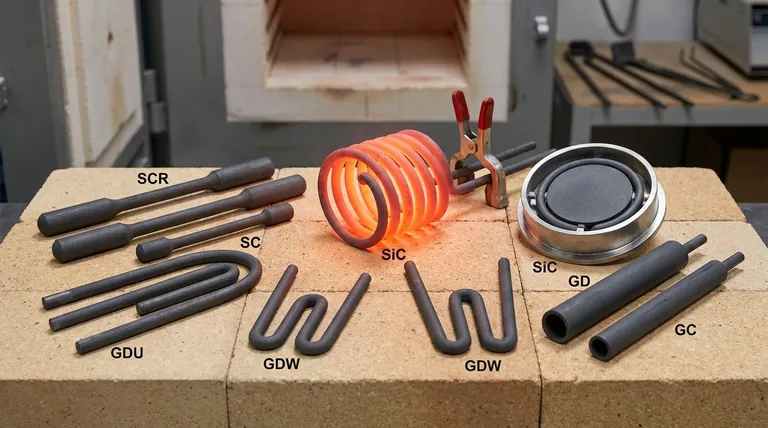
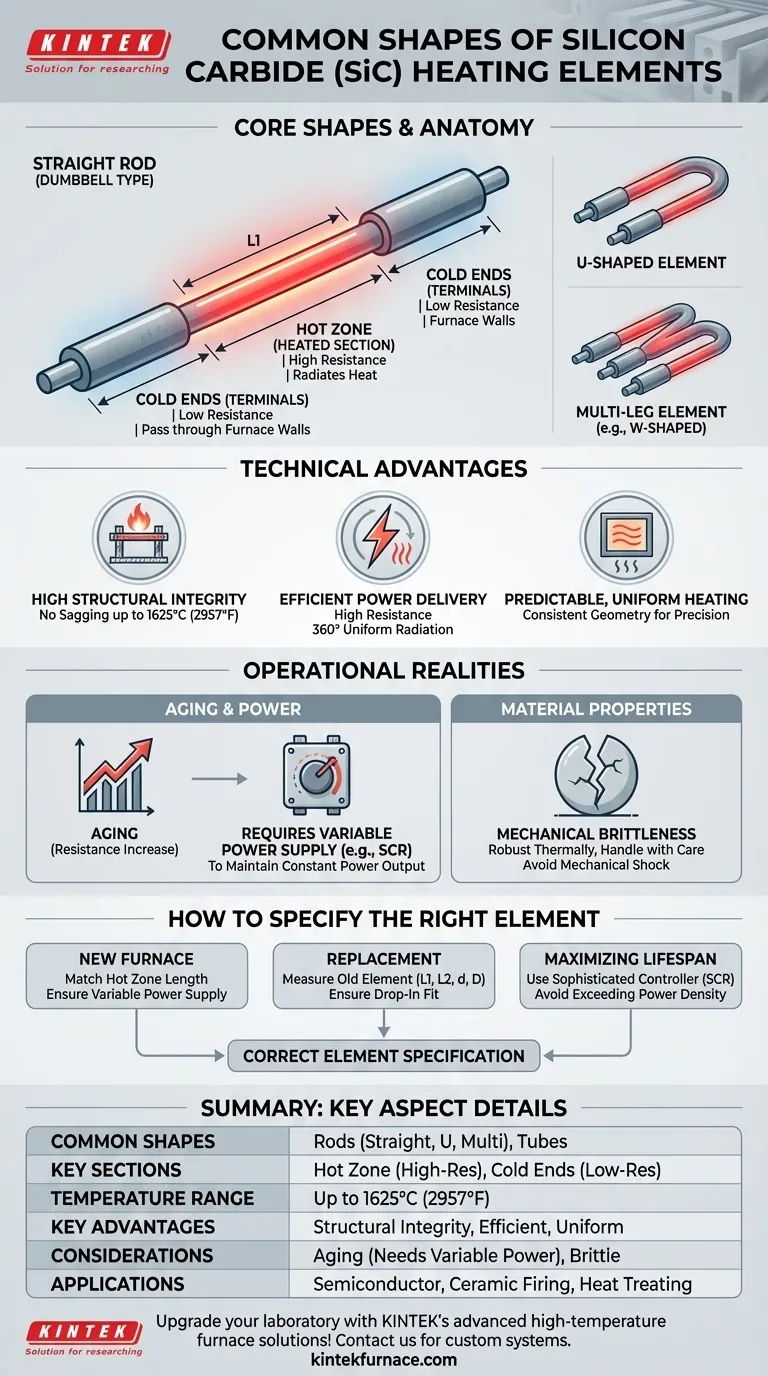
At their core, the most common shapes for silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are rods and tubes. These foundational shapes are typically configured with distinct sections for heating and electrical connection, often resulting in a "dumbbell" appearance with a thinner, high-resistance hot zone and thicker, low-resistance cold ends.
