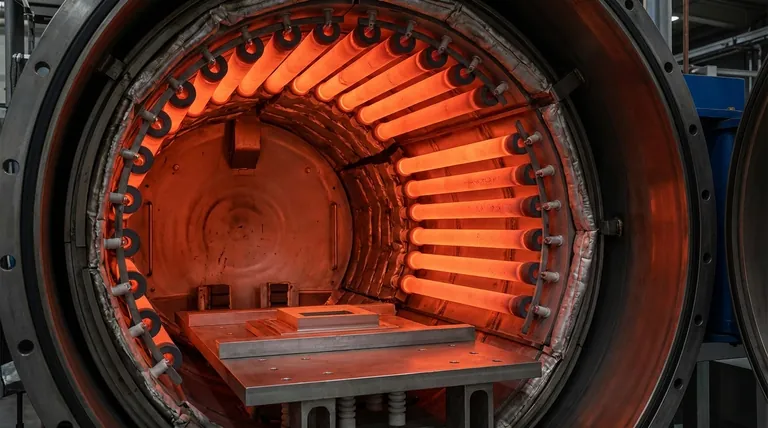
In the demanding environment of a vacuum furnace, graphite stands out as a premier material for heating elements due to its exceptional performance at extreme temperatures. Its unique combination of thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength allows it to generate intense, uniform heat reliably in the non-oxidizing conditions of a vacuum. This makes it a foundational component for many high-temperature industrial processes.
The core reason for graphite's dominance is not just its ability to get incredibly hot, but its capacity to deliver stable, uniform, and controllable heat. Its properties work in concert to create an efficient and robust heating system perfectly suited for the vacuum furnace environment.
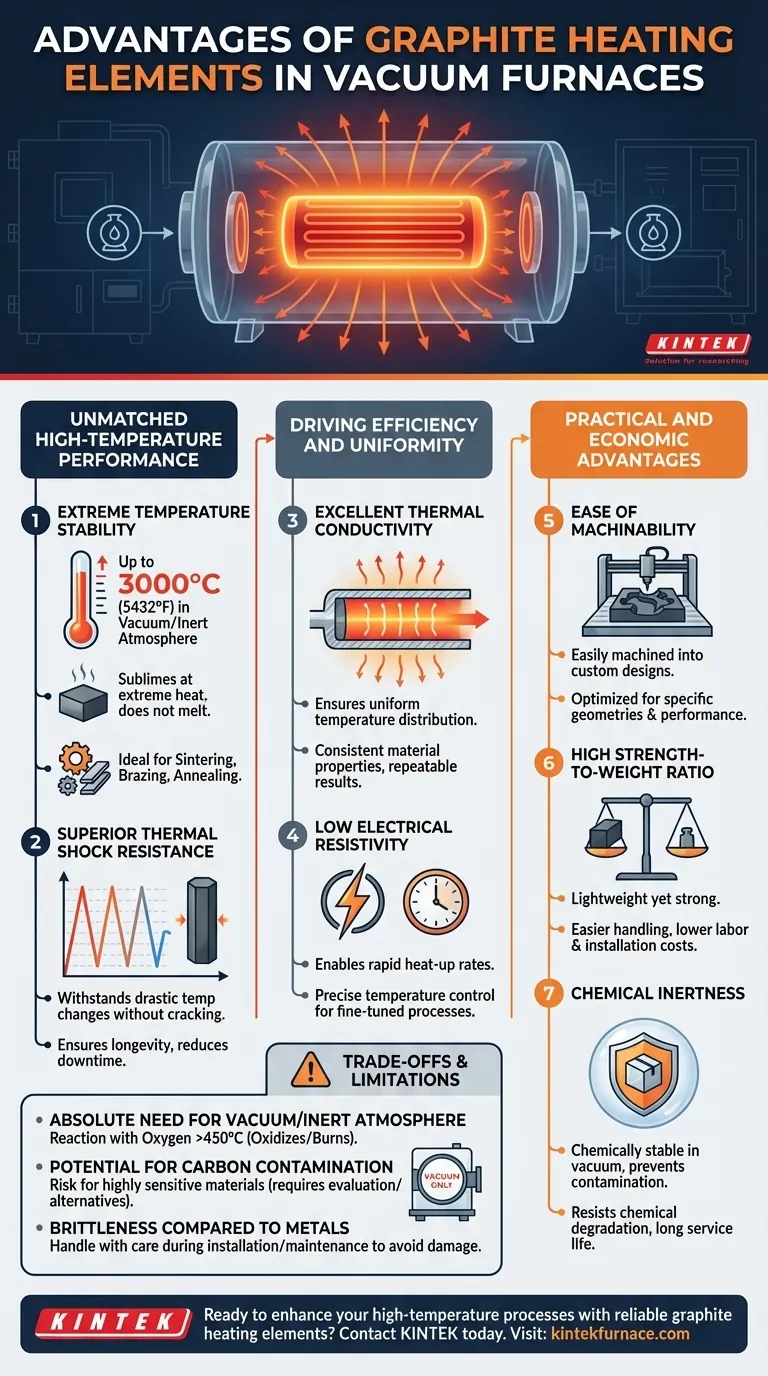
The Foundation: Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
Graphite's primary advantage is its ability to maintain structural integrity and perform its function at temperatures that would cause most other materials to melt or degrade.
