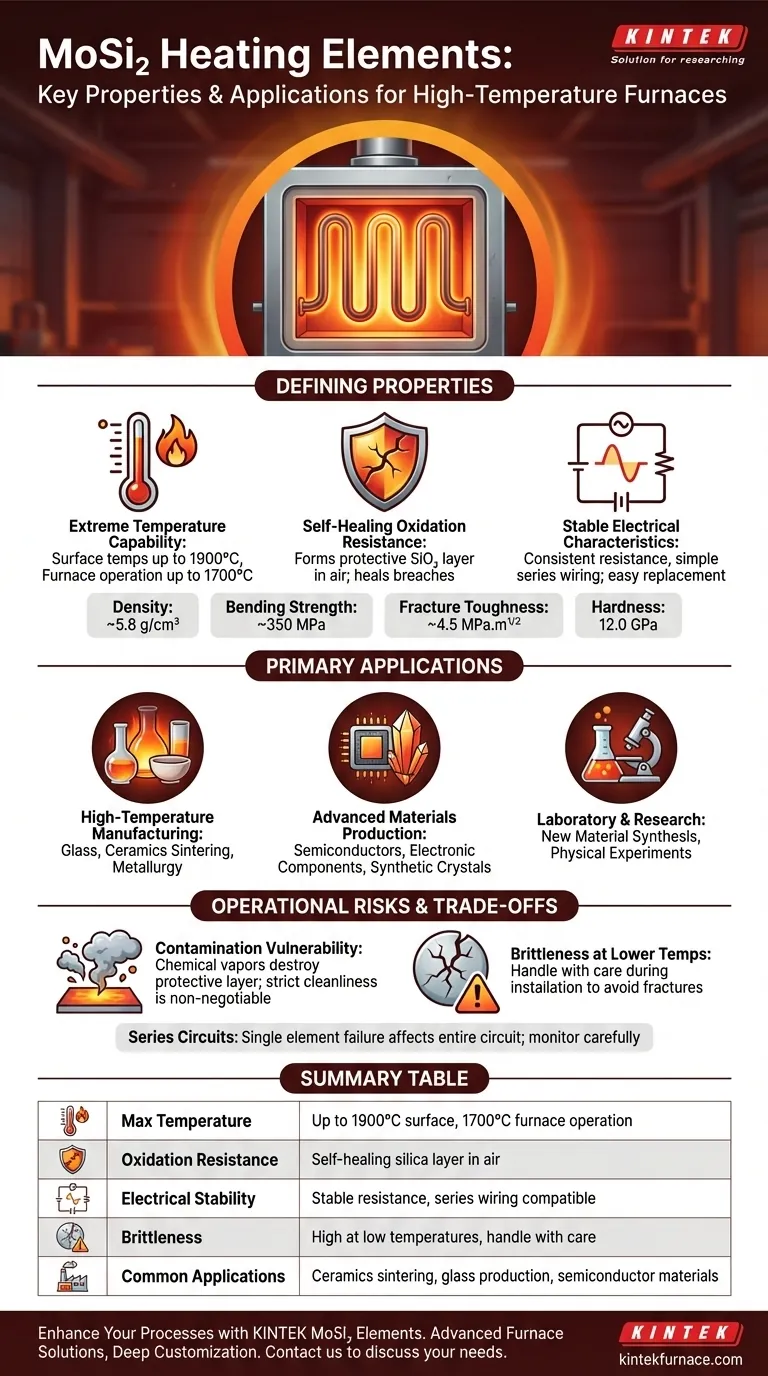
At their core, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements are specialized components designed for electric furnaces operating at extreme temperatures. Their defining feature is exceptional oxidation resistance, allowing them to function reliably in air at temperatures up to 1700°C and even higher, making them essential for processes like ceramics sintering, glass production, and advanced materials research.
The unparalleled high-temperature performance of MoSi₂ elements stems from a protective, self-healing layer of silica glass that forms on their surface. However, this same mechanism makes them highly vulnerable to contamination, meaning their longevity is dictated as much by furnace maintenance as by their inherent properties.
