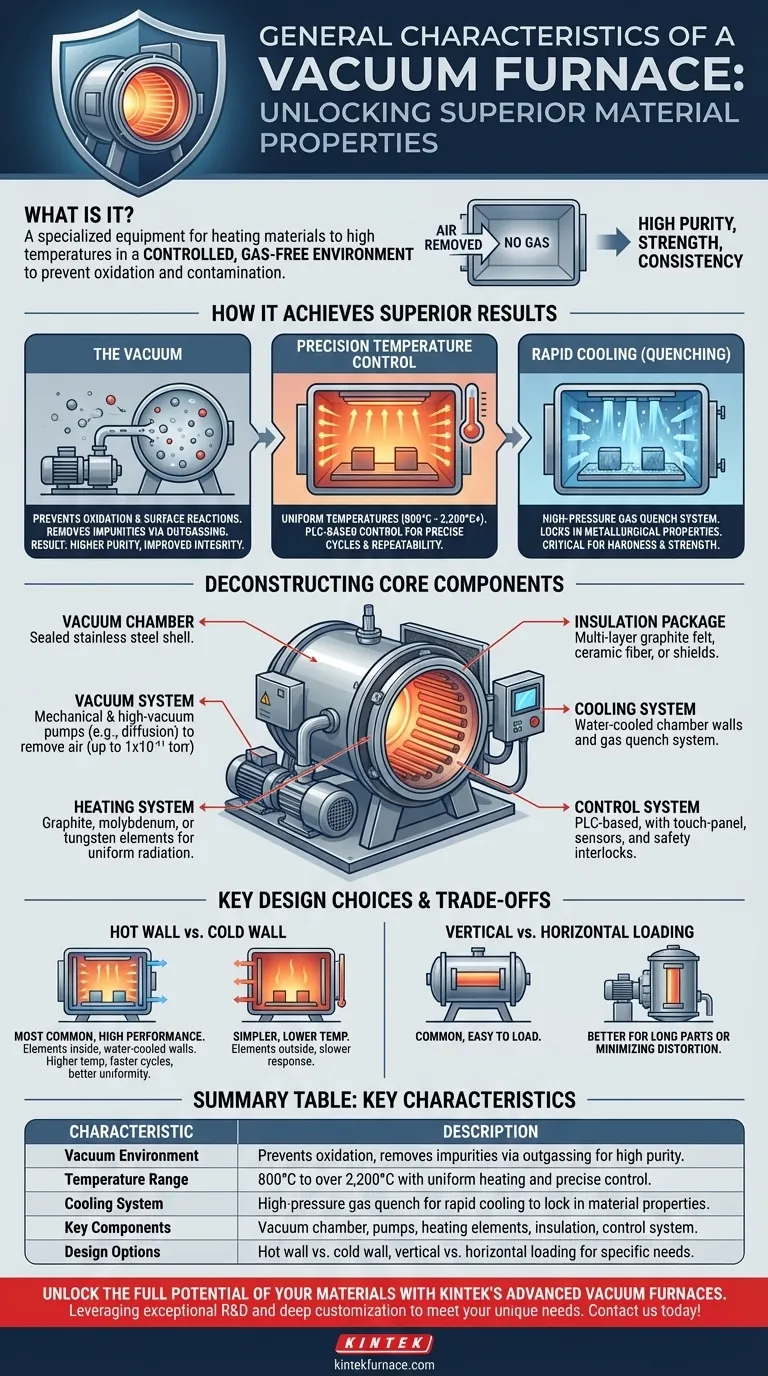
In essence, a vacuum furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed to heat materials to extremely high temperatures within a controlled, gas-free environment. Its primary purpose is to enable heat treatment processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering without the risk of oxidation or contamination that would occur in open air. This results in materials with superior purity, strength, and consistency.
The defining characteristic of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create a near-perfect vacuum before applying intense, uniform heat. This fundamental capability prevents unwanted chemical reactions, removes impurities, and allows for precise control over the final material properties.

How a Vacuum Furnace Achieves Superior Results
The unique environment inside a vacuum furnace unlocks material properties that are impossible to achieve with conventional atmospheric furnaces. This is accomplished through the interplay of vacuum, temperature, and controlled cooling.
The Role of the Vacuum
By removing air and other gases, the vacuum system serves two critical functions. First, it prevents oxidation and other unwanted surface reactions that can weaken or contaminate the material.
