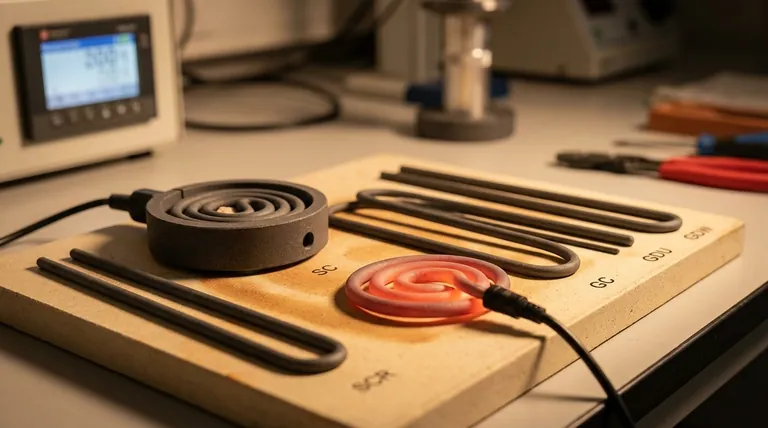
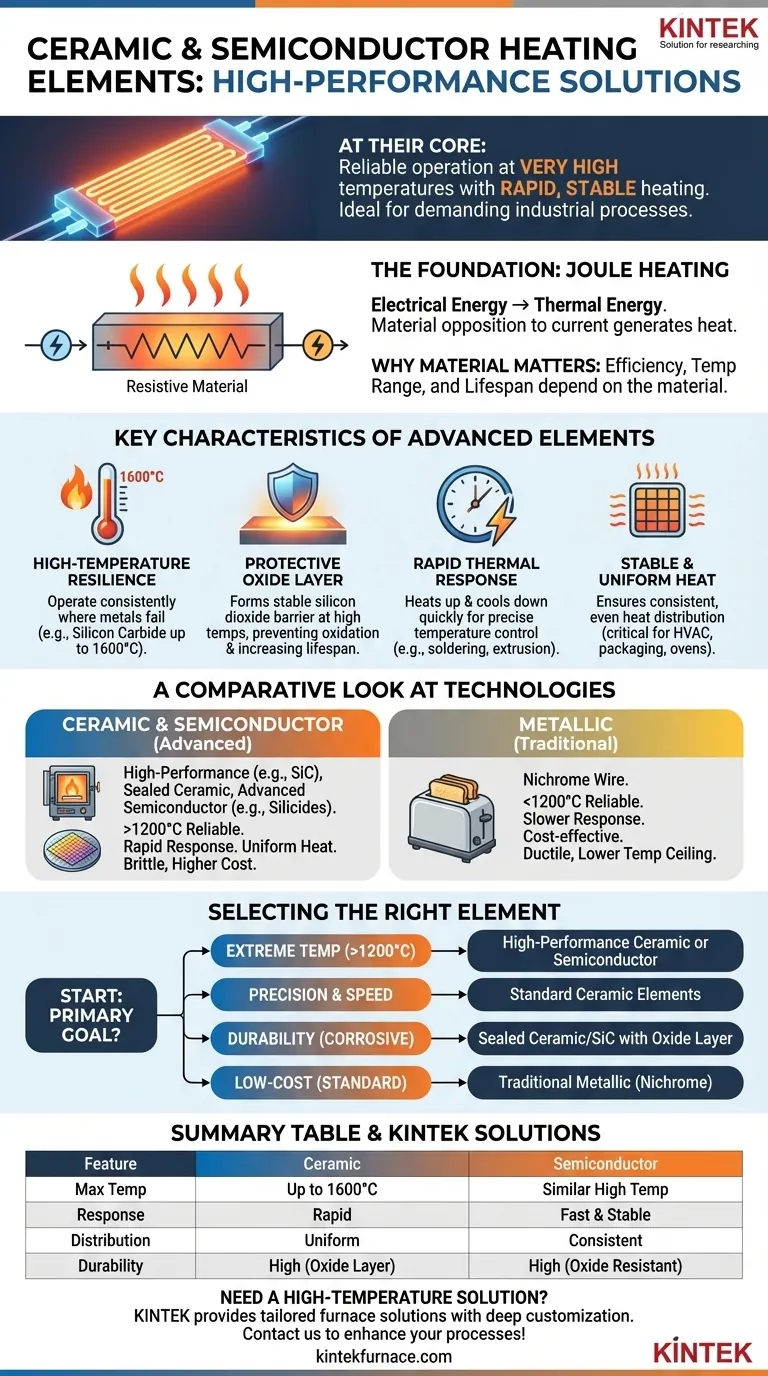
At their core, ceramic and semiconductor heating elements are defined by their ability to operate reliably at very high temperatures while offering rapid, stable heating. Unlike common metallic heaters, they possess a unique combination of thermal resilience and chemical inertness, making them ideal for demanding industrial processes like furnace heating, glass manufacturing, and precision soldering.
