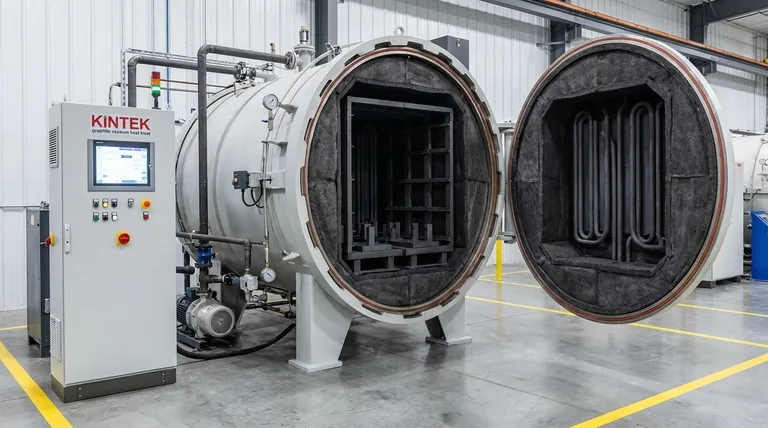
In short, graphite is used extensively in vacuum furnaces for heating elements, thermal insulation, and structural components like fixtures, tooling, and retorts. Its unique ability to maintain strength and stability at extreme temperatures up to 3000°C in an inert atmosphere makes it the material of choice for these demanding applications.
Graphite is not simply a convenient material for high-temperature work; it is the foundational element that enables the precise, controlled environment of a modern vacuum furnace. Its selection is driven by a unique combination of extreme thermal resistance, chemical stability, and excellent machinability.

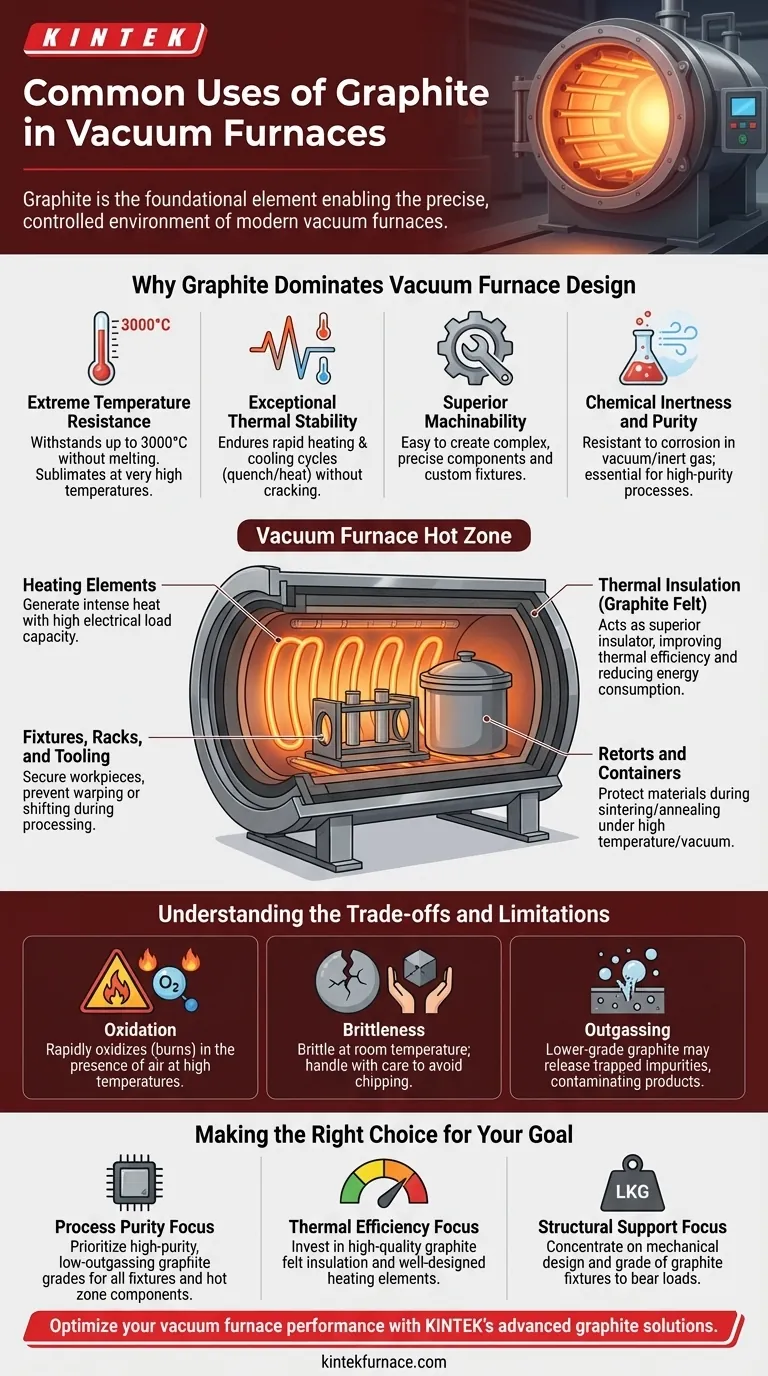
Why Graphite Dominates Vacuum Furnace Design
A vacuum furnace creates an environment free of oxygen and other reactive gases, allowing materials to be processed at extreme temperatures without contamination or oxidation. Graphite's properties are uniquely suited to creating and maintaining this specialized environment.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Graphite's primary advantage is its ability to withstand temperatures up to 3000°C in a vacuum or inert gas. Unlike refractory metals, it does not melt but instead sublimates at very high temperatures, maintaining its structural integrity far beyond the limits of most other materials.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Graphite exhibits outstanding resistance to thermal shock. It can endure rapid heating and cooling cycles (quench and heat) without cracking or failing, a critical requirement for the operational cycles of heat treating and brazing furnaces.
