The primary cost disadvantages of a vacuum furnace are its high initial equipment price and significant ongoing expenses for maintenance and supporting infrastructure. Unlike conventional furnaces, the complexity of creating and maintaining a vacuum environment introduces substantial costs that extend far beyond the initial purchase.
The true financial drawback of a vacuum furnace is not just its high sticker price, but its total cost of ownership. This includes the initial capital outlay for the furnace and its essential support systems, compounded by specialized, often expensive, operational and maintenance requirements.

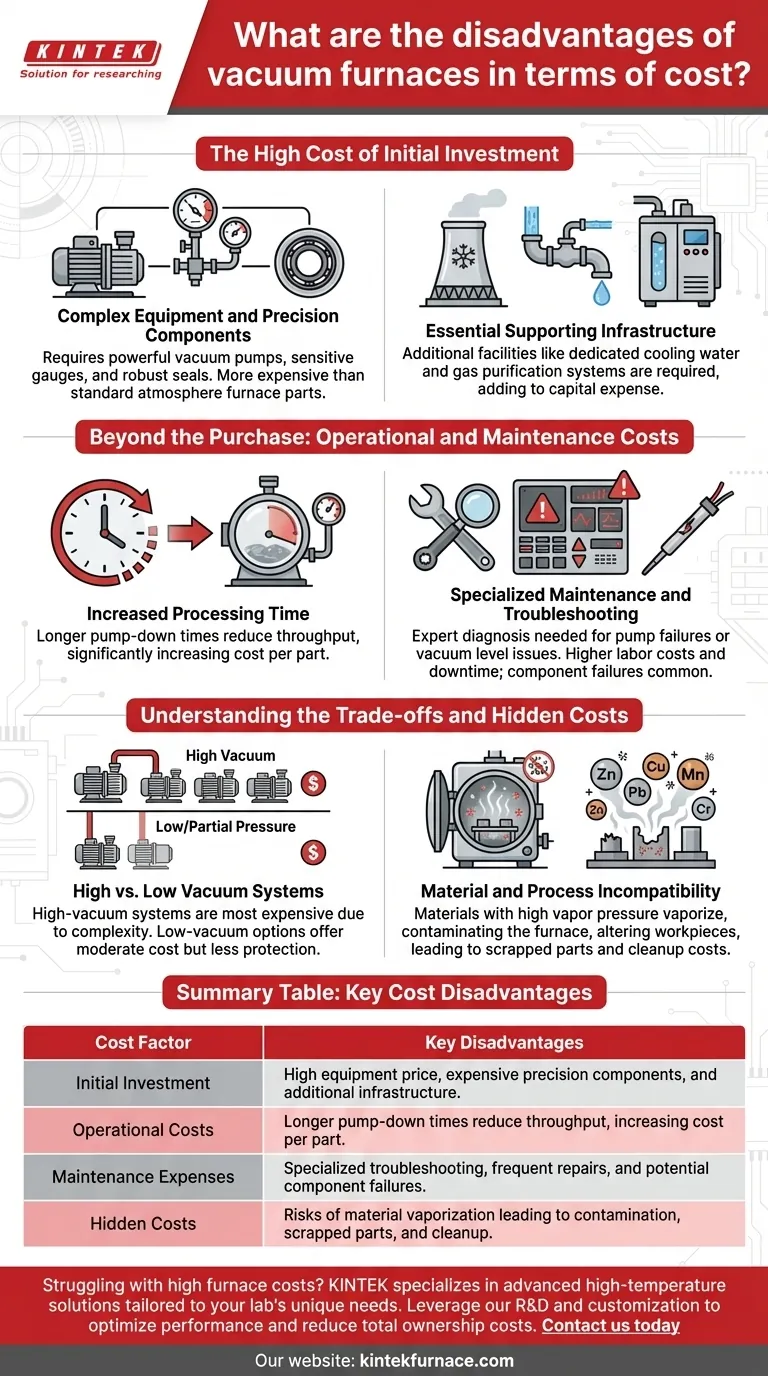
The High Cost of Initial Investment
The upfront cost of a vacuum furnace is a major barrier, driven by the need for sophisticated engineering and components to achieve a controlled, air-free environment.
Complex Equipment and Precision Components
A vacuum furnace is not a simple insulated box. It requires a complex system of high-precision components, including powerful vacuum pumps, sensitive gauges, and robust, high-integrity seals.
These components must meet stringent manufacturing requirements to create and hold a high-purity vacuum, making them inherently more expensive than parts for a standard atmosphere furnace.
Essential Supporting Infrastructure
The investment does not end with the furnace itself. You must also budget for additional supporting facilities that are critical for operation.
This often includes dedicated cooling water systems to manage the intense heat and may involve gas purification systems for processes that require high-purity backfilling. These systems represent a significant additional capital expense.
Beyond the Purchase: Operational and Maintenance Costs
The financial demands of a vacuum furnace continue long after installation. Its operational and maintenance profile is more complex and costly than that of simpler furnace types.
Increased Processing Time
Achieving the required vacuum level takes time. The longer pump-down times inherent to vacuum furnace operation can reduce overall throughput compared to atmosphere furnaces.
This lower cycle rate means the cost per part processed can be significantly higher, impacting the economic viability for high-volume production of standard components.
Specialized Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining a vacuum furnace is a specialized task. The stringent vacuum requirements mean that any issue, from pump failures to vacuum level inconsistencies, requires expert diagnosis.
Troubleshooting these systems is more complex and time-consuming, often leading to higher labor costs and extended downtime. Components like thermocouples can also fail due to material outgassing, adding to repair frequency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Hidden Costs
The decision to invest in a vacuum furnace involves weighing its high cost against its unique capabilities. However, there are critical limitations that can act as hidden financial penalties if ignored.
High vs. Low Vacuum Systems
Not all vacuum furnaces are the same. High-vacuum furnaces command the highest costs for both initial equipment and ongoing maintenance due to their complexity.
In contrast, low-vacuum or partial-pressure systems offer a more moderate cost profile but provide less protection against oxidation and are unsuitable for the most sensitive materials.
Material and Process Incompatibility
One of the most significant hidden costs is process failure due to material incompatibility. Vacuum furnaces are unsuitable for processing materials with high saturated vapor pressure at heating temperatures.
Elements like zinc, lead, copper, manganese, and chromium can vaporize in a vacuum, contaminating the furnace interior and altering the surface properties of the workpiece. This can lead to scrapped parts, costly furnace cleanup, and significant financial losses.
Making a Financially Sound Decision
To determine if a vacuum furnace is the right investment, you must align its cost profile with your specific processing goals and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital outlay: A conventional atmosphere furnace or a low-vacuum system may be more appropriate, provided your materials are not highly sensitive to oxidation.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals or high-performance superalloys: The high cost of a high-vacuum furnace is a necessary investment to prevent contamination and achieve the required material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of standard materials: The longer cycle times and higher operational costs of a vacuum furnace may make it a less cost-effective choice than faster, simpler alternatives.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is a strategic investment that is justified only when its unique processing capabilities are essential for achieving your final product's quality and performance standards.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Key Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High equipment price, expensive precision components, and additional infrastructure like cooling systems. |
| Operational Costs | Longer pump-down times reduce throughput, increasing cost per part. |
| Maintenance Expenses | Specialized troubleshooting, frequent repairs, and potential for component failures due to material incompatibility. |
| Hidden Costs | Risks of material vaporization leading to contamination, scrapped parts, and cleanup expenses. |
Struggling with high furnace costs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored to your lab's unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to optimize performance and reduce total ownership costs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your efficiency and budget!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















