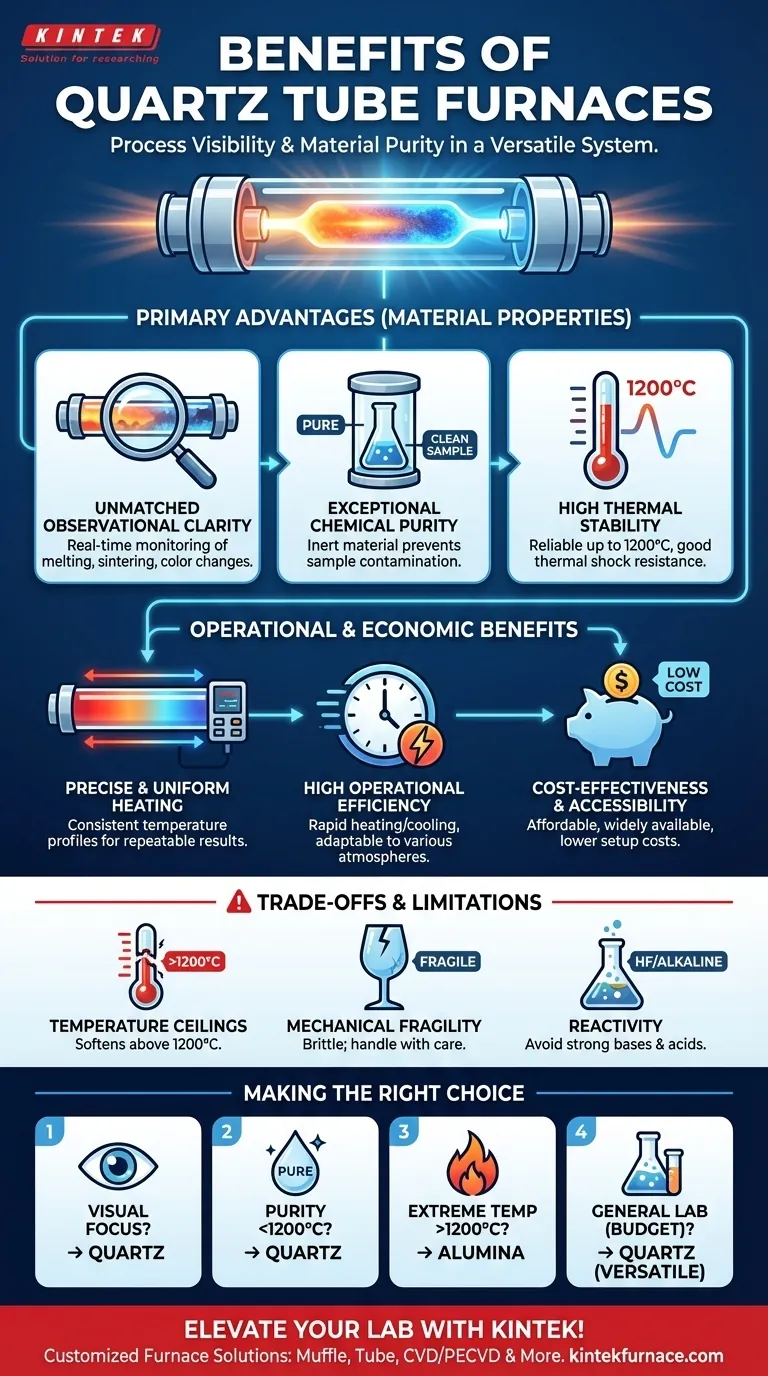
At their core, quartz tube furnaces provide a unique combination of process visibility and material purity. They are standard equipment in research and industrial settings because they offer high heat resistance up to 1200°C, excellent chemical stability for most applications, and unparalleled optical transparency. This allows for direct, real-time observation of a sample during complex thermal processing.
While many furnaces can deliver high temperatures, a quartz tube furnace becomes the definitive choice when you must visually monitor your process and simultaneously guarantee the chemical purity of your sample in a versatile and cost-effective system.