Superior Machinability
Despite its strength at high temperatures, graphite is relatively soft and easy to machine. This allows for the creation of complex and precise components, from intricate heating elements to custom-designed fixtures for holding workpieces.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
Graphite is naturally resistant to corrosion from acids and alkalis. In a vacuum, it provides a clean, stable environment, which is essential for high-purity processes found in the aeronautics, electronics, and semiconductor industries.
Key Graphite Components in a Vacuum Furnace
Graphite is not used for just one purpose but forms a complete system within the furnace's "hot zone."
Heating Elements
Graphite heating elements are responsible for generating the intense heat required for furnace operations. Its large radiation area and ability to handle high electrical loads make it an efficient and reliable heat source.
Thermal Insulation (Graphite Felt)
The hot zone is lined with layers of graphite felt. This lightweight, strong material acts as a superior insulator, containing the extreme heat, improving thermal efficiency, and reducing energy consumption.
Fixtures, Racks, and Tooling
To hold workpieces securely in place during a process, furnaces use graphite fixtures, racks, and tooling. These are custom-machined to support parts during heat treating or brazing, ensuring they do not warp or shift.
Retorts and Containers
For processes like sintering or annealing, powdered metals or other materials are often held in graphite retorts. These lidded containers can withstand the high temperatures and vacuum conditions while protecting the material being processed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While invaluable, graphite is not without its operational considerations. Understanding these is key to its successful application.
Oxidation in the Presence of Air
Graphite's high-temperature capabilities are entirely dependent on a vacuum or inert gas environment. If exposed to oxygen at high temperatures, it will rapidly oxidize (burn), leading to component failure.
Brittleness and Handling
At room temperature, graphite can be brittle and must be handled with care to avoid chipping or cracking. Its strength is most apparent under high-heat conditions.
Outgassing and Material Purity
Different grades of graphite have varying levels of purity. For ultra-sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing, using a lower-grade graphite can lead to "outgassing"—the release of trapped impurities that can contaminate the product. Selecting the correct grade is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific type and application of graphite should align directly with your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is process purity (e.g., semiconductors, medical implants): Prioritize the use of high-purity, low-outgassing graphite grades for all fixtures and hot zone components to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is thermal efficiency and cycle time: Invest in high-quality graphite felt insulation and a well-designed heating element system to minimize heat loss and ensure rapid, uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is structural support for heavy or complex parts: Concentrate on the mechanical design and grade of your graphite fixtures and tooling to ensure they can bear the load without failure at peak temperature.
Understanding graphite's role is fundamental to mastering high-temperature vacuum furnace operations.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Generate intense heat | High electrical load capacity, efficient radiation |
| Thermal Insulation (Graphite Felt) | Contain heat in the hot zone | Superior insulation, reduces energy consumption |
| Fixtures & Tooling | Hold workpieces during processing | Custom-machinable, maintains part integrity |
| Retorts & Containers | Protect materials during sintering/annealing | Withstands high temperatures and vacuum conditions |
Optimize your vacuum furnace performance with KINTEK's advanced graphite solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to their unique needs. Our product line—including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, and more—is complemented by deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in graphite components can enhance your process purity, thermal efficiency, and structural support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity



