Extreme Temperature Stability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure but sublimes (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at very high temperatures. In a vacuum or inert atmosphere, it can be used stably as a heating element at temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F).
This capability is essential for processes like sintering, brazing, and annealing advanced materials that require extreme heat.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Vacuum furnace processes often involve rapid heating and cooling cycles. Graphite can withstand these drastic temperature changes without cracking or failing.
This resistance to thermal shock ensures the longevity of the heating elements, reduces downtime, and allows for more aggressive and efficient process cycles compared to more brittle ceramic alternatives.
Driving Efficiency and Uniformity
Beyond simply resisting heat, graphite's properties actively contribute to a more efficient and uniform heating process, which is critical for product quality.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
Graphite conducts heat very effectively. This property ensures that the temperature across the heating element and throughout the furnace's hot zone is remarkably uniform.
Excellent temperature uniformity is crucial for ensuring that every part of a workpiece receives the same thermal treatment, leading to consistent material properties and repeatable results.
Low Electrical Resistivity
Graphite heating elements work by passing an electrical current through them, generating heat through resistance (Joule heating). Graphite's relatively low resistivity allows it to carry high currents efficiently.
This translates to rapid heat-up rates and precise temperature control, giving operators fine-tuned command over the thermal process.
Practical and Economic Advantages
Graphite delivers significant benefits in the design, fabrication, and maintenance of the furnace itself, contributing to lower overall costs.
Ease of Machinability
Unlike many high-temperature ceramics or refractory metals, graphite is easily machined into complex shapes.
This allows for the creation of custom-designed heating elements that are optimized for specific furnace geometries and heating requirements, maximizing efficiency and performance.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Graphite is both strong and lightweight. This makes the large heating elements and support structures inside a furnace easier and safer to handle during assembly and maintenance.
The lower mass also reduces the need for heavy internal support structures and can contribute to lower labor and installation costs.
Chemical Inertness
In a vacuum environment, graphite is chemically stable and does not react with most materials.
This prevents contamination of the product being heat-treated and contributes to the long service life of the heating element, as it resists chemical degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While graphite is an exceptional material, its use comes with critical operating requirements and considerations that must be respected.
The Absolute Need for a Vacuum or Inert Atmosphere
Graphite's single greatest limitation is its reaction with oxygen at high temperatures. In the presence of air, it will rapidly oxidize (burn) at temperatures above approximately 450°C.
Therefore, its use as a heating element is strictly limited to vacuum environments or furnaces backfilled with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen. Any air leak can lead to rapid destruction of the hot zone.
Potential for Carbon Contamination
For certain highly sensitive applications, there is a risk that the graphite elements can introduce carbon into the workpiece or furnace atmosphere through outgassing.
While this is not a concern for most processes, materials that are highly sensitive to carbon content may require alternative heating elements (like molybdenum or tungsten) or the use of specialized, coated graphite.
Brittleness Compared to Metals
Although graphite is readily machinable, it is a brittle material compared to metallic heating elements. It must be handled with care during installation and maintenance to avoid chipping or cracking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Ultimately, selecting graphite is a decision based on the specific demands of your thermal application.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (>2000°C) and rapid cycling: Graphite is the superior choice due to its unmatched temperature stability and thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective design and temperature uniformity: Graphite's machinability and high thermal conductivity allow for optimized, efficient, and long-lasting hot zone designs.
- If your process is sensitive to carbon contamination: You must evaluate the risk and consider alternatives or specialized coated graphite to ensure product purity.
By understanding these properties, you can leverage graphite to build highly reliable and efficient high-temperature processes.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Stability | Operates stably up to 3000°C in vacuum or inert atmospheres, ideal for high-heat processes like sintering and annealing. |
| Superior Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking, ensuring longevity and reduced downtime. |
| Excellent Thermal Conductivity | Provides uniform temperature distribution for consistent results and repeatable material properties. |
| Low Electrical Resistivity | Enables rapid heat-up rates and precise temperature control for efficient Joule heating. |
| Ease of Machinability | Allows custom-designed heating elements for optimized furnace performance and specific requirements. |
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Lightweight yet strong, reducing installation and maintenance costs with easier handling. |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination in vacuum environments, extending service life and maintaining product purity. |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable graphite heating elements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance, efficiency, and cost savings. Don't let thermal challenges hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision



















