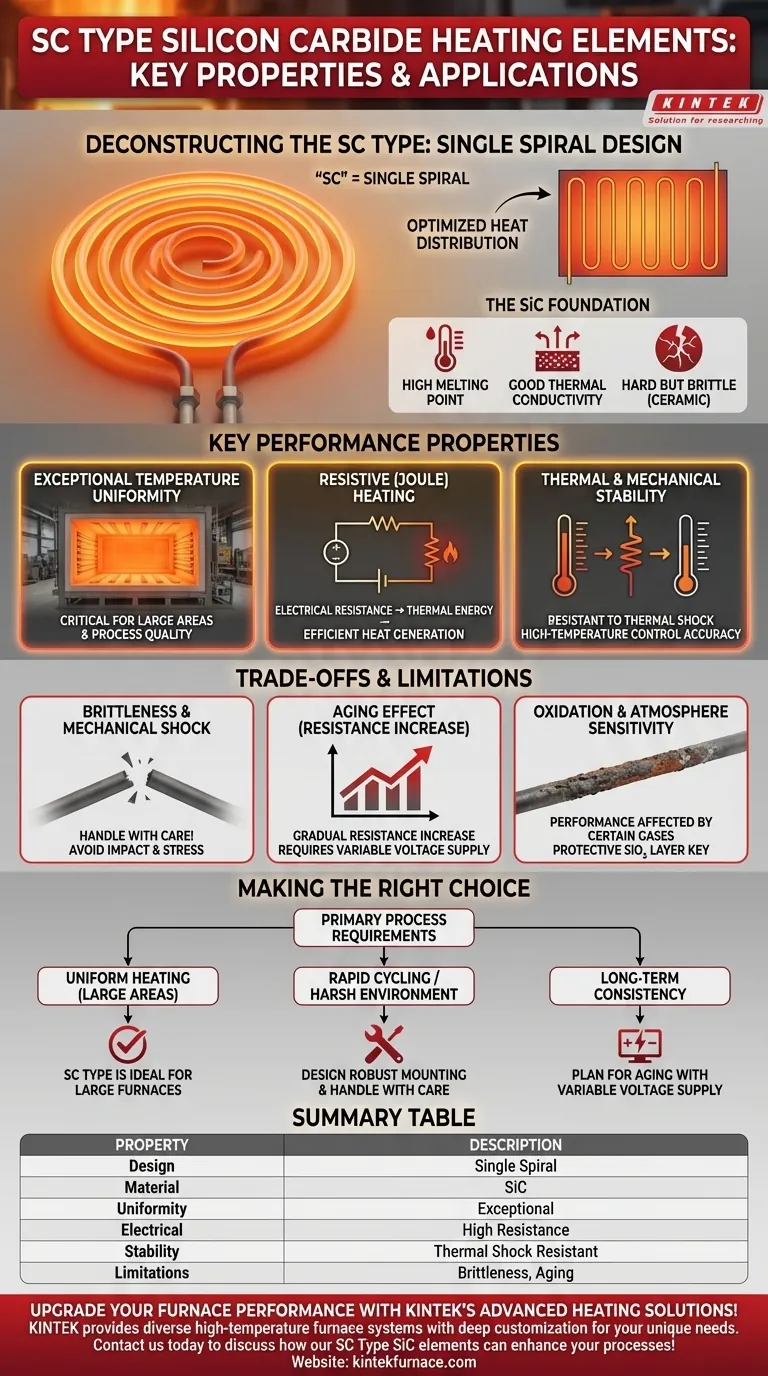
At their core, SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are defined by their unique Single Spiral configuration and foundational material properties. This design delivers exceptional temperature uniformity, high-temperature stability, and the specific electrical resistance needed for efficient heat generation in industrial and laboratory furnaces.
The "SC" designation refers to the element's Single Spiral construction. This is not a minor detail; it is the core design choice that makes this element type the definitive solution for applications demanding consistent, uniform heat across a large surface area.

Deconstructing the SC Type: From Material to Design
Understanding the SC Type element requires looking at both its physical shape and the intrinsic properties of the material from which it is made.
What "SC" Signifies: The Single Spiral
The "SC" in the name explicitly stands for Single Spiral. This physical configuration is the primary differentiator.
This design is engineered to optimize the distribution of heat, making it particularly effective for creating a consistent thermal environment over a large plane.
The Silicon Carbide (SiC) Foundation
The element is manufactured from silicon carbide, a hard, brittle ceramic material. This base material provides the fundamental characteristics required for high-temperature operation.
Key material properties include a high melting point, good thermal conductivity, and resistance to deformation at extreme temperatures.
Key Performance Properties Explained
The combination of the SiC material and the Single Spiral design results in a specific set of performance characteristics that dictate its ideal use cases.
Primary Benefit: Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
The single spiral design, combined with SiC's good thermal conductivity, ensures a very small temperature difference across the element's surface.
This is critical in applications like large box furnaces or trolley furnaces where spatial temperature uniformity is crucial for process quality, such as in metal treatment or firing ceramics.
Electrical Properties: The Principle of Resistive Heating
These elements function through resistive (Joule) heating. They are designed to have a high but not insulating electrical resistance.
When an electrical current passes through the SiC material, this resistance causes the element to heat up, converting electrical energy into thermal energy. This requires a material that is conductive enough to allow current to flow but resistive enough to generate substantial heat.
Thermal & Mechanical Stability
SC Type elements are known for their ability to withstand high temperatures without deforming or melting. They are also resistant to damage from rapid heating and cooling cycles (thermal shock).
This stability allows for high-temperature control accuracy, providing a reliable and stable heat source for demanding processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No component is perfect for every scenario. Acknowledging the limitations of SC Type elements is critical for successful implementation and long-term reliability.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Like most ceramics, silicon carbide is hard but brittle. This makes the elements susceptible to fracture if subjected to mechanical impact or improper handling and installation.
Care must be taken during installation and maintenance to avoid physical stress on the elements.
The Aging Effect: A Gradual Increase in Resistance
Over its operational life, a silicon carbide element's electrical resistance will gradually increase. This phenomenon is known as aging.
This change is predictable but must be managed. It often requires a power supply system (typically using transformers or thyristors) that can increase voltage over time to maintain the desired power output and temperature.
Oxidation and Atmosphere Sensitivity
While SiC is resistant to oxidation, its performance and lifespan can be affected by the furnace atmosphere. Certain reactive gases can accelerate the aging process or cause premature failure.
The protective silicon dioxide (SiO₂) layer that forms on the element's surface is key to its longevity, but this layer can be compromised in specific chemical environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element depends entirely on your primary process requirements. Use these properties as a guide to determine if the SC Type is the right fit.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating over large areas: The SC Type's Single Spiral design is engineered specifically for this and is an ideal choice for large chamber furnaces.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling or a mechanically harsh environment: You must account for the element's brittleness and design a robust mounting system to prevent mechanical shock.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational consistency: Plan for the element's natural aging by incorporating a variable voltage power supply to maintain stable heat output over its lifespan.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is about aligning the component's inherent properties with the critical demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Design | Single Spiral configuration for optimized heat distribution |
| Material | Silicon Carbide (SiC) with high melting point and thermal conductivity |
| Temperature Uniformity | Exceptional consistency across large surface areas |
| Electrical Properties | High resistance for efficient resistive (Joule) heating |
| Thermal Stability | Resistant to deformation and thermal shock at high temperatures |
| Limitations | Brittleness, aging (resistance increase), and sensitivity to certain atmospheres |
Upgrade your furnace performance with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable, uniform heating and long-term efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our SC Type SiC heating elements can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















