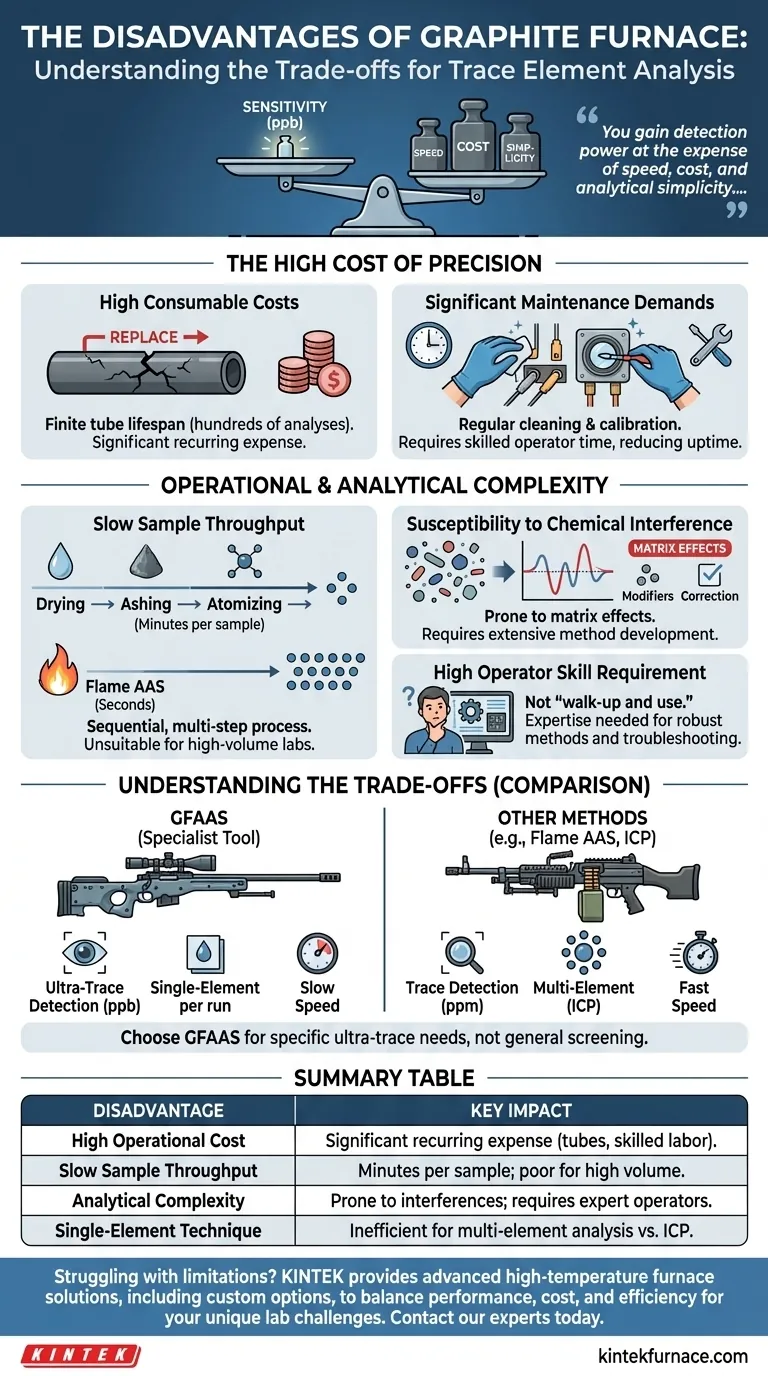
The primary disadvantages of a graphite furnace are its significant operational costs, slow sample throughput, and the technical complexity required to achieve accurate results. While it offers exceptional detection limits, these drawbacks make it a specialized tool rather than a general-purpose instrument.
While offering unparalleled sensitivity for trace element analysis, a graphite furnace imposes a clear trade-off. You gain detection power at the expense of speed, cost, and analytical simplicity, making it ideal for specific applications but impractical for others.

The High Cost of Precision
The primary barrier for many labs considering Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS) is financial. The costs are not limited to the initial purchase but are a persistent operational factor.