The specific shape of a silicon carbide element is less important than its fundamental design. The key is understanding how the standard rod-like structure is engineered with separate "hot" and "cold" zones to deliver heat efficiently inside a furnace while minimizing heat loss at the terminals.

The Anatomy of a SiC Element
While appearing simple, the cylindrical design of a SiC element is highly engineered for performance and longevity at extreme temperatures. It is not a uniform rod but a component with distinct functional sections.
The Hot Zone (Heated Section)
This is the central, working part of the element. It has a smaller diameter and higher electrical resistance, causing it to heat up intensely when current is applied. This is the section that resides inside the furnace chamber and radiates heat to the workload.
The Cold Ends (Terminals)
These are the thicker sections at each end of the element. They are manufactured to have significantly lower electrical resistance than the hot zone. This design ensures they remain relatively cool as they pass through the furnace's insulated walls to connect to the power supply, preventing energy waste and damage to the furnace structure.
Common Configurations
Based on this fundamental "hot zone/cold end" design, a few standard configurations meet most industrial needs:
- Straight Rods (Dumbbell Type): The most common variant, used in pairs or sets and mounted horizontally or vertically.
- U-Shaped Elements: These consist of two connected rods, allowing both electrical terminals to be on the same side of the furnace for simplified wiring.
- Multi-Leg Elements (e.g., W-Shaped): These provide higher power density in a compact space and are often used for specialized heating applications.
Why This Design Is a Technical Advantage
The simple rod shape is not an accident; it is a direct result of silicon carbide's unique material properties and delivers several key benefits.
High Structural Integrity
SiC material has no liquid phase, meaning it does not soften, sag, or creep under its own weight even at extreme temperatures up to 1625°C (2957°F). The rigid, self-supporting rod shape is a mechanically simple and stable way to leverage this incredible high-temperature strength.
Efficient Power Delivery
Silicon carbide has a high resistance to electric current. This property means that electrical energy is converted into heat with exceptional efficiency, and the cylindrical shape radiates this thermal energy uniformly in all directions (360°).
Predictable, Uniform Heating
The consistent geometry of the rod's hot zone ensures even and predictable heat distribution within a furnace chamber. This is critical for processes that require precise temperature uniformity, such as in semiconductor manufacturing, ceramic firing, and metal heat treating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Realities
While highly effective, SiC elements have specific operational characteristics that you must manage to ensure proper performance and a long service life.
The Challenge of "Aging"
Over time and exposure to high temperatures, SiC elements gradually oxidize. This process, known as aging, causes the element's electrical resistance to slowly and permanently increase.
The Need for Variable Power
Because the resistance increases with age, applying a fixed voltage would cause the power output (and thus the heat) to drop over time. To counteract this, SiC heating systems require a variable voltage power supply, such as a multi-tap transformer or a Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR). This allows you to increase the voltage over the element's lifespan to maintain constant power output.
Mechanical Brittleness
Like most ceramics, SiC is very hard but also brittle. The elements are robust against thermal stress but can be easily damaged by mechanical shock or impact. Careful handling during installation and maintenance is essential.
How to Specify the Right Element for Your Application
Choosing the correct element involves matching its physical dimensions and electrical properties to your furnace and power system.
- If your primary focus is building a new furnace: Ensure the element's hot zone length matches your chamber's internal dimensions and that your power supply controller is designed to manage the voltage increase required by SiC aging.
- If your primary focus is replacing existing elements: Precisely measure the dimensions of the old element—especially the hot zone length (L1), cold end length (L2), hot zone diameter (d), and cold end diameter (D)—to ensure a correct drop-in replacement.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lifespan: Use a sophisticated power controller (like an SCR) that can precisely manage the voltage, and design the system to avoid exceeding the element's maximum recommended power density (watts per square inch).
Ultimately, the simple, robust shape of a SiC element is its greatest strength, offering predictable performance when its core operational needs are met.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Shapes | Rods (straight, U-shaped, multi-leg) and tubes |
| Key Sections | Hot zone (high-resistance, heats up) and cold ends (low-resistance, terminals) |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1625°C (2957°F) |
| Material Properties | High structural integrity, efficient power delivery, uniform heating |
| Operational Considerations | Aging (resistance increases), requires variable power supply, brittle (handle with care) |
| Applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, ceramic firing, metal heat treating |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable silicon carbide heating elements and custom furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature applications and deliver tailored solutions for superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















