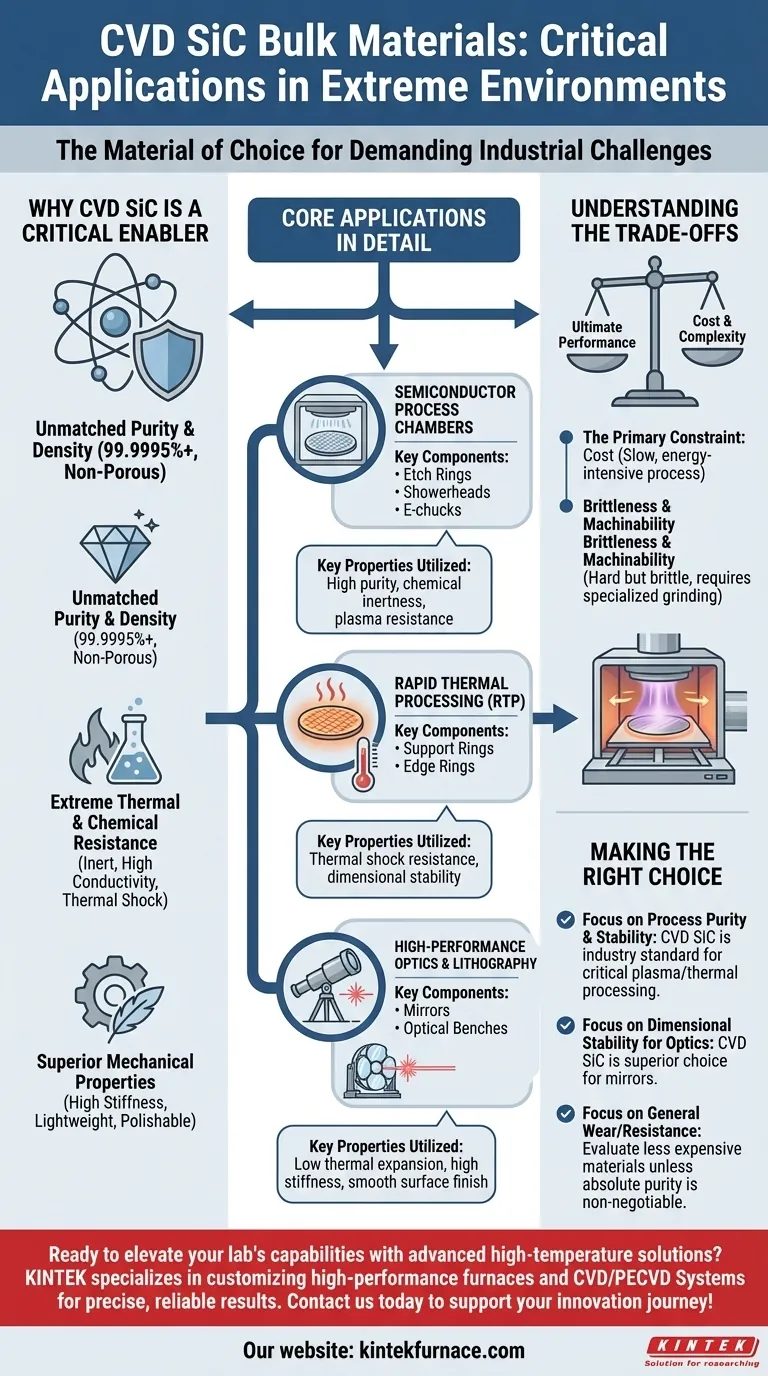
In the most demanding industrial environments, bulk Silicon Carbide (SiC) produced via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the material of choice for critical components. Its primary applications are in semiconductor manufacturing for components like etch and rapid thermal processing (RTP) rings, in high-performance reflective optics, and as structural supports in advanced microelectronics processing.
The decision to use CVD SiC is not about finding a general-purpose material, but about strategically deploying an ultra-pure, exceptionally stable ceramic in environments where temperature, chemical corrosion, and precision are so extreme that conventional materials would fail.

Why CVD SiC is a Critical Enabler
The value of CVD SiC comes from the combination of Silicon Carbide's inherent properties with the unique advantages of the CVD manufacturing process. This results in a material that solves problems other ceramics or metals cannot.
