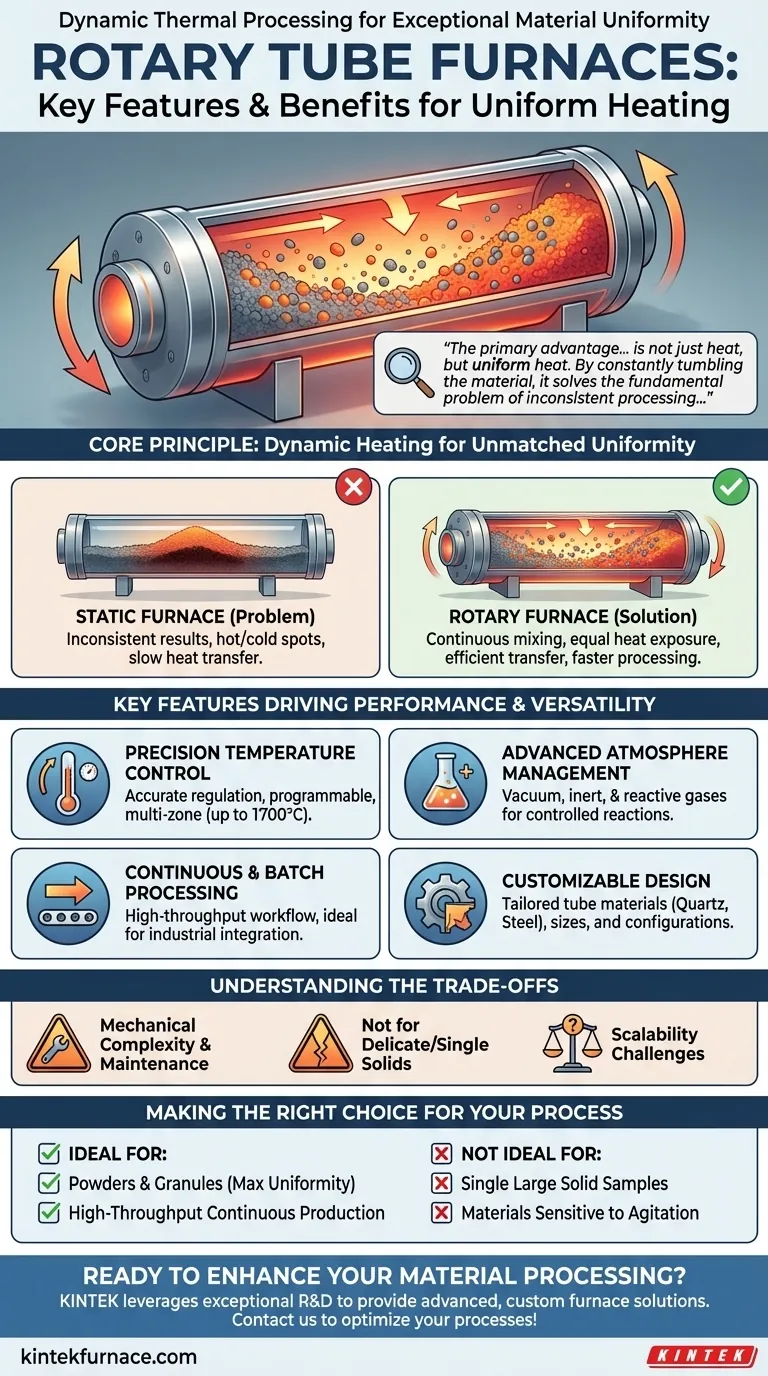
At its core, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized thermal processing instrument designed for exceptional material uniformity. Its defining feature is a cylindrical tube that rotates during operation, ensuring that the entire sample is heated evenly and efficiently. This dynamic heating method offers precise control over temperature and atmospheric conditions, making it ideal for continuous batch processing of powders, granules, and other loose materials.
