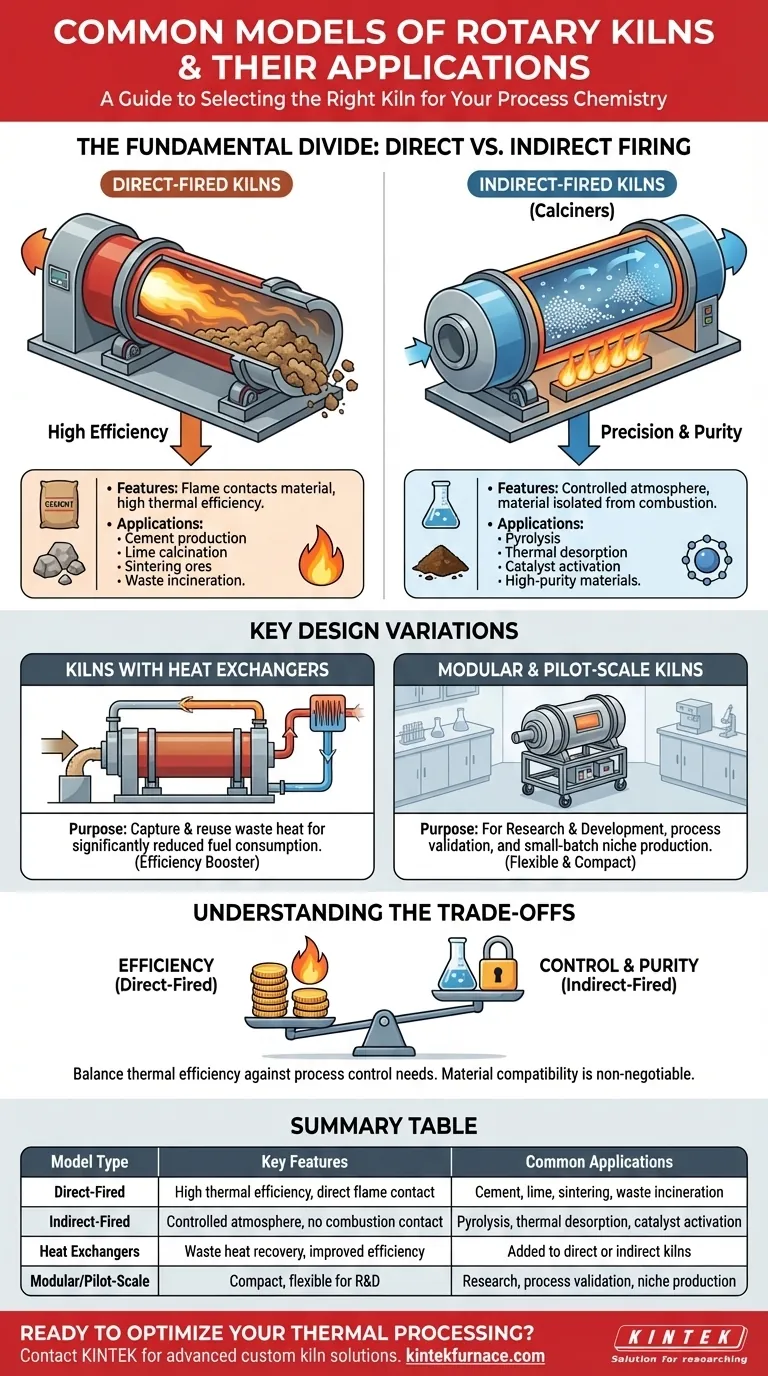
Rotary kilns are broadly categorized into two fundamental models based on how heat is applied: direct-fired and indirect-fired. Direct-fired kilns, where the material directly contacts the flame and combustion gases, are high-efficiency workhorses for bulk processes like cement manufacturing. Indirect-fired kilns heat the material through the shell of a rotating drum, making them ideal for processing delicate materials or for reactions that require a controlled atmosphere.
The critical distinction between kiln models is not a matter of features, but of process chemistry. Your choice depends entirely on a single question: can your material be exposed to combustion byproducts, or does it require an isolated, precisely controlled environment to achieve the desired transformation?
