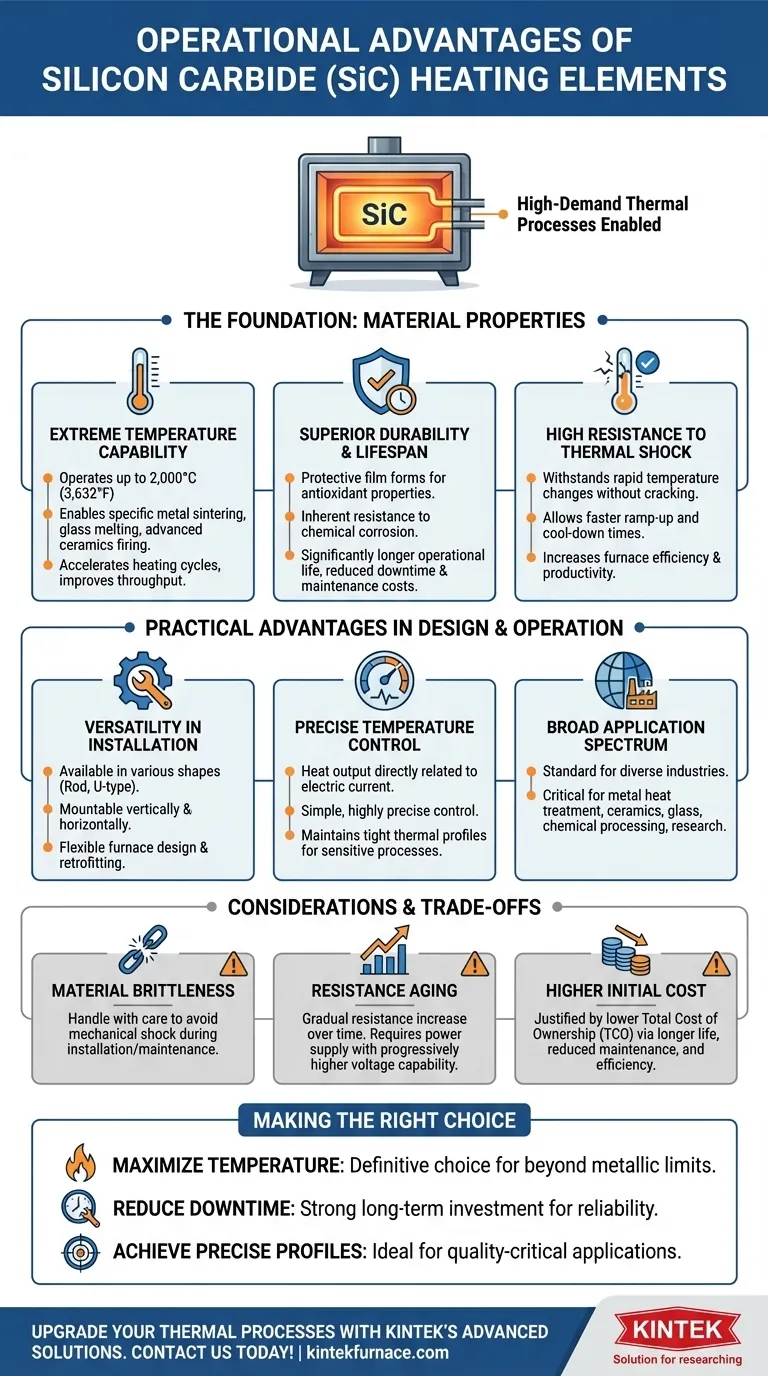
From an operational standpoint, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements offer significant advantages over traditional metallic options, primarily centered on their ability to operate at much higher temperatures. This core capability is supported by their longer operational lifespan, superior resistance to thermal shock, and enhanced durability against chemical corrosion and oxidation.
The decision to use silicon carbide heating elements is a strategic choice for enabling high-demand thermal processes. Their true value lies not just in reaching higher temperatures, but in delivering the operational stability, longevity, and process consistency required for high-quality industrial manufacturing.

The Foundation of SiC Performance: Material Properties
To understand the operational advantages, we must first look at the inherent properties of silicon carbide. The manufacturing process, which uses high-purity green silicon carbide powder, results in a dense, uniform material that forms the basis for its superior performance.
Extreme Temperature Capability
Silicon carbide elements can operate at furnace temperatures far exceeding the limits of traditional metallic elements, in some cases over 2,000°C (3,632°F).
This allows for processes that are simply not possible with other materials, such as specific types of metal sintering, glass melting, and advanced ceramics firing. It can also significantly accelerate heating cycles, improving overall throughput.
Superior Durability and Lifespan
The surface of a SiC element naturally forms a protective film that enhances its antioxidant properties. This, combined with its inherent resistance to chemical corrosion, results in a significantly longer operational life.
