In short, the primary disadvantages of electric kilns are their typically slower firing cycles, a lower maximum temperature compared to gas kilns, and a clean, oxygen-rich environment that prevents the unique glaze effects possible with fuel-burning kilns. These factors can limit the types of clay bodies and glaze finishes a ceramic artist can achieve.
While prized for their consistency and ease of use, electric kilns lack the high-temperature capabilities and atmospheric control of gas kilns. This makes them less suitable for artists who rely on the unique, often unpredictable results of high-fire reduction techniques.

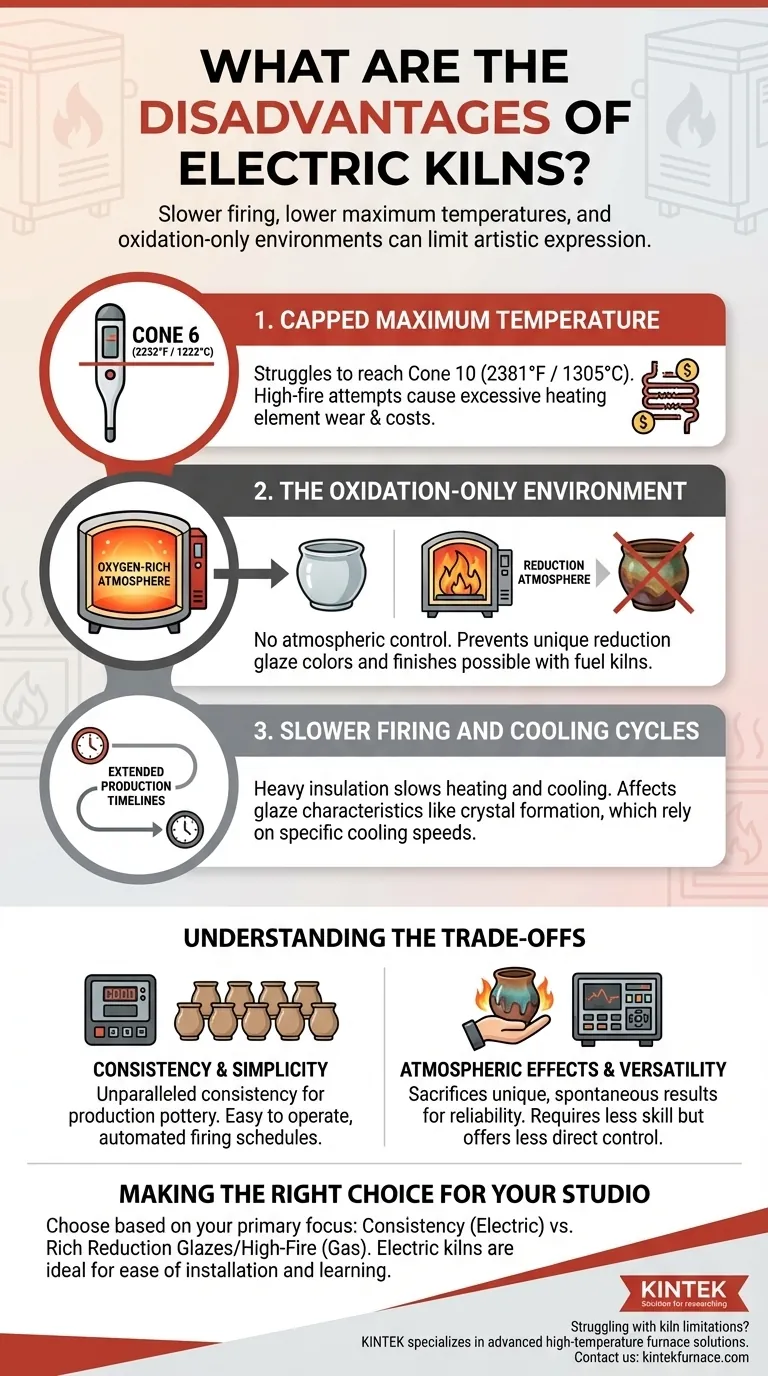
The Core Limitations of Electric Firing
To understand if an electric kiln is right for you, we must look beyond its convenience and examine its inherent operational constraints. These limitations directly impact the final look and feel of your ceramic work.
