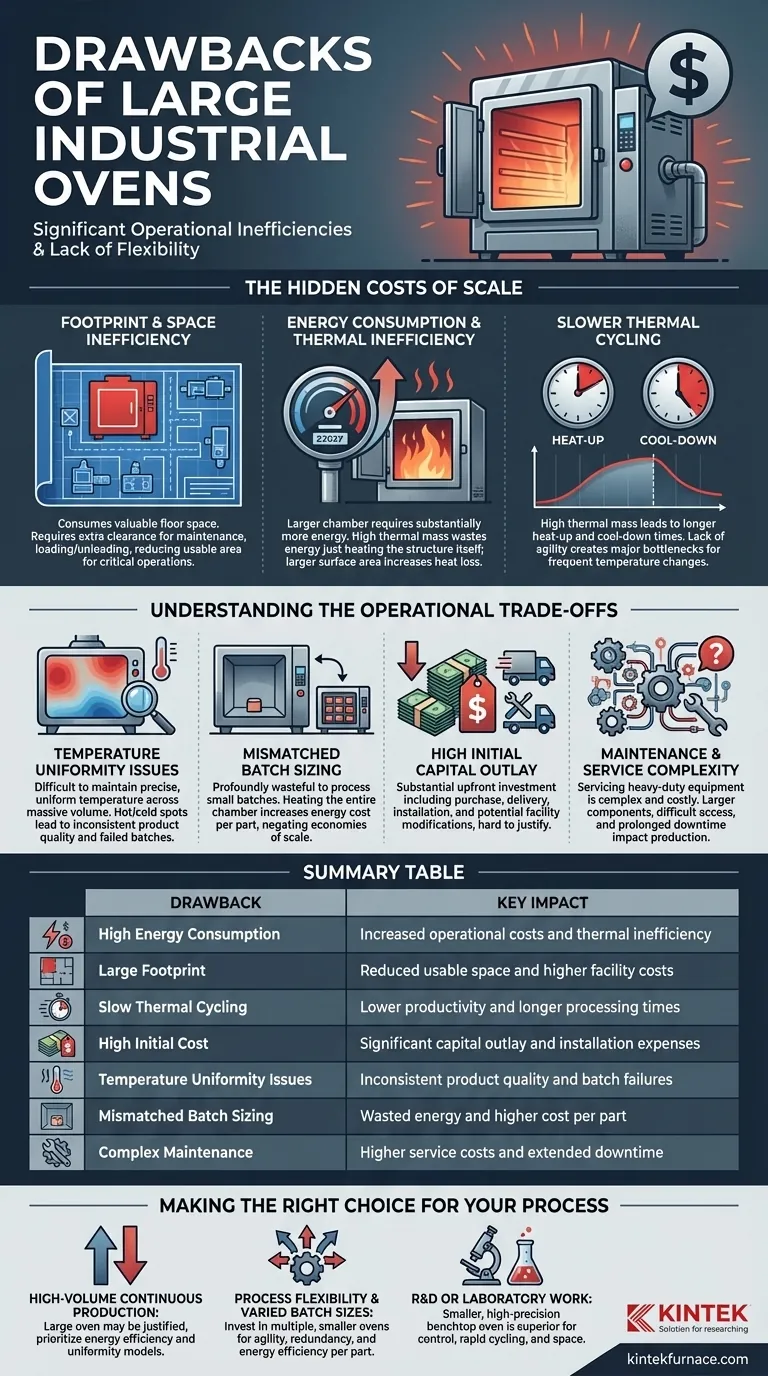
While seemingly powerful, a large industrial oven's primary drawbacks center on significant operational inefficiencies and a lack of flexibility. Their substantial physical footprint and high energy consumption are the most immediate concerns, but these surface-level issues point to deeper challenges in cost, workflow integration, and process control that can negatively impact a facility's bottom line.
The core issue is not the size itself, but the potential for a fundamental mismatch between the oven's capabilities and your actual production needs. An oversized oven introduces systemic waste in space, energy, and time, making it a liability for any process that isn't consistently running at maximum capacity.

The Hidden Costs of Scale
Choosing a large oven involves more than just allocating floor space. The decision carries long-term financial and operational implications that are often underestimated during initial procurement.
Footprint and Space Inefficiency
A large industrial oven consumes a significant amount of valuable floor space. In a busy production facility or a constrained laboratory, this space comes at a premium.
This isn't just about the physical footprint of the machine itself. You must also account for necessary clearance for maintenance access, loading/unloading zones, and ventilation, further reducing the usable area for other critical operations.
Energy Consumption and Thermal Inefficiency
The most significant operational drawback is energy consumption. A larger chamber volume requires substantially more energy to heat and maintain temperature.
This inefficiency is rooted in two principles. First, the oven's greater thermal mass (the amount of energy its own structure absorbs) means more energy is wasted just heating the oven itself. Second, its larger surface area provides more opportunity for heat to escape into the surrounding environment.
Slower Thermal Cycling
The same thermal mass that increases energy use also results in much longer heat-up and cool-down times.
This lack of agility directly impacts productivity. If your process requires frequent temperature changes or involves running multiple different batches per day, the time spent waiting for the oven to reach its setpoint or become safe to open becomes a major bottleneck.
Higher Initial Capital Outlay
Beyond the operational costs, the upfront investment for a large industrial oven is substantial. The purchase price, delivery, and installation—which may require facility modifications—all contribute to a high initial capital expenditure that can be difficult to justify.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The decision to use a large oven forces a series of compromises that can affect product quality and overall operational agility. Understanding these trade-offs is critical.
The Challenge of Temperature Uniformity
Achieving and maintaining a precise, uniform temperature across a massive internal volume is a significant engineering challenge.
Hot and cold spots can develop, leading to inconsistent product quality. For sensitive processes like curing, annealing, or sterilizing, a lack of temperature uniformity can result in failed batches and wasted materials.
Mismatched Batch Sizing
A large oven is only efficient when it is fully loaded. Using a large oven to process a small batch is profoundly wasteful.
You pay to heat the entire chamber volume, regardless of the load size. This common scenario dramatically increases the energy cost per part and negates any potential economies of scale, much like using a city bus to transport a single passenger.
Maintenance and Service Complexity
Servicing a large, heavy-duty piece of equipment is inherently more complex and costly.
Components are larger, access can be more difficult, and downtime often has a greater impact on production schedules. Finding technicians qualified to service specialized, large-scale systems can also be a challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To avoid these drawbacks, the selection process must be driven by a realistic assessment of your specific operational needs, not just your maximum potential capacity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of a single product: A large oven may be justified, but you must prioritize models designed for energy efficiency and proven temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and varied batch sizes: Investing in multiple, smaller ovens provides far greater agility, redundancy, and energy efficiency per part.
- If your primary focus is R&D or laboratory work: A smaller, high-precision benchtop or cabinet oven is almost always the superior choice for its precise control, rapid cycling, and efficient use of space.
Ultimately, the optimal choice is the one that aligns most closely with your daily operational reality, not your theoretical maximum.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Energy Consumption | Increased operational costs and thermal inefficiency |
| Large Footprint | Reduced usable space and higher facility costs |
| Slow Thermal Cycling | Lower productivity and longer processing times |
| High Initial Cost | Significant capital outlay and installation expenses |
| Temperature Uniformity Issues | Inconsistent product quality and batch failures |
| Mismatched Batch Sizing | Wasted energy and higher cost per part |
| Complex Maintenance | Higher service costs and extended downtime |
Struggling with oven inefficiencies? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to eliminate drawbacks like high energy use and poor flexibility. Enhance your lab's efficiency and reduce costs—contact us today for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