For operators, this translates directly into reduced downtime for element replacement, lower maintenance costs, and more predictable and consistent heating performance over thousands of hours.
High Resistance to Thermal Shock
Unlike many other ceramic materials, silicon carbide withstands rapid changes in temperature without cracking or failing.
This operational advantage is critical in applications with frequent heating and cooling cycles. It allows for faster process ramp-up and cool-down times, increasing the efficiency and productivity of the furnace or kiln.
Practical Advantages in Design and Operation
Beyond the core material science, SiC elements are engineered for practical, real-world industrial environments. Their design flexibility makes them adaptable to a wide range of equipment and processes.
Versatility in Installation
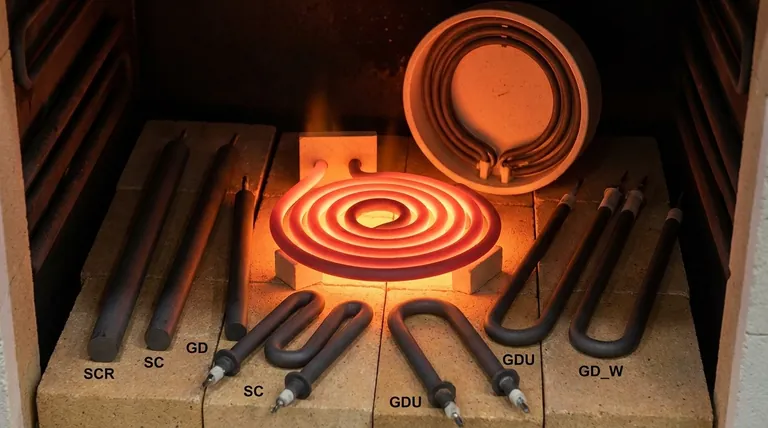
SiC elements are manufactured in various shapes and sizes, including common rod and U-type configurations. This allows for customization to fit the specific needs of a furnace.
Furthermore, they can be mounted both vertically and horizontally, providing engineers with significant flexibility when designing or retrofitting heating systems.
Precise Temperature Control
The heat output of a SiC element is a direct function of the electric current passed through it. This relationship allows for simple and highly precise temperature control.
By adjusting the current, operators can maintain the tight thermal profiles required for sensitive processes like semiconductor manufacturing, alloy heat treating, and laboratory experiments.
Broad Application Spectrum
The unique combination of high temperature, durability, and control makes SiC elements the standard for a vast range of industries.
They are critical components in industrial furnaces for metal heat treatment, ceramics and glass production, chemical processing, and scientific research.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly advantageous, SiC elements have specific characteristics that must be managed for optimal performance. An objective assessment requires acknowledging these factors.
Material Brittleness
As a ceramic material, silicon carbide is more brittle than metallic alloys. The elements must be handled with care during shipping, installation, and maintenance to avoid mechanical shock, which can cause them to crack or break.
Resistance Aging
Over their operational life, SiC elements experience a gradual increase in electrical resistance. This is a normal and predictable aging process.
To maintain constant power output (and thus stable temperature), the power supply system must be capable of delivering progressively higher voltage over time to compensate for this increased resistance. This capability must be factored into the initial system design.
Higher Initial Cost
The initial procurement cost for SiC elements is typically higher than for conventional metallic elements.
This higher upfront investment is often justified by a lower total cost of ownership (TCO), which is achieved through longer element life, reduced maintenance needs, and improved process efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of heating element should be guided by the specific demands of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing process temperature: SiC is the definitive choice for applications that require temperatures beyond the capabilities of metallic elements.
- If your primary focus is reducing downtime and maintenance: The extended lifespan and durability of SiC make it a strong long-term investment for improving operational reliability and lowering TCO.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise and repeatable thermal profiles: The stability and excellent controllability of SiC elements are ideal for quality-critical applications like electronics or advanced materials processing.
Ultimately, adopting silicon carbide heating elements is an investment in process capability and long-term operational excellence.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Capability | Operates up to 2000°C, enabling high-demand processes like metal sintering and ceramics firing |
| Superior Durability and Lifespan | Protective film and corrosion resistance reduce downtime and maintenance costs |
| High Resistance to Thermal Shock | Withstands rapid temperature changes for faster heating cycles and improved productivity |
| Versatility in Installation | Customizable shapes (e.g., rod, U-type) and flexible mounting options for various furnace designs |
| Precise Temperature Control | Direct current-to-heat relationship allows tight thermal profiles for sensitive applications |
| Broad Application Spectrum | Used in metal heat treatment, glass production, chemical processing, and research |
Upgrade your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide silicon carbide heating elements and custom furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique needs, delivering superior temperature control, durability, and efficiency. Contact us today to enhance your lab's performance and reduce operational costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















