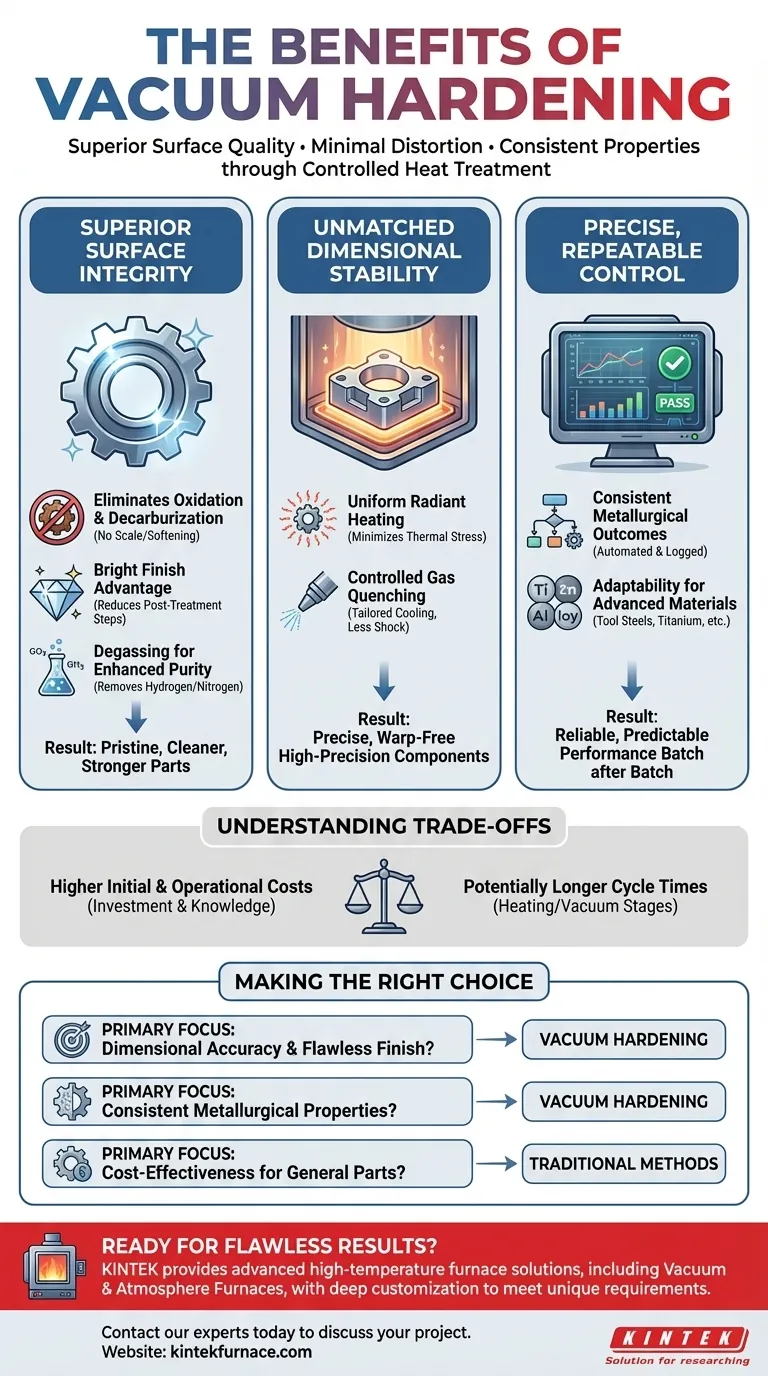
Fundamentally, vacuum hardening is a heat treatment process that yields superior surface quality, minimal part distortion, and exceptionally consistent metallurgical properties. By conducting the heating and quenching process in a controlled, low-pressure environment, it eliminates many of the variables and negative side effects associated with traditional atmospheric hardening methods.
The core advantage of vacuum hardening is control. By removing reactive gases like oxygen from the equation, the process prevents surface defects and allows for extremely precise thermal management, resulting in parts that are cleaner, stronger, and more dimensionally accurate.