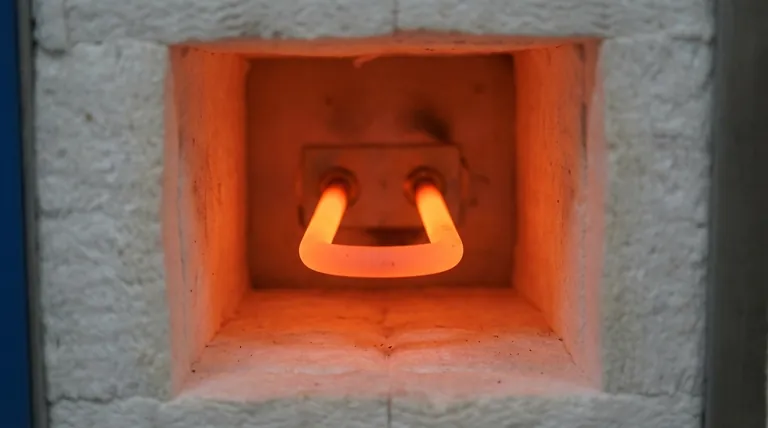

The Defining Properties of MoSi₂
MoSi₂ elements are not a universal solution; they are chosen for specific characteristics that are mission-critical in certain high-temperature environments.
Extreme Temperature Capability
These elements can achieve very high surface temperatures, often between 1800°C and 1900°C. This allows the furnace chamber itself to reliably maintain operating temperatures in the 1600°C to 1700°C range, a feat few other electric elements can sustain.
The Self-Healing Oxidation Resistance
When heated in an oxygen-containing atmosphere, a thin, non-porous layer of glassy silica (SiO₂) forms on the element's surface. This passive layer prevents the underlying material from further oxidation. If the layer is scratched or damaged, the exposed MoSi₂ will simply form new silica to "heal" the breach, granting the element a long operational life.
Stable Electrical Characteristics
MoSi₂ elements possess stable electrical resistance over their lifespan, which simplifies power control system design. They are typically wired in a series circuit. A key advantage is that new elements can be connected in series with old ones without issue, making replacement straightforward.
Key Physical and Mechanical Data
The material itself has a distinct set of physical properties that influence its use.
- Density: ~5.8 g/cm³
- Bending Strength: ~350 MPa
- Fracture Toughness: ~4.5 MPa.m¹/²
- Hardness: 12.0 GPa (Knoop)
These figures indicate a hard but relatively brittle material, especially at lower temperatures.
Primary Applications in Industry and Research
The unique properties of MoSi₂ elements make them indispensable in several key sectors that rely on clean, high-heat processing.
High-Temperature Manufacturing
Industries like glass manufacturing, ceramics sintering, and metallurgy use MoSi₂-equipped furnaces for melting, annealing, and heat treatment. Their ability to provide sustained, uniform heat is critical for product quality.
Advanced Materials Production
The production of semiconductor materials, electronic components, and synthetic crystals often requires pristine, high-temperature environments free from the byproducts of combustion. MoSi₂ elements provide this clean electric heat reliably.
Laboratory and Research Settings
In research and development, furnaces with MoSi₂ elements are used for a wide range of applications, including new material synthesis and high-temperature physical experiments where precise temperature control is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Risks
Choosing MoSi₂ elements requires a clear understanding of their operational limitations. Ignoring these can lead to premature and costly failure.
The Critical Vulnerability to Contamination
This is the single most important risk factor. The protective silica layer can be aggressively attacked by certain chemical vapors. For example, using paints or colorants on zirconia without proper drying and ventilation can release compounds that destroy the element's surface, leading to rapid failure. Strict furnace maintenance and cleanliness are non-negotiable.
Brittleness at Lower Temperatures
Like many ceramics, MoSi₂ elements are brittle at room temperature. Care must be taken during installation and handling to avoid mechanical shock or stress, which can cause them to crack or fracture.
Implications of Series Circuits
While wiring elements in series simplifies the electrical design, the failure of a single element can break the entire circuit, shutting down the furnace. This necessitates careful monitoring and having replacement elements on hand.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use MoSi₂ should be based on a clear-eyed assessment of your process requirements against the element's inherent characteristics.
- If your primary focus is maximum operating temperature in a clean environment: MoSi₂ elements are an industry standard and one of the best choices available due to their self-healing properties.
- If your process involves materials that release volatile compounds: You must implement strict furnace burnout and ventilation protocols to protect the elements from chemical attack.
- If you require frequent thermal cycling from high to low temperatures: Be aware that this can introduce mechanical stress, and ensure the elements are properly supported within the furnace structure.
By understanding both their unique strengths and critical vulnerabilities, you can reliably harness the high-temperature capabilities of MoSi₂ elements for your specific goals.
Summary Table:
| Property/Application | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1900°C surface, 1700°C furnace operation |
| Oxidation Resistance | Self-healing silica layer in air |
| Electrical Stability | Stable resistance, series wiring compatible |
| Brittleness | High at low temperatures, handle with care |
| Common Applications | Ceramics sintering, glass production, semiconductor materials |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable MoSi2 heating elements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your laboratory or production line!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