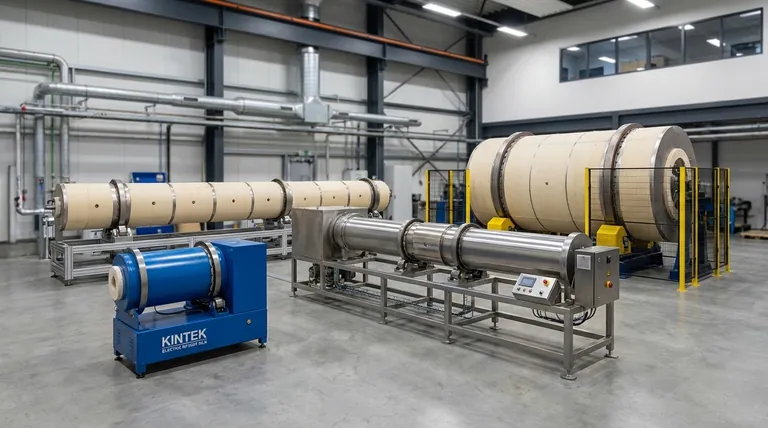

The Fundamental Divide: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
The core design principle of any rotary kiln is its method of heat transfer. This single factor determines the kiln's applications, efficiency, and limitations.
Direct-Fired Kilns: The Workhorse of Bulk Processing
A direct-fired kiln introduces a flame and hot process gases directly into the kiln cylinder, where they make intimate contact with the material being processed. This is the most common and thermally efficient design.
These systems excel at high-temperature applications where the material is robust and unaffected by the combustion atmosphere. The direct contact allows for rapid and efficient heat transfer.
Common applications include cement production, lime calcination, sintering of ores, and bulk waste incineration.
Indirect-Fired Kilns (Calciners): Precision and Purity
An indirect-fired kiln, often called a calciner, works by heating the exterior of the rotating drum. The material inside never contacts the flame or combustion gases.
This design provides a highly controlled environment, essential when the process atmosphere must be specific (e.g., inert or reducing) or when the material cannot be contaminated.
Typical uses include pyrolysis, thermal desorption of soil contaminants, activating catalysts, and processing heat-sensitive or high-purity materials.
Understanding Key Design Variations
Beyond the core firing method, other design features optimize kilns for specific goals like efficiency or scale.
Kilns with Heat Exchangers: Driving Efficiency
Heat exchangers are not a distinct type of kiln but an ancillary system that can be added to either direct or indirect designs.
Their purpose is to capture and reuse waste heat from the exiting process gas or solids. This recovered energy is typically used to pre-heat the incoming feed material, significantly reducing overall fuel consumption.
Modular and Pilot-Scale Kilns: For Research and Niche Production
These are compact, often skid-mounted systems designed for smaller throughput.
Their primary role is in research and development, process validation, and pilot-scale testing before investing in a full-scale production line. They are also used for small-batch production of high-value materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a kiln involves balancing thermal efficiency against the need for process control. Misunderstanding this trade-off is a common and costly mistake.
The Cost of Control
Direct-fired kilns are inherently more thermally efficient because heat is transferred directly to the material. This generally results in lower capital and operating costs for a given throughput.
Indirect-fired kilns lose some efficiency transferring heat through the kiln shell. This makes them more expensive to build and operate, but it is the necessary price for achieving atmospheric purity and precise control.
Material Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
The most critical factor is the material itself. Exposing a sensitive material to the combustion gases in a direct-fired kiln can cause unwanted side reactions or outright contamination, ruining the final product.
Conversely, using a complex and expensive indirect-fired kiln for a simple, robust process like making cement would be needlessly inefficient and uneconomical. The process dictates the equipment.
How to Select the Right Kiln for Your Process
Your final decision must be guided by the specific chemical and physical transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of robust minerals (like cement or lime): A direct-fired kiln is almost always the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing delicate materials or requires a specific atmosphere (like pyrolysis or catalyst activation): An indirect-fired kiln is essential to prevent contamination and control the reaction.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency: Investigate integrating a heat exchanger into your kiln design, regardless of the firing type.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-batch production: A modular or pilot-scale kiln provides the necessary flexibility without the capital expense of a full-scale system.
Ultimately, the right kiln is the one that masters the specific thermal and atmospheric conditions your material demands.
Summary Table:
| Model Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired Kilns | High thermal efficiency, direct flame contact | Cement production, lime calcination, sintering, waste incineration |
| Indirect-Fired Kilns | Controlled atmosphere, no combustion contact | Pyrolysis, thermal desorption, catalyst activation, high-purity materials |
| Kilns with Heat Exchangers | Waste heat recovery, improved efficiency | Added to direct or indirect kilns for energy savings |
| Modular/Pilot-Scale Kilns | Compact, flexible for R&D and small batches | Research, process validation, niche production |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with the right rotary kiln? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need a direct-fired kiln for bulk materials or an indirect-fired system for delicate processes, we can tailor a solution to enhance efficiency and control. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















