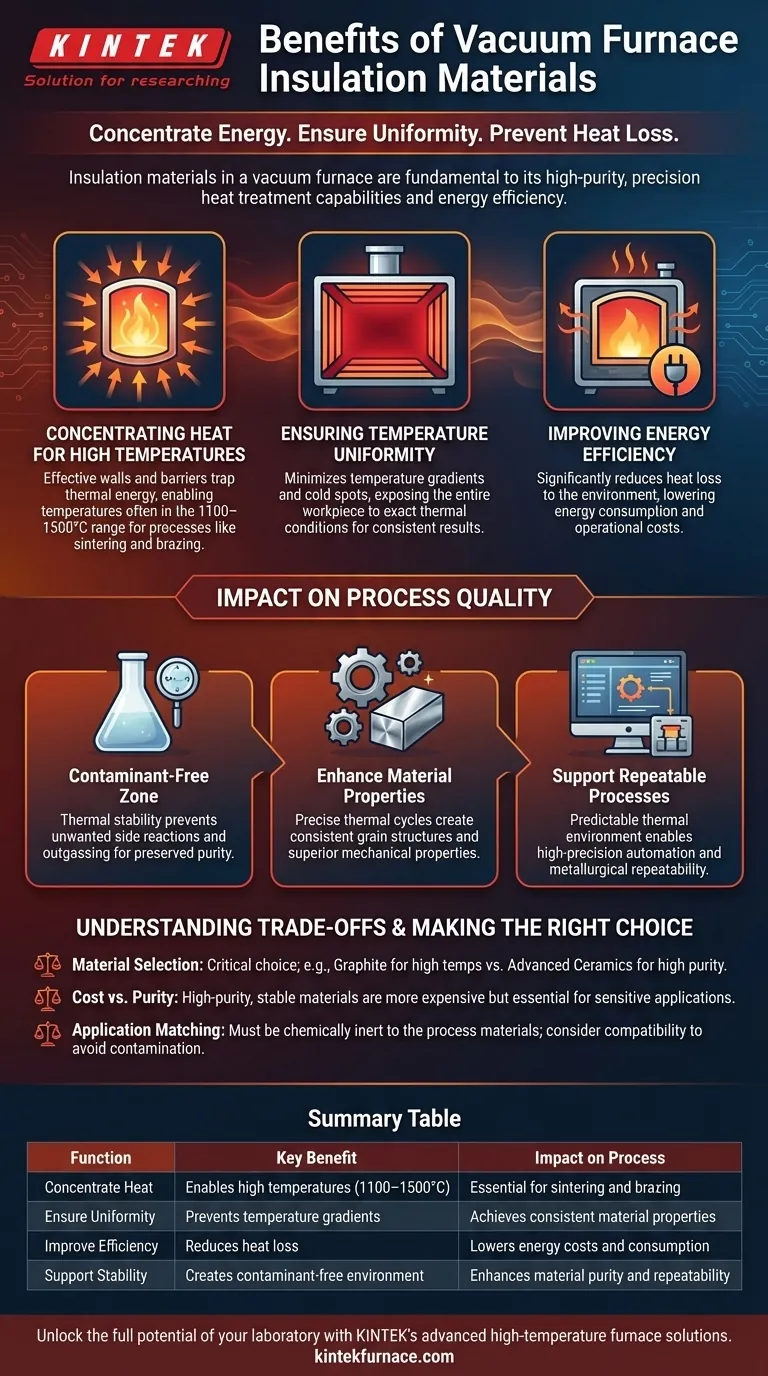
At their core, the insulation materials in a vacuum furnace serve three primary functions. They are designed to concentrate thermal energy, maintain uniform temperatures throughout the heating zone, and prevent heat loss. This dramatically improves the furnace's overall energy efficiency and is fundamental to its ability to perform high-purity, precision heat treatment.
The benefits of vacuum furnace insulation extend far beyond simple energy savings. These materials are the enabling technology that allows the furnace to create the stable, precise, and repeatable high-temperature environment required for processing advanced materials.

How Insulation Enables Precision and Efficiency
The performance of a vacuum furnace is directly tied to its ability to control heat. The insulation system is the foundation of that control.
Concentrating Heat for High Temperatures
Insulation walls and barriers effectively trap thermal energy generated by the heating elements. This concentration allows the furnace to reach and sustain the extremely high and uniform temperatures—often in the 1100–1500°C range—required for processes like sintering and brazing.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
By preventing heat from escaping, insulation minimizes temperature gradients and cold spots within the heating chamber. This ensures that the entire workpiece is exposed to the exact same thermal conditions, which is critical for consistent results.
Improving Energy Efficiency
A well-insulated furnace loses significantly less heat to the surrounding environment. This directly translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs, as the heating system does not have to work as hard to maintain the target temperature.
The Impact of Insulation on Process Quality
The stable thermal environment created by the insulation has a profound effect on the final quality of the processed materials. It's a key factor in achieving the primary advantages of vacuum processing.
Creating a Stable, Contaminant-Free Zone
While the vacuum itself removes reactive gases like oxygen, the insulation ensures the thermal stability needed for a clean process. Predictable and uniform temperatures prevent unwanted side reactions and outgassing, preserving the purity of the material being treated.
Enhancing Material Properties
Processes like sintering and brazing rely on precise thermal cycles to achieve desired material characteristics. The temperature uniformity guaranteed by effective insulation leads to consistent grain structures, high-quality brazed joints, and superior mechanical properties in the final product.
Supporting Repeatable, Computer-Controlled Processes
Modern vacuum furnaces rely on computer controls to ensure metallurgical repeatability. This automation is only effective if the thermal environment is predictable. Insulation creates a stable system that the control software can manage with high precision, ensuring every batch meets the same exacting standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of insulation material is a critical design decision with significant consequences for performance and cost. It is not a one-size-fits-all component.
Material Selection is Critical
The materials used for insulation, much like the heating elements, must be carefully chosen. Materials like graphite are excellent for very high temperatures, while advanced ceramics may be preferred for applications where even minimal carbon contamination is unacceptable.
Balancing Cost vs. Purity
High-purity insulation materials that are stable at extreme temperatures and do not outgas are significantly more expensive. For less sensitive applications, a lower-grade material might be sufficient, but this introduces a trade-off between initial cost and potential process contamination.
Matching Insulation to the Application
The insulation must be chemically inert relative to the materials being processed. For example, when sintering certain sensitive alloys, using graphite-based insulation could introduce carbon into the material, altering its properties. This makes material compatibility a crucial consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal insulation strategy depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality: Prioritize insulation that offers the highest degree of temperature uniformity across the entire heating zone.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and operational cost: Select an insulation package with the lowest possible thermal conductivity to minimize heat loss and reduce power consumption.
- If your primary focus is material purity and avoiding contamination: Choose a high-purity insulation material, such as ceramic fiber, that is chemically inert and has low outgassing properties at your target temperature.
Ultimately, viewing insulation as an active and critical component—not just a passive barrier—is the key to unlocking the full potential of your vacuum furnace.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrate Heat | Enables high temperatures (1100–1500°C) | Essential for sintering and brazing |
| Ensure Uniformity | Prevents temperature gradients | Achieves consistent material properties |
| Improve Efficiency | Reduces heat loss | Lowers energy costs and consumption |
| Support Stability | Creates contaminant-free environment | Enhances material purity and repeatability |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















