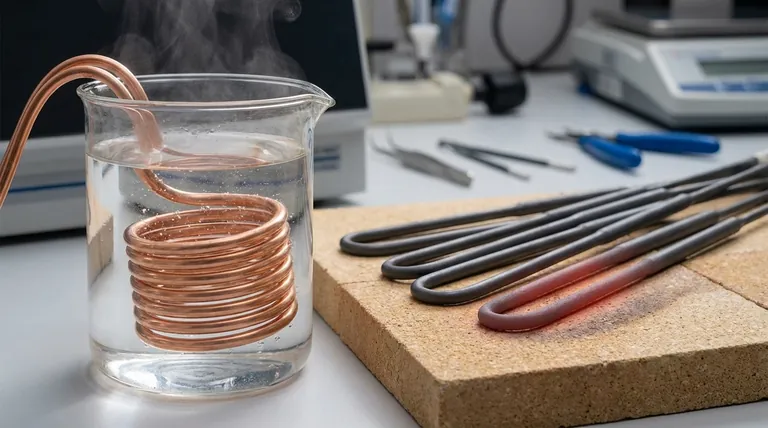
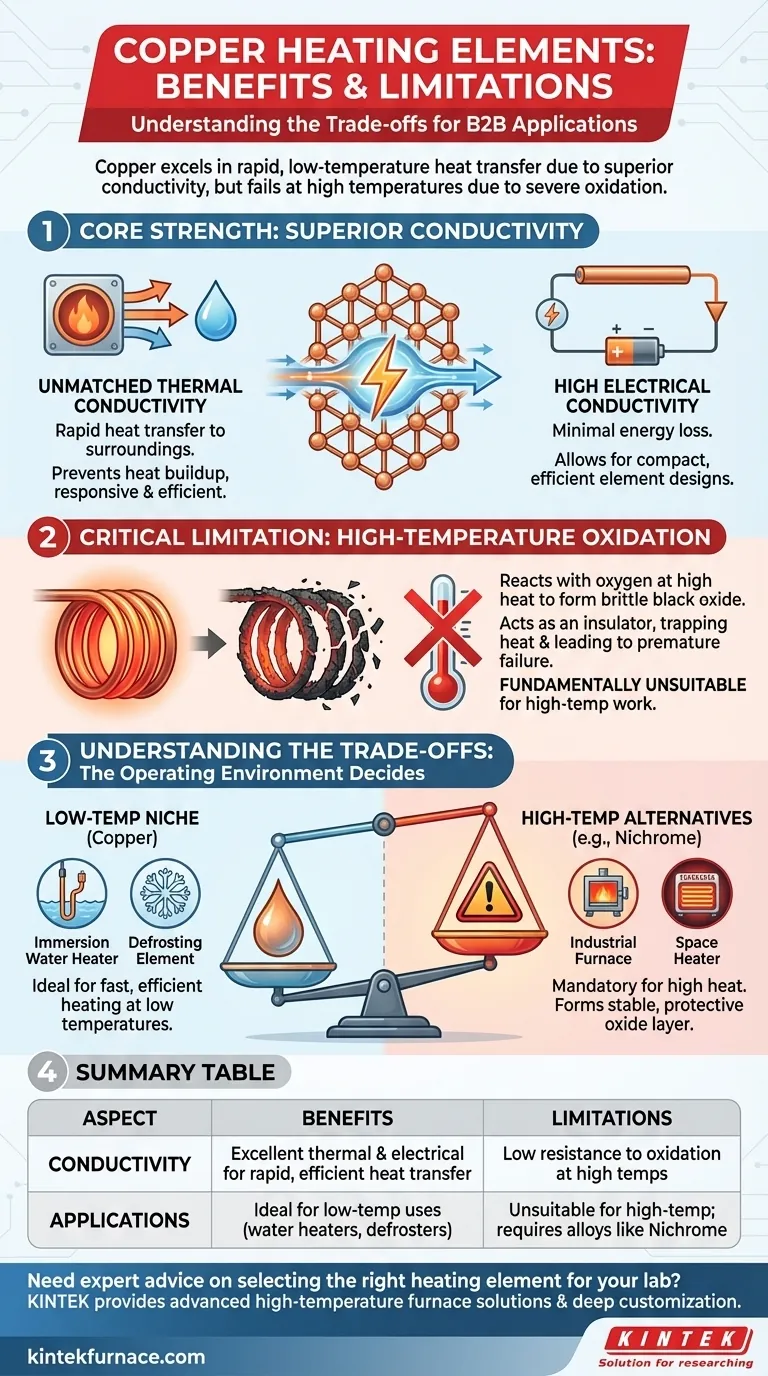
In short, copper's primary benefit for heating elements is its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity, allowing for rapid and efficient heat transfer. However, its significant limitation is a low resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, which causes it to corrode and fail, restricting its use to low-temperature applications.