High Consumable Costs
A core component, the graphite tube, is a consumable with a finite lifespan. Each time the furnace heats and cools, the graphite degrades slightly.
A single tube may last for only a few hundred analyses, depending on the sample matrix and temperature program. This constant replacement cycle represents a significant and recurring operational expense.
Significant Maintenance Demands
Beyond tube replacement, the furnace requires regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent contamination and ensure performance. The auto-sampler, furnace contacts, and optical windows must be kept in pristine condition.
This maintenance requires skilled operator time and adds to the overall cost of ownership, reducing instrument uptime compared to less complex methods.
Operational and Analytical Complexity
Operating a graphite furnace effectively is more of a technical craft than a routine procedure. It demands a deeper understanding of analytical chemistry compared to other techniques.
Slow Sample Throughput
GFAAS is a sequential technique. Each sample is individually pipetted into the furnace and run through a multi-step temperature program (drying, ashing, atomization, cleaning) that can take several minutes.
This stands in stark contrast to techniques like Flame AAS or ICP, which can analyze samples in seconds. This makes GFAAS unsuitable for high-throughput environments where hundreds of samples must be processed daily.
Susceptibility to Chemical Interference
The sample is atomized from a solid surface within a small, enclosed space. This environment is highly prone to matrix interferences, where other components in the sample affect the signal of the element being measured.
Overcoming these interferences requires extensive method development, the use of chemical modifiers, and advanced background correction systems, adding layers of complexity to the analysis.
High Operator Skill Requirement
Achieving accurate and repeatable results with GFAAS is highly dependent on the operator. Developing a robust temperature program and diagnosing interference problems requires significant expertise and experience.
This is not a "walk-up and use" instrument. A poorly trained operator can easily produce inaccurate data due to unnoticed interferences or improper setup.
Understanding the Trade-offs: GFAAS vs. Other Methods
The disadvantages of a graphite furnace are best understood by comparing it to alternative elemental analysis techniques. It is a specialist's tool, not a universal solution.
GFAAS vs. Flame AAS
Think of GFAAS as a sniper rifle and Flame AAS as a machine gun. GFAAS offers incredible precision and sensitivity, capable of detecting elements at parts-per-billion (ppb) levels. Flame AAS is faster and more rugged but is typically limited to parts-per-million (ppm) levels.
If you need speed and are measuring higher concentrations, Flame AAS is superior. If you need to detect ultra-trace amounts of an element, GFAAS is necessary despite its slowness.
GFAAS vs. ICP-MS/OES
ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) techniques excel at multi-element analysis. They can measure dozens of elements simultaneously from a single sample run, making them ideal for surveys or analyzing complex materials.
GFAAS, by contrast, is almost exclusively a single-element technique. Changing the element requires changing the lamp and reloading methods, making it highly inefficient for determining the composition of an unknown sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct analytical technique requires a clear understanding of your primary objective. The disadvantages of the graphite furnace are only disadvantages if they do not align with your goal.
- If your primary focus is ultra-trace detection of one or two specific elements: GFAAS is often the most cost-effective and powerful tool for the job, provided you can accept the low throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening of many samples for elements in the ppm range: Flame AAS is a far more practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is a comprehensive elemental survey or multi-element quantification: An ICP-OES or ICP-MS system is the undisputed choice, as GFAAS is fundamentally unsuited for this task.
Understanding these inherent limitations empowers you to deploy the graphite furnace for its intended purpose: achieving exceptional sensitivity when it is truly required.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Operational Cost | Significant recurring expense from graphite tube replacement and skilled maintenance. |
| Slow Sample Throughput | Sequential analysis takes minutes per sample, unsuitable for high-volume labs. |
| Analytical Complexity | Prone to matrix interferences; requires expert operators for accurate results. |
| Single-Element Technique | Inefficient for multi-element analysis compared to ICP-OES/MS. |
Struggling with the limitations of your current furnace system? KINTEK understands that every laboratory has unique challenges and throughput requirements. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Let's discuss a furnace solution that balances performance, cost, and efficiency for your lab. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