The decision between heating element types is fundamentally about matching the material's properties to the operational demands. While traditional metal heaters suffice for basic applications, ceramic and semiconductor elements provide the high-performance stability, speed, and durability required for advanced or extreme-temperature systems.

The Foundation of Electric Heating
All resistive heating elements operate on a single, fundamental principle, but the material used dictates the outcome.
The Principle of Joule Heating
Every electric heating element works by converting electrical energy into thermal energy. This process, known as Joule heating, occurs when electrical current encounters resistance as it flows through a material. The material's opposition to the current generates heat.
Why Material Choice is Critical
The efficiency, temperature range, and lifespan of a heating element are determined entirely by the material used. A material must not only have sufficient electrical resistance but also be able to withstand high temperatures and resist degradation over time. This is where the distinction between metal, ceramic, and semiconductor elements becomes crucial.
Key Characteristics of Ceramic & Semiconductor Heaters
These advanced materials share a set of high-performance characteristics that set them apart from standard metallic coils.
High-Temperature Resilience
Ceramic and semiconductor elements, such as silicon carbide and silicides, have extremely high melting points. They are engineered to operate consistently at temperatures where most metals would quickly fail. Silicon carbide, for instance, can function at up to 1600°C.
Protective Oxide Layer
At high temperatures, these materials form a stable, protective layer of silicon dioxide on their surface. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing further oxidation and chemical reactions, which dramatically increases the element's lifespan and reliability in harsh environments.
Rapid Thermal Response
Ceramics are known for their ability to heat up and cool down quickly. This rapid response time allows for precise temperature control, which is critical in applications like soldering, plastic extrusion, and semiconductor manufacturing where temperature fluctuations can ruin the product.
Stable and Uniform Heat
These elements provide highly stable and even heat distribution. This consistency is essential for processes in HVAC systems, packaging machinery, and industrial ovens that depend on uniform temperature across a surface or within a space.
A Comparative Look at Heating Technologies
While they share a common purpose, different heating elements are designed for vastly different operational contexts.
Conventional Ceramic Heaters
Sealed ceramic elements are workhorses for a variety of applications. Their durability and uniform heating make them ideal for consumer products like space heaters and industrial equipment like plastic extruders and packaging machines.
High-Performance Ceramics (e.g., Silicon Carbide)
When applications require extreme heat, high-performance ceramics are the definitive choice. Their ability to operate reliably above 1200°C makes them indispensable for high-temperature furnaces used in metallurgy, glass manufacturing, and materials testing.
Advanced Semiconductor Elements (e.g., Silicides)
Semiconductor-based heaters, such as those made from silicides, offer similar high-temperature performance. They are frequently used in highly controlled environments like semiconductor manufacturing furnaces and specialized heat-treatment processes.
The Metallic Alternative (e.g., Nichrome)
For contrast, consider the common nichrome wire found in toasters and hair dryers. These metallic elements are cost-effective and reliable for lower-temperature applications (typically below 1200°C). However, they lack the extreme temperature ceiling and chemical inertness of their ceramic counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an advanced heating element involves balancing performance benefits with practical constraints.
Performance vs. Cost
The superior temperature range and durability of ceramic and semiconductor elements come at a higher initial cost compared to simple metallic elements. The investment is justified by longer life and enabling processes that are otherwise impossible.
Mechanical Brittleness
Unlike ductile metals that can be easily formed into coils, ceramics are inherently brittle. They are more susceptible to failure from mechanical shock or stress and require careful design considerations for mounting and support.
System Control Complexity
The rapid thermal response of ceramic elements is a significant advantage, but it can also present a control challenge. To prevent temperature overshoot and maintain stability, they often require more sophisticated PID controllers and power management systems compared to slower-responding metallic elements.
How to Select the Right Heating Element
Your final choice should be guided by the primary goal of your application.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (above 1200°C): High-performance ceramics like Silicon Carbide or advanced semiconductor elements are the only viable options.
- If your primary focus is precision control and speed: Standard ceramic elements provide the fast thermal response needed for soldering, molding, and packaging.
- If your primary focus is durability in a corrosive environment: The protective oxide layer on sealed ceramic and silicon carbide elements offers superior longevity.
- If your primary focus is low-cost heating for a standard application: Traditional metallic elements like nichrome remain the most economical and practical choice.
By understanding these core material characteristics, you can select a heating element that delivers not just heat, but also the precise performance and reliability your system demands.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Ceramic Heating Elements | Semiconductor Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1600°C (e.g., Silicon Carbide) | Similar high-temperature performance (e.g., Silicides) |
| Thermal Response | Rapid heating and cooling | Fast and stable |
| Heat Distribution | Uniform and stable | Consistent and precise |
| Durability | High, with protective oxide layer | High, resistant to oxidation |
| Common Applications | Space heaters, plastic extruders, high-temperature furnaces | Semiconductor manufacturing, specialized heat-treatment |
| Key Trade-offs | Brittle, requires careful handling; higher cost | Higher cost; may need advanced control systems |
Need a high-temperature heating solution tailored to your lab's unique needs?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements can enhance your processes with superior performance, durability, and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