The decision to use copper for a heating element is not about its performance but its operating environment. It is an ideal material for fast, efficient heating at low temperatures, but it is fundamentally unsuitable for high-temperature applications where specialized alloys are required.

The Core Strength: Superior Conductivity
Copper's value in heating is rooted in its ability to move energy—both thermal and electrical—with very little resistance. This property makes it uniquely suited for specific types of heating tasks.
Unmatched Thermal Conductivity
Copper is one of the best thermal conductors among common metals. This means it transfers heat away from the source and into the surrounding medium (like air or water) extremely quickly.
This rapid transfer prevents heat from building up excessively within the element itself, leading to a very responsive and efficient heating system.
High Electrical Conductivity
While it may seem counterintuitive to use a good electrical conductor for a resistive heater, this property is crucial for efficiency.
Because copper conducts electricity so well, an element can be designed to carry the necessary current to generate heat with minimal energy loss in the connecting wires. This allows for more compact and efficient element designs, especially in low-voltage systems.
The Critical Limitation: High-Temperature Oxidation
Copper’s single greatest weakness is its reaction to heat and oxygen. This chemical process, known as oxidation, makes it entirely unsuitable for high-temperature work.
The Process of Corrosion
When heated in the presence of air, copper readily reacts with oxygen to form a layer of black copper oxide on its surface.
Unlike the protective oxide layers formed on other alloys, this layer is brittle, flakes off easily, and does not prevent further corrosion underneath.
The Impact on Performance
The copper oxide layer is a poor conductor of both heat and electricity. As it forms, it acts as an insulator, trapping heat inside the element and dramatically reducing its ability to heat the surrounding environment.
This process quickly degrades performance and leads to premature failure of the heating element.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between copper and other materials is a clear-cut decision based on the required operating temperature.
The Niche for Copper
Copper excels in low-temperature applications where rapid heat transfer is the goal.
Common examples include immersion water heaters, defrosting elements in refrigeration systems, and heat exchangers where the primary goal is moving heat, not generating it to high temperatures.
When to Use Alternatives like Nichrome
For high-temperature applications like space heaters, furnaces, or toasters—where the element must glow red-hot—specialized alloys are mandatory.
Materials like Nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy) are designed to form a stable, adherent oxide layer that protects the metal from further corrosion, even at extreme temperatures. This is a feature copper fundamentally lacks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection must be dictated by the operating temperature range of your project.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-temperature heating (e.g., water kettles, defrosters): Copper's superior conductivity makes it an excellent and highly efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating (e.g., kilns, electric stoves, space heaters): You must use a specialized heating alloy like Nichrome or Kanthal, as copper will quickly corrode and fail.
Understanding this fundamental temperature limitation is the key to designing a reliable and long-lasting heating system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity for rapid, efficient heat transfer | Low resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, leading to corrosion and failure |
| Applications | Ideal for low-temperature uses like water heaters and defrosters | Unsuitable for high-temperature applications; requires alloys like Nichrome |
Need expert advice on selecting the right heating element for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)

