Why a Vacuum Creates Superior Surface Integrity
The most visible benefit of vacuum hardening is the pristine condition of the part's surface. This is a direct result of the controlled atmosphere, which prevents unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
In traditional furnaces, the presence of oxygen causes oxidation, forming a layer of scale or discoloration on the part's surface. The vacuum environment, by definition, removes this oxygen, completely preventing this reaction. This also prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of the steel—which can soften the part and reduce its wear resistance.
The "Bright Finish" Advantage
Because no oxidation or scale forms, parts emerge from a vacuum furnace with a bright, clean metallic surface. This often eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations like sandblasting, grinding, or chemical cleaning, reducing overall cycle time and preserving the part's precise dimensions.
Degassing for Enhanced Purity
The vacuum actively pulls trapped gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the metal itself. This degassing function improves the material's purity, which can significantly enhance mechanical properties like toughness, plasticity, and fatigue strength while mitigating the risk of hydrogen embrittlement.
Achieving Unmatched Dimensional Stability
For high-precision components like molds, dies, and gears, maintaining dimensional accuracy is critical. Vacuum hardening excels at minimizing the distortion that can occur during the intense heating and cooling cycles of heat treatment.
Uniform Heating Reduces Thermal Stress
In a vacuum, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation, which heats the workpiece slowly and uniformly. This is unlike conventional furnaces that rely on convection, which can create hot spots. This uniform heating minimizes internal thermal stresses, which are a primary cause of warping and distortion.
Controlled Quenching Minimizes Shock
Instead of being plunged into a liquid like oil or water, parts in a vacuum furnace are typically cooled (quenched) using a high-pressure inert gas like nitrogen. The pressure, flow, and temperature of this gas can be precisely controlled, allowing for a tailored cooling rate. This less severe, highly controlled quench further reduces thermal shock and distortion.
The Power of Precise, Repeatable Control
The highly automated and computer-controlled nature of modern vacuum furnaces translates directly into reliable and predictable results.
Consistent Metallurgical Outcomes
Every critical variable—temperature, time, vacuum level, and quenching pressure—is precisely managed and logged. This ensures that every part in a batch, and every subsequent batch, receives the exact same treatment. The result is unparalleled repeatability, delivering consistent hardness, case depth, and microstructure every time.
Adaptability for Advanced Materials
The precise control offered by vacuum technology makes it ideal for heat treating advanced and sensitive materials. This includes high-alloy tool steels, titanium, and other refractory metals that are highly reactive or have very specific heat treatment requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum hardening is not the default solution for every application. Objectively weighing its trade-offs is key to making a sound engineering decision.
Higher Initial and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. Their complexity also leads to higher maintenance costs and requires more specialized operational knowledge.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
While the overall process can be faster by eliminating post-treatment cleaning, the heating and cooling cycles within the furnace can sometimes be longer. Radiant heating is inherently slower than convection, and achieving a deep vacuum takes time.
Over-specification for Simple Parts
For low-tolerance, general-purpose components where a perfect surface finish and minimal distortion are not critical requirements, the benefits of vacuum hardening may not justify the added cost. Traditional methods are often more economical for these applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a hardening method requires aligning the process capabilities with your project's most critical requirements.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy and a flawless finish: Vacuum hardening is the definitive choice for high-precision components like injection molds, aerospace parts, and complex tooling.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific, repeatable metallurgical properties: The precise digital control of vacuum hardening ensures consistent performance and reliability across large production runs.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose parts: Traditional atmospheric or salt bath hardening may be sufficient and more economical for components with wider tolerances and less critical surface requirements.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the hardening process that delivers the precise outcome your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Surface Integrity | Prevents oxidation/decarburization; eliminates need for post-treatment cleaning. |
| Unmatched Dimensional Stability | Uniform radiant heating & controlled gas quenching minimize part distortion. |
| Precise, Repeatable Control | Automated process ensures consistent hardness and microstructure batch after batch. |
| Ideal for Advanced Materials | Perfect for heat treating sensitive alloys like tool steels and titanium. |
Ready to achieve flawless results for your high-precision components?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique heat treatment requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum hardening solutions can enhance your project's quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