Capped Maximum Temperature
Most standard electric kilns are designed for low-fire and mid-fire ranges, comfortably reaching temperatures for Cone 6 (about 2232°F / 1222°C).
However, many struggle to reliably reach or sustain the higher temperatures required for Cone 10 stoneware or porcelain (about 2381°F / 1305°C). Pushing an electric kiln to its absolute limit repeatedly can cause excessive wear on its heating elements, leading to more frequent and costly replacements.
The Oxidation-Only Environment
Electric kilns heat by passing electricity through coiled elements. This process creates a very clean, oxygen-rich environment inside the kiln, known as an oxidation atmosphere.
This is a significant disadvantage if you want to achieve "reduction" effects. In a gas kiln, you can starve the flame of oxygen, forcing it to pull oxygen molecules from the clay body and glazes. This reduction atmosphere creates rich, earthy, and often unpredictable colors that are impossible to replicate in the sterile environment of an electric kiln.
Slower Firing and Cooling Cycles
The heavy insulation that makes electric kilns energy-efficient also means they heat up and, more importantly, cool down slowly.
While a controlled cooling cycle can be beneficial, an inherently slow process can extend production timelines. More critically, it can affect certain glaze characteristics, like crystal formation, that rely on specific cooling speeds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a kiln is not about finding a "perfect" option, but about aligning the tool's characteristics with your artistic goals. The disadvantages of an electric kiln are balanced by significant advantages in other areas.
Consistency vs. Atmospheric Effects
An electric kiln with a digital controller offers unparalleled consistency and predictability. You can run the same firing program repeatedly and achieve nearly identical results, which is ideal for production pottery.
The trade-off is the loss of the spontaneous and unique effects that come from the flame paths and atmospheric variations in a gas or wood kiln. You sacrifice serendipity for reliability.
Operating Costs and Infrastructure
While electricity prices can make firing costs higher than gas in some regions, this is not the full picture. Electric kilns have a much lower upfront infrastructure cost.
They do not require the complex venting, dedicated gas lines, and larger safety clearances that a gas kiln demands. This makes them far easier and cheaper to install, especially in a home studio or small-scale setting.
Simplicity vs. Versatility
Electric kilns are exceptionally easy to operate. Modern digital controllers automate the entire firing schedule, making them accessible to beginners and ideal for educational settings.
This simplicity comes at the cost of versatility. A gas kiln requires more skill to fire correctly, but it grants the user direct control over the kiln's atmosphere, unlocking a far wider palette of glaze possibilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Studio
Your decision must be guided by the type of work you want to create. There is no single best kiln, only the best kiln for your specific purpose.
- If your primary focus is consistency for functional mid-fire pottery: The reliability, ease of use, and predictable results of an electric kiln make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving rich, complex reduction glazes or high-fire porcelain: A gas kiln is essential to create the necessary high temperatures and atmospheric conditions.
- If your primary focus is ease of installation and learning ceramics: An electric kiln's simplicity and lower setup requirements make it the most practical and accessible starting point.
Understanding these fundamental differences ensures you choose a kiln that empowers your artistic vision, not one that restricts it.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Ceramics |
|---|---|
| Capped Maximum Temperature | Limits high-fire work like Cone 10 stoneware, risking element wear |
| Oxidation-Only Environment | Prevents reduction effects, restricting glaze colors and finishes |
| Slower Firing and Cooling Cycles | Extends production time and affects glaze characteristics like crystal formation |
Struggling with kiln limitations for your ceramics? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet unique experimental requirements. Enhance your studio's capabilities—contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained



