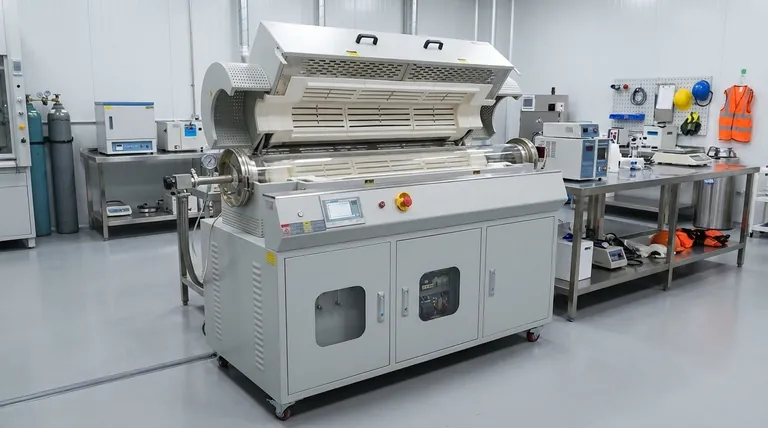
The primary advantage of a rotary tube furnace is not just heat, but uniform heat. By constantly tumbling the material, it solves the fundamental problem of inconsistent processing, ensuring every particle undergoes the same thermal treatment.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Heating for Unmatched Uniformity
The key difference between a rotary tube furnace and a static one is movement. This rotation is the foundation of its primary benefits.
How Rotation Solves the Static Heating Problem
In a stationary furnace, materials at the bottom and center of a sample may receive less heat than those on the top and sides, leading to inconsistent results.
A rotary furnace eliminates this issue. The gentle tumbling motion continuously mixes the material, exposing all particles to the heat source equally and preventing hot or cold spots.
The Impact on Heat Transfer Efficiency
This constant movement dramatically improves heat transfer. As new surfaces are constantly exposed to the furnace walls and atmosphere, the material reaches the target temperature more quickly and uniformly than in a static system.
This efficiency allows for shorter processing times and can lead to significant energy savings, especially in continuous industrial applications.
Key Features Driving Performance and Versatility
The performance of a rotary tube furnace stems from a combination of its dynamic design and advanced control systems.
Precision Temperature Control
These furnaces offer highly accurate temperature regulation, often with fully programmable digital controllers. Many models support multi-zone heating, allowing for tailored temperature profiles along the length of the tube.
Depending on the model and tube material, operating temperatures can range up to 1200°C for quartz tubes or exceed 1700°C for specialized ceramic tubes.
Advanced Atmosphere Management
Processing materials often requires a specific atmosphere. Rotary tube furnaces excel here, featuring sealed end caps that allow for operation under vacuum (down to 10⁻⁵ torr), with a flow of inert gas like argon, or even with reactive gases.
Integrated gas mixing systems can provide precise gas compositions, offering researchers and engineers enhanced control over the chemical reactions during processing.
Continuous and Batch Processing
The design is perfectly suited for continuous processing. Material can be fed into one end of the tilted, rotating tube and discharged at the other, creating a high-throughput workflow that minimizes manual handling. This makes them invaluable in production environments.
Customizable Design and Materials
Rotary tube furnaces are highly configurable. The work tube can be made from materials like quartz (for visibility and chemical purity at lower temperatures) or stainless steel (for durability). The size, heating elements, and control systems can all be tailored to specific application needs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary design introduces specific considerations that make it unsuitable for every application.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating mechanism, including seals and the drive motor, adds mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. These components require regular maintenance and can be potential points of failure over the system's lifetime.
Material Limitations
The tumbling action is a disadvantage for certain materials. It is not ideal for processing single large solid samples, delicate structures that could be damaged by mechanical agitation, or materials prone to sticking and clumping.
Process Scalability
While excellent for continuous flow, scaling a specific batch process can be complex. The dynamics of heat transfer and material flow can change with the diameter and length of the tube, requiring process re-validation when scaling up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace requires aligning the equipment's strengths with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granules with maximum uniformity: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice over static alternatives due to its dynamic mixing action.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous production: The design is ideal for integrating into an automated manufacturing line, reducing labor and improving efficiency.
- If you are working with single solid samples or materials sensitive to mechanical agitation: A simpler static tube furnace is a more appropriate and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding how the rotational movement fundamentally changes the heating process is the key to leveraging this technology effectively.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Ensures uniform heating and mixing of materials |
| Precision Temperature Control | Accurate regulation up to 1700°C with programmable settings |
| Advanced Atmosphere Management | Supports vacuum, inert, and reactive gases for controlled reactions |
| Continuous Processing | Enables high-throughput workflows for industrial applications |
| Customizable Design | Tailored tube materials (e.g., quartz, stainless steel) and configurations |
| Dynamic Heat Transfer | Reduces processing time and energy consumption |
Ready to enhance your material processing with uniform heating and high efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your lab. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary tube furnaces can optimize your processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