Unmatched Purity and Density
The CVD process builds the material atom-by-atom from gaseous precursors. This creates a fully dense, non-porous solid with exceptional purity (99.9995% or higher).
This purity is non-negotiable in semiconductor fabrication, where even minuscule contamination from a component can ruin entire batches of microchips.
Extreme Thermal & Chemical Resistance
SiC is intrinsically hard, chemically inert, and stable at very high temperatures. It resists the aggressive plasma and corrosive gases used in semiconductor etching processes.
Furthermore, it exhibits high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion, meaning it dissipates heat quickly and maintains its shape and dimensions even under rapid temperature changes (thermal shock).
Superior Mechanical Properties
CVD SiC is exceptionally stiff and lightweight. This high stiffness-to-weight ratio prevents components from sagging or vibrating, which is critical for large, thin parts like wafer chucks or massive telescope mirrors.
It can also be polished to an incredibly smooth, defect-free surface, making it an ideal substrate for high-performance optical mirrors.
Core Applications in Detail
The unique properties of CVD SiC make it indispensable in a few key high-tech fields. It is not a versatile material; it is a specialist material.
Semiconductor Process Chambers
In semiconductor manufacturing, CVD SiC is used for "chamber furniture" — the critical components inside the process tools. This includes etch rings, showerheads, and electrostatic chucks (E-chucks).
Here, the material's chemical inertness prevents it from being eroded by plasma, ensuring process stability and reducing particle generation that would otherwise contaminate the silicon wafers.
Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP)
RTP involves heating silicon wafers to over 1000°C in seconds. CVD SiC is used for support rings and edge rings that hold the wafer.
Its ability to withstand extreme thermal shock without warping or releasing particles is essential for maintaining the temperature uniformity required for this precise process.
High-Performance Optics and Lithography
CVD SiC is a premier material for mirrors and optical benches used in satellites, high-energy laser systems, and modern lithography equipment.
Its high stiffness and low thermal expansion ensure the mirror's figure remains perfect, even when subjected to thermal loads or mechanical stress, guaranteeing a stable and accurate optical performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its performance is exceptional, CVD SiC is not a universally applicable solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Primary Constraint: Cost
The CVD process is slow, complex, and energy-intensive. As a result, bulk CVD SiC is significantly more expensive than other ceramics like alumina or even other grades of silicon carbide.
Its use is therefore reserved for applications where the cost of component failure or process instability is unacceptably high.
Brittleness and Machinability
Like most advanced ceramics, SiC is very hard but also brittle. It is susceptible to fracture from sharp impacts and requires specialized diamond grinding techniques to shape.
This difficult machinability adds to the final cost and complexity of producing finished components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to specify CVD SiC is an engineering trade-off between ultimate performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is process purity and stability in semiconductor fabrication: CVD SiC is the industry standard for critical plasma and thermal processing components; its performance justifies the cost.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability for precision optics: The combination of low thermal expansion and high stiffness makes CVD SiC the superior choice for high-performance mirrors and optical structures.
- If your primary focus is general wear or high-temperature resistance: You should first evaluate less expensive materials, such as sintered SiC or other technical ceramics, unless the absolute purity and thermal shock resistance of CVD SiC is a non-negotiable requirement.
Ultimately, selecting bulk CVD SiC is a strategic decision to eliminate material performance as a variable in the world's most demanding technological applications.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Components | Key Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Process Chambers | Etch rings, showerheads, E-chucks | High purity, chemical inertness, plasma resistance |
| Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) | Support rings, edge rings | Thermal shock resistance, dimensional stability |
| High-Performance Optics | Mirrors, optical benches | Low thermal expansion, high stiffness, smooth surface finish |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with advanced high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in customizing high-performance furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems to meet your unique experimental needs. Leveraging our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we ensure precise, reliable results for demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation journey!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How does a Tube Furnace facilitate precise control during CVD? Master Stoichiometry and Phase Purity
- What role does a tube furnace play within a Vapor Transport Deposition (VTD) system? Essential Role in Thin Film Growth
- What role do CVD furnaces play in the semiconductor industry? Essential for Precise Thin-Film Deposition in Chip Fabrication
- What is tube CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Synthesis
- What is the role of a tube furnace system in the growth of bilayer MoS2? Master CVD Synthesis with Precision Control



