Second, the vacuum actively pulls volatile impurities and by-products out of the material as it is heated, a process known as outgassing. This results in a final product with significantly higher purity and improved structural integrity.
Precision Temperature Control
Vacuum furnaces operate at extremely high and uniform temperatures, often ranging from 800°C to over 2,200°C (1,500°F to 4,000°F).
Modern PLC-based control systems allow for programmable heating cycles with precise ramps (rate of temperature increase) and soaks (holding at a specific temperature). This ensures that every part in a batch, and every subsequent batch, receives the exact same thermal treatment for unmatched repeatability.
The Importance of Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
After the heating cycle, the material must be cooled in a controlled manner to lock in the desired metallurgical properties.
Vacuum furnaces use a high-pressure gas quench system, rapidly introducing an inert gas like nitrogen or argon into the chamber. This quick cooling process is critical for achieving specific hardness and strength characteristics in metals and alloys.
Deconstructing the Core Components
A vacuum furnace is a complex system where several key components work in concert to create the ideal processing environment.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the sealed furnace shell or body, typically constructed from stainless steel. It is designed to withstand both extreme internal temperatures and the powerful external pressure of the atmosphere when a vacuum is pulled.
The Vacuum System
A multi-stage system of pumps, including mechanical pumps and high-vacuum pumps (like molecular or diffusion pumps), works to remove air and create the contamination-free environment. Vacuum levels can reach as low as 1x10⁻¹¹ torr.
The Heating System
Heating elements are made from materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten. These elements radiate heat uniformly throughout the chamber to ensure the workpiece is heated evenly.
The Insulation Package
To contain the intense heat and protect the chamber walls, a multi-layer insulation package is used. This is often made of graphite felt, ceramic fiber, or reflective metal shields made of molybdenum.
The Cooling System
The furnace chamber walls are almost always water-cooled to keep the vessel shell at a safe temperature. This system works alongside the internal gas quenching system used for cooling the processed material.
The Control System
This is the "brain" of the furnace. It consists of a touch-panel operator interface, a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), sensors like thermocouples, and safety interlocks. It automates the entire process from pump-down to heating, soaking, and quenching.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Design Choices
Not all vacuum furnaces are the same. The design is tailored to the specific application, involving critical trade-offs in performance, capability, and cost.
Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall Design
Cold wall furnaces are the most common type for high-performance applications. The heating elements are inside the vacuum chamber, and the chamber walls are water-cooled. This allows for higher operating temperatures, faster heating and cooling cycles, and better temperature uniformity.
Hot wall furnaces, where the heating elements are outside the vacuum retort, are simpler but are limited to lower temperatures and have slower response times.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Loading
The orientation of the furnace depends on the workpiece. Horizontal furnaces are common and easy to load. Vertical furnaces are better for long, cylindrical parts or to minimize distortion in sensitive components during heating.
Safety and Operational Considerations
These systems operate under extreme conditions and incorporate critical safety features. This includes automatic power shut-off when the door is opened and over-temperature controllers. A reliable cooling water supply is non-negotiable, and backup systems are often required to prevent catastrophic damage in case of a water pressure failure.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Understanding these characteristics allows you to determine if a vacuum furnace aligns with your specific manufacturing or research goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material purity and strength: A vacuum furnace is essential for preventing oxidation and removing contaminants that compromise material performance.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and precision: The computer-controlled heating and cooling profiles of a vacuum furnace ensure every batch meets identical, exacting standards.
- If your primary focus is processing high-performance alloys, ceramics, or composites: The extremely high and uniform temperatures achievable are often the only way to properly process these advanced materials.
By controlling the processing environment at a fundamental level, a vacuum furnace gives you unparalleled power to define the final quality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation, removes impurities via outgassing for high purity |
| Temperature Range | 800°C to over 2,200°C with uniform heating and precise control |
| Cooling System | High-pressure gas quench for rapid cooling to lock in material properties |
| Key Components | Vacuum chamber, pumps, heating elements, insulation, control system |
| Design Options | Hot wall vs. cold wall, vertical vs. horizontal loading for specific needs |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Materials with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're processing high-performance alloys, ceramics, or composites, our vacuum furnaces deliver superior purity, strength, and repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and elevate your research or manufacturing processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















