Complexity
Automation and advanced sensor arrays introduce a higher level of technical complexity. Operating and maintaining these systems requires a more skilled workforce. A failure in a digital control component can be as disruptive as a mechanical failure, requiring specialized diagnostic expertise.
Material Properties Remain Paramount
No amount of technology can compensate for a poor understanding of the material being processed. Key characteristics like particle size distribution, bulk density, moisture content, and chemical properties still fundamentally dictate the kiln's design. Pilot-scale testing remains a critical step to gather this data and ensure the final design is tailored for success.
Retrofitting vs. a New Build
Integrating the latest innovations into an existing, older kiln can be challenging and expensive. While retrofitting emission controls or a new burner is often feasible, achieving the full benefit of a fully automated, energy-efficient design is typically only possible with a new, purpose-built system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right design elements depends entirely on your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency and reducing operational costs: Prioritize a design with advanced automation, real-time controls, and integrated heat recovery systems.
- If your primary focus is ensuring strict regulatory compliance: Invest heavily in the best available emission reduction technologies and continuous monitoring systems.
- If your primary focus is increasing plant uptime and durability: Specify advanced refractory materials and robust mechanical components, even if the initial cost is higher.
- If your primary focus is process development or short-term production: Explore modular and mobile kiln systems to provide flexibility without the long-term capital commitment.
Ultimately, modern innovations transform the rotary kiln from a brute-force instrument into a precise and intelligent tool for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Innovation Area | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automation & Digital Control | SCADA systems, real-time monitoring | Precise process control, improved efficiency, higher product quality |
| Advanced Materials | Superior refractory linings | Longer lifespan, reduced maintenance, better heat retention |
| Energy Efficiency | Heat exchangers, alternative fuel use | Lower operational costs, reduced carbon footprint |
| Emission Reduction | Scrubbers, baghouses | Regulatory compliance, reduced environmental impact |
| Modularity & Mobility | Containerized, skid-mounted designs | Flexibility for testing, small runs, remote sites |
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing with cutting-edge rotary kiln solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our innovations can enhance your efficiency, sustainability, and compliance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















