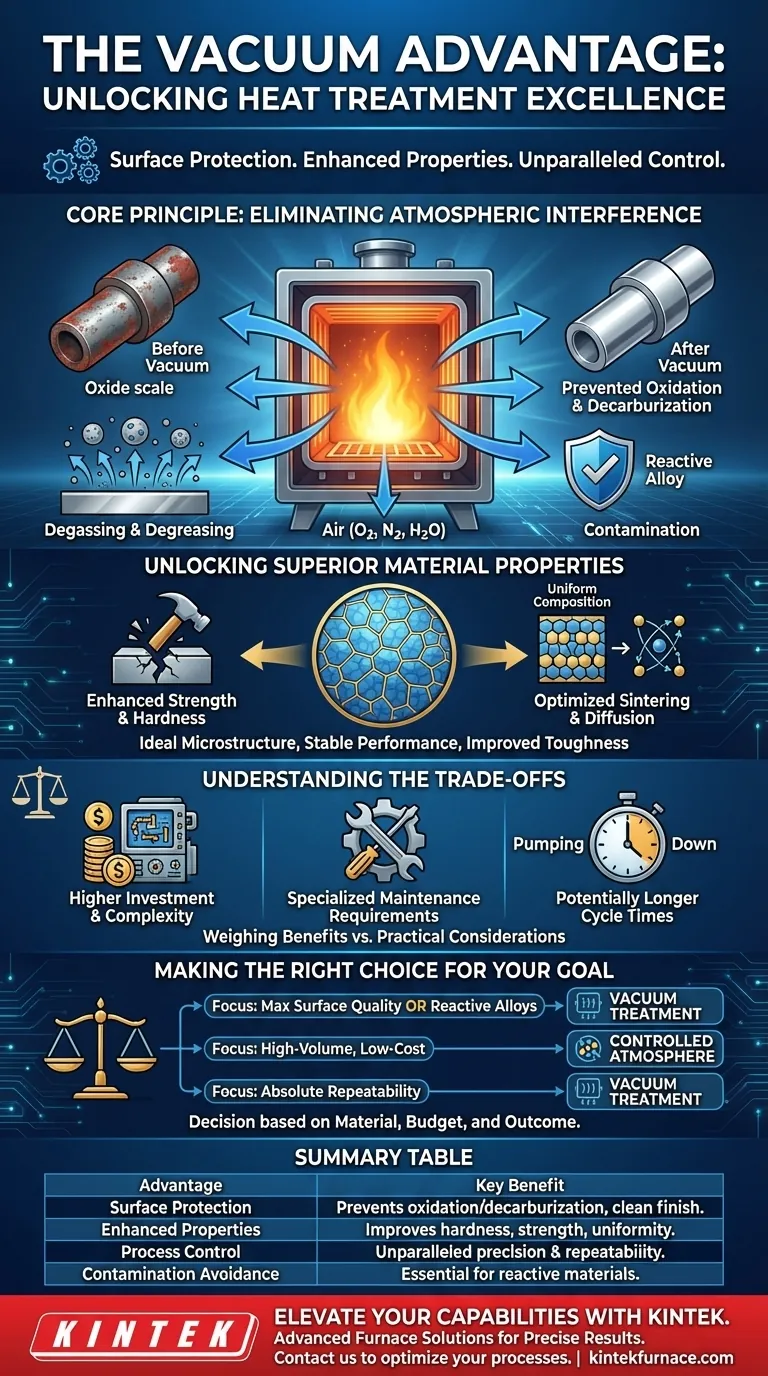
In short, a vacuum environment in a heat treatment furnace provides three primary advantages: it protects the material's surface, improves its internal properties, and allows for unparalleled process control. By removing reactive atmospheric gases like oxygen, it prevents oxidation and decarburization, resulting in a clean, bright finish and preserving the workpiece's intended chemical composition.
The fundamental advantage of a vacuum is not simply the removal of air, but the creation of a chemically inert and highly stable environment. This eliminates unwanted variables, enabling a level of precision and material purity that is often unattainable with conventional atmosphere-based methods.

The Core Principle: Eliminating Atmospheric Interference
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove the air—and specifically the oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor—that can react harmfully with metals at high temperatures.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
At elevated temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen, forming a layer of oxide scale on the surface. A vacuum environment starves the process of this reactant, completely preventing oxidation.
Similarly, the carbon within steel alloys can react with oxygen and escape the material's surface, a phenomenon known as decarburization. This weakens the surface layer, but is entirely avoided in a vacuum.
Achieving Ultimate Surface Purity
Because no oxidation occurs, parts emerge from a vacuum furnace with a bright, clean surface finish. This often eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning or machining to remove scale.
Furthermore, the low-pressure environment facilitates degassing and degreasing. Volatile contaminants, oils, or trace elements on the workpiece surface are vaporized and drawn out by the vacuum system, leading to a purer final product.
Avoiding Contamination
For highly reactive materials like titanium or superalloys, even trace amounts of atmospheric gases can cause contamination that compromises their mechanical properties. A vacuum is essential for processing these high-performance materials without degrading their integrity.
Unlocking Superior Material Properties
By controlling the thermal and chemical environment so precisely, vacuum heat treatment directly enhances the final quality of the workpiece.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
The ability to heat uniformly and then cool at a precisely controlled rate allows for the development of an ideal metallurgical microstructure. This results in more uniform material structure and stable performance.
This precision directly improves critical mechanical properties like hardness, strength, and toughness, ensuring the component meets its design specifications.
Ensuring Chemical Integrity
Without atmospheric reactions, the alloy's chemical composition remains exactly as intended from the surface to the core. This is crucial for applications where the precise balance of alloying elements dictates performance.
Optimizing Specialized Materials
In processes like sintering, the vacuum facilitates atomic diffusion, helping particles bond more effectively to form a solid, high-density product. For magnetic materials, precise thermal cycles in a vacuum can significantly improve their magnetic properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution. Their advantages must be weighed against practical considerations.
Higher Initial Investment and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive to build and purchase than their atmospheric counterparts. The need for vacuum pumps, robust seals, and precise instrumentation adds to the initial cost.
Maintenance Requirements
The vacuum system, including pumps, seals, and gauges, requires specialized and diligent maintenance to ensure it operates correctly and holds a proper vacuum level. Leaks can compromise an entire batch.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The step of "pumping down" the furnace chamber to the required vacuum level adds time to the beginning of every cycle. While heating and cooling can be rapid, this initial pump-down phase must be factored into overall throughput calculations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on your material, your budget, and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface quality: Vacuum treatment is the definitive choice, as it eliminates the need for post-process cleaning.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or high-performance alloys: A vacuum environment is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic material contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost treatment: A traditional controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon) furnace may be more cost-effective if some surface oxidation is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is absolute process repeatability: The stable and controllable nature of a vacuum provides unparalleled consistency from batch to batch.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize control and quality above all else.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Surface Protection | Prevents oxidation and decarburization for a clean finish |
| Enhanced Properties | Improves hardness, strength, and microstructural uniformity |
| Process Control | Offers unparalleled precision and repeatability in thermal cycles |
| Contamination Avoidance | Essential for reactive materials like titanium and superalloys |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide vacuum and atmosphere furnaces, CVD/PECVD systems, and more, tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for industries handling reactive alloys and demanding heat treatments. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