The Primary Advantages of Using Quartz
The material properties of quartz are directly responsible for the furnace's most significant benefits. These characteristics make it uniquely suited for applications where process control and sample integrity are paramount.
Unmatched Observational Clarity
The most distinct advantage of a quartz tube is its high transparency. This allows operators and researchers to directly watch the sample as it is heated.
You can visually confirm critical transformations like melting, sintering, color changes, or decomposition. This real-time feedback is invaluable for process development and failure analysis.
Exceptional Chemical Purity
Quartz is chemically inert to a vast range of materials, even at high temperatures. This means the tube itself will not react with or contaminate your sample.
This purity is essential in fields like semiconductor manufacturing, specialty glass formulation, and advanced materials science, where even trace contaminants can ruin an entire batch.
High Thermal Stability
Quartz tubes can reliably operate at sustained temperatures, typically up to 1100°C, and can handle peaks approaching 1200°C.
They also possess good resistance to thermal shock, allowing for relatively rapid heating and cooling cycles without fracturing, which improves laboratory throughput.
Operational and Economic Benefits
Beyond the material itself, the design and economics of quartz tube furnaces provide tangible advantages for day-to-day operations.
Precise and Uniform Heating
Tube furnaces are designed to create a highly uniform temperature zone along the length of the tube. This ensures that the entire sample is subjected to the same thermal conditions.
Combined with modern digital controllers, this allows for extremely precise and repeatable temperature profiles. This level of control is fundamental for achieving consistent results in both research and production.
High Operational Efficiency
The simple structure allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles compared to larger, more heavily insulated batch furnaces. This reduces energy consumption and shortens the time between experimental runs.
Furthermore, their adaptability to different atmospheres—such as vacuum, inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), or reactive gases—makes them a highly versatile tool for a wide range of processes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
Compared to tubes made from more exotic materials like alumina or sapphire, quartz tubes are relatively low-cost and widely available.
This makes initial setup more affordable and reduces the financial impact of accidental breakage, which is a practical consideration in any lab environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single solution is perfect for every scenario. Being an effective technical professional requires understanding a tool's limitations as well as its strengths.
Temperature Ceilings
While excellent for many applications, quartz begins to soften and devitrify (become crystalline and brittle) at temperatures above 1200°C. For processes requiring extreme temperatures, furnaces with alumina or other advanced ceramic tubes are necessary.
Mechanical Fragility
Quartz is a type of glass and is inherently brittle. It can be easily fractured by mechanical shock or improper handling. Care must be taken when loading samples and securing the furnace assembly to avoid costly breaks.
Reactivity with Certain Compounds
Although broadly inert, quartz can be attacked by strong alkaline substances (like sodium hydroxide) and certain acids (like hydrofluoric acid) at high temperatures. You must verify chemical compatibility before running experiments with these materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the specific requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is visual process monitoring: The transparency of a quartz tube furnace is non-negotiable for observing real-time sample changes.
- If your primary focus is sample purity below 1200°C: The chemical inertness of quartz makes it the ideal choice for sensitive materials processing, such as semiconductor fabrication or chemical vapor deposition.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures above 1200°C: You must choose a furnace with a tube made from alumina or another specialized ceramic.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work on a budget: The versatility, low cost, and ease of use of a quartz tube furnace make it an excellent default choice for a wide array of research applications.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select the right tool to achieve precise and repeatable results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Observational Clarity | Direct real-time sample monitoring for process control and analysis. |
| Chemical Purity | Inert material prevents sample contamination, ideal for sensitive applications. |
| Thermal Stability | Operates up to 1200°C with good shock resistance for efficient cycling. |
| Heating Uniformity | Ensures consistent temperature profiles for repeatable results. |
| Operational Efficiency | Fast heating/cooling, adaptable to various atmospheres, and energy-saving. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Affordable and widely available, reducing setup and replacement costs. |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, driving innovation and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your thermal processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















